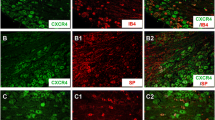
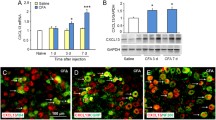
Abstract
Stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1)/chemokine CXC motif ligand 12 (CXCL12), a chemokine that is upregulated in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) during chronic pain models, has recently been found to play a central role in pain hypersensitivity. The purpose of present study is to investigate the functional impact of SDF-1 and its receptor, chemokine CXC motif receptor 4 (CXCR4), on two TTXR sodium channels in rat DRG using electrophysiological techniques. Preincubation with SDF-1 caused a concentration-dependent increase of Nav1.8 and Nav1.9 currents amplitudes in acutely isolated small diameter DRG neurons in short-term culture. As to Nav1.9, changes in current density and kinetic properties of Nav1.9 current evoked by SDF-1(50 ng/ml) was eliminated by CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor LY294002. The increase in Nav1.9 current was also blocked by pertussis toxin (PTX) but not cholera toxin (CTX), showing involvement of Gi/o but not Gs subunits. As to Nav1.8, inhibitors (AMD3100, PTX, CTX, LY294002) used in present study didn’t inhibit the increased amplitude of Nav1.8 current and shifted activation curve of Nav1.8 in a hyperpolarizing direction in the presence of SDF-1 (50 ng/ml). In conclusion, our data demonstrated that SDF-1 may excite primary nociceptive sensory neurons by acting on the biophysical properties of Nav1.8 and Nav1.9 currents but via different mechanisms.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbadie C, Bhangoo S, De Koninck Y, Malcangio M, Melik-Parsadaniantz S, White FA (2009) Chemokines and pain mechanisms. Brain Res Rev 60(1):125–134. doi:10.1016/j.brainresrev.2008.12.002
Miller RJ, Jung H, Bhangoo SK, White FA (2009) Cytokine and chemokine regulation of sensory neuron function. Handb Exp Pharmacol 194:417–449. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-79090-7_12
Gao YJ, Ji RR (2010) Chemokines, neuronal-glial interactions, and central processing of neuropathic pain. Pharmacol Ther 126(1):56–68. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.01.002
Ren K, Dubner R (2010) Interactions between the immune and nervous systems in pain. Nat Med 16(11):1267–1276. doi:10.1038/nm.2234
Bajetto A, Bonavia R, Barbero S, Piccioli P, Costa A, Florio T, Schettini G (1999) Glial and neuronal cells express functional chemokine receptor CXCR4 and its natural ligand stromal cell-derived factor 1. J Neurochem 73(6):2348–2357
Rostasy K, Egles C, Chauhan A, Kneissl M, Bahrani P, Yiannoutsos C, Hunter DD, Nath A, Hedreen JC, Navia BA (2003) SDF-1alpha is expressed in astrocytes and neurons in the AIDS dementia complex: an in vivo and in vitro study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62(6):617–626
Tham TN, Lazarini F, Franceschini IA, Lachapelle F, Amara A, Dubois-Dalcq M (2001) Developmental pattern of expression of the alpha chemokine stromal cell-derived factor 1 in the rat central nervous system. Eur J Neurosci 13(5):845–856
Bhangoo SK, Ripsch MS, Buchanan DJ, Miller RJ, White FA (2009) Increased chemokine signaling in a model of HIV1-associated peripheral neuropathy. Mol Pain 5:48. doi:10.1186/1744-8069-5-48
White F, Wilson N (2010) Opiate-induced hypernociception and chemokine receptors. Neuropharmacology 58(1):35–37. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.07.012
Bhangoo SK, Ren D, Miller RJ, Chan DM, Ripsch MS, Weiss C, McGinnis C, White FA (2007) CXCR4 chemokine receptor signaling mediates pain hypersensitivity in association with antiretroviral toxic neuropathy. Brain Behav Immun 21(5):581–591. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2006.12.003
Wilson NM, Jung H, Ripsch MS, Miller RJ, White FA (2011) CXCR4 signaling mediates morphine-induced tactile hyperalgesia. Brain Behav Immun 25(3):565–573. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2010.12.014
Bhangoo S, Ren D, Miller RJ, Henry KJ, Lineswala J, Hamdouchi C, Li B, Monahan PE, Chan DM, Ripsch MS, White FA (2007) Delayