Abstract
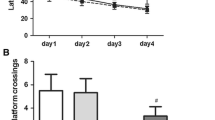
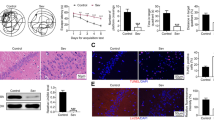
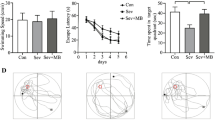
Isoflurane, a commonly used inhalation anesthetic, may induce neurocognitive deficits, especially in elderly patients after surgery. Recent study demonstrated that isoflurane caused endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and subsequent neuronal apoptosis in the brain, contributing to cognitive deficits. Taurine, a major intracellular free amino acid, has been shown to inhibit ER stress and neuronal apoptosis in several neurological disorders. Here, we examined whether taurine can prevent isoflurane-induced ER stress and cognitive impairment in aged rats. Thirty minutes prior to a 4-h 1.3 % isoflurane exposure, aged rats were treated with vehicle or taurine at low, middle and high doses. Aged rats without any treatment served as control. The brains were harvested 6 h after isoflurane exposure for molecular measurements, and behavioral study was performed 2 weeks later. Compared with control, isoflurane increased expression of hippocampal ER stress biomarkers including glucose-regulated protein 78, phosphorylated (P-) inositol-requiring enzyme 1, P-eukaryotic initiation factor 2-α (EIF2α), activating transcription factor 4 (ATF-4), cleaved ATF-6 and C/EBP homologous protein, along with activation of apoptosis pathways as indicated by decreased B cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2)/BCL2-associated X protein, increased expressions of cytochrome-c and cleaved caspase-3. Taurine pretreatment dose-dependently inhibited isoflurane-induced increase in expression of ER stress biomarkers except for P-EIF2α and ATF-4, and reversed isoflurane-induced changes in apoptosis-related proteins. Moreover, isoflurane caused spatial working memory deficits in aged rats, which were prevented by taurine pretreatment. The results indicate that taurine pretreatment prevents anesthetic isoflurane-induced cognitive impairment by inhibiting ER stress-mediated activation of apoptosis pathways in the hippocampus in aged rats.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shoair OA, Grasso Ii MP, Lahaye LA, Daniel R, Biddle CJ, Slattum PW (2015) Incidence and risk factors for postoperative cognitive dysfunction in older adults undergoing major noncardiac surgery: a prospective study. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol 31:30–36
Rundshagen I (2014) Postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Dtsch Arztebl Int 111:119–125
Mangoni AA, Jackson SH (2004) Age-related changes in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: basic principles and practical applications. Br J Clin Pharmacol 57:6–14
Lewis MC, Nevo I, Paniagua MA, Ben-Ari A, Pretto E, Eisdorfer S, Davidson E, Matot I, Eisdorfer C (2007) Uncomplicated general anesthesia in the elderly results in cognitive decline: does cognitive decline predict morbidity and mortality? Med Hypotheses 68:484–492
Pieperhoff P, Homke L, Schneider F, Habel U, Shah NJ, Zilles K, Amunts K (2008) Deformation field morphometry reveals age-related structural differences between the brains of adults up to 51 years. J Neurosci 28:828–842
Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Absalom AR, Blomgren K, Brambrink A, Crosby G, Culley DJ, Fiskum G, Giffard RG, Herold KF, Loepke AW, Ma D, Orser BA, Planel E, Slikker W Jr, Soriano SG, Stratmann G, Vutskits L, Xie Z, Hemmings HC Jr (2013) Anaesthetic neurotoxicity and neuroplasticity: an expert group report and statement based on the BJA Salzburg Seminar. Br J Anaesth 111:143–151
Ge HW, Hu WW, Ma LL, Kong FJ (2015) Endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway mediates isoflurane-induced neuroapoptosis and cognitive impairments in aged rats. Physiol Behav 151:16–23
Ni C, Li Z, Qian M, Zhou Y, Wang J, Guo X (2015) Isoflurane induced cognitive impairment in aged rats through hippocampal calcineurin/NFAT signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 460:889–895
Kong FJ, Ma LL, Zhang HH, Zhou JQ (2015) Alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist GTS-21 mitigates isoflurane-induced cognitive impairment in aged rats. J Surg Res 194:255–261
Zhang B, Tian M, Zhen Y, Yue Y, Sherman J, Zheng H, Li S, Tanzi RE, Marcantonio ER, Xie Z (2012) The effects of isoflurane and desflurane on cognitive function in humans. Anesth Analg 114:410–415
Doyle KM, Kennedy D, Gorman AM, Gupta S, Healy SJ, Samali A (2011) Unfolded proteins and endoplasmic reticulum stress in neurodegenerative disorders. J Cell Mol Med 15:2025–2039
Wang H, Dong Y, Zhang J, Xu Z, Wang G, Swain CA, Zhang Y, Xie Z (2014) Isoflurane induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and caspase activation through ryanodine receptors. Br J Anaesth 113:695–707
Birdsall TC (1998) Therapeutic applications of taurine. Altern Med Rev 3:128–136
Louzada PR, Paula Lima AC, Mendonca-Silva DL, Noel F, De Mello FG, Ferreira ST (2004) Taurine prevents the neurotoxicity of beta-amyloid and glutamate receptor agonists: activation of GABA receptors and possible implications for Alzheimer’s disease and other neurological disorders. Fed Am Soc Exp Biol J 18:511–518
Sun M, Xu C (2008) Neuroprotective mechanism of taurine due to up-regulating calpastatin and down-regulating calpain and caspase-3 during focal cerebral ischemia. Cell Mol Neurobiol 28:593–611
Chao CC, Chan P, Kuo CS, Gong CL, Cheng TH, Liu ZM, Shen PC, Huang CC, Leung YM (2014) Protection of differentiated neuronal NG108-15 cells from P2X7 receptor-mediated toxicity by taurine. Pharmacol Rep 66:576–584
Gharibani P, Modi J, Menzie J, Alexandrescu A, Ma Z, Tao R, Prentice H, Wu JY (2015) Comparison between single and combined post-treatment with S-methyl-N, N-diethylthiolcarbamate sulfoxide and taurine following transient focal cerebral ischemia in rat brain. Neuroscience 300:460–473
Gharibani PM, Modi J, Pan C, Menzie J, Ma Z, Chen PC, Tao R, Prentice H, Wu JY (2013) The mechanism of taurine protection against endoplasmic reticulum stress in an animal stroke model of cerebral artery occlusion and stroke-related conditions in primary neuronal cell culture. Adv Exp Med Biol 776:241–258
Valentim AM, Di Giminiani P, Ribeiro PO, Rodrigues P, Olsson IA, Antunes LM (2010) Lower isoflurane concentration affects spatial learning and neurodegeneration in adult mice compared with higher concentrations. Anesthesiology 113:1099–1108
Wang WY, Luo Y, Jia LJ, Hu SF, Lou XK, Shen SL, Lu H, Zhang HH, Yang R, Wang H, Ma ZW, Xue QS, Yu BW (2014) Inhibition of aberrant cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activity attenuates isoflurane neurotoxicity in the developing brain. Neuropharmacology 77:90–99
Hetz C, Martinon F, Rodriguez D, Glimcher LH (2011) The unfolded protein response: integrating stress signals through the stress sensor IRE1alpha. Physiol Rev 91:1219–1243
Ellgaard L, Helenius A (2003) Quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:181–191
Kim I, Xu W, Reed JC (2008) Cell death and endoplasmic reticulum stress: disease relevance and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:1013–1030
Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Gorman AM, Samali A (2006) Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. Eur Mol Biol Organ Rep 7:880–885
Kuhn HG, Biebl M, Wilhelm D, Li M, Friedlander RM, Winkler J (2005) Increased generation of granule cells in adult Bcl-2-overexpressing mice: a role for cell death during continued hippocampal neurogenesis. Eur J Neurosci 22:1907–1915
Sun XQ, Xu ZP, Zhang S, Cao XS, Liu TS (2009) Simulated weightlessness aggravates hypergravity-induced impairment of learning and memory and neuronal apoptosis in rats. Behav Brain Res 199:197–202
Chen PC, Pan C, Gharibani PM, Prentice H, Wu JY (2013) Taurine exerts robust protection against hypoxia and oxygen/glucose deprivation in human neuroblastoma cell culture. Adv Exp Med Biol 775:167–175
Sun M, Gu Y, Zhao Y, Xu C (2011) Protective functions of taurine against experimental stroke through depressing mitochondria-mediated cell death in rats. Amino Acids 40:1419–1429
Pan C, Giraldo GS, Prentice H, Wu JY (2010) Taurine protection of PC12 cells against endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by oxidative stress. J Biomed Sci 17(Suppl 1):S17
Foos TM, Wu JY (2002) The role of taurine in the central nervous system and the modulation of intracellular calcium homeostasis. Neurochem Res 27:21–26
Benrabh H, Bourre JM, Lefauconnier JM (1995) Taurine transport at the blood–brain barrier: an in vivo brain perfusion study. Brain Res 692:57–65
Tamai I, Senmaru M, Terasaki T, Tsuji A (1995) Na(+)- and Cl(−)-dependent transport of taurine at the blood–brain barrier. Biochem Pharmacol 50:1783–1793
Pow DV, Sullivan R, Reye P, Hermanussen S (2002) Localization of taurine transporters, taurine, and (3)H taurine accumulation in the rat retina, pituitary, and brain. Glia 37:153–168
Ni M, Zhang Y, Lee AS (2011) Beyond the endoplasmic reticulum: atypical GRP78 in cell viability, signalling and therapeutic targeting. Biochem J 434:181–188
Pinton P, Giorgi C, Siviero R, Zecchini E, Rizzuto R (2008) Calcium and apoptosis: ER-mitochondria Ca2+ transfer in the control of apoptosis. Oncogene 27:6407–6418
Liu H, Dai T, Guo W (2013) Isoflurane-induced neuronal apoptosis in developing hippocampal neurons. Neural Regen Res 8:825–832
Wu H, Jin Y, Wei J, Jin H, Sha D, Wu JY (2005) Mode of action of taurine as a neuroprotector. Brain Res 1038:123–131
Wu JY, Prentice H (2010) Role of taurine in the central nervous system. J Biomed Sci 17(Suppl 1):S1
Gebara E, Udry F, Sultan S, Toni N (2015) Taurine increases hippocampal neurogenesis in aging mice. Stem Cell Res 14:369–379
El Idrissi A (2008) Taurine improves learning and retention in aged mice. Neurosci Lett 436:19–22
Bach ME, Barad M, Son H, Zhuo M, Lu YF, Shih R, Mansuy I, Hawkins RD, Kandel ER (1999) Age-related defects in spatial memory are correlated with defects in the late phase of hippocampal long-term potentiation in vitro and are attenuated by drugs that enhance the cAMP signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:5280–5285
Dominy J Jr, Thinschmidt JS, Peris J, Dawson R Jr, Papke RL (2004) Taurine-induced long-lasting potentiation in the rat hippocampus shows a partial dissociation from total hippocampal taurine content and independence from activation of known taurine transporters. J Neurochem 89:1195–1205
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Youth Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Li, D., Li, H. et al. Taurine Pretreatment Prevents Isoflurane-Induced Cognitive Impairment by Inhibiting ER Stress-Mediated Activation of Apoptosis Pathways in the Hippocampus in Aged Rats. Neurochem Res 41, 2517–2525 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1963-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1963-4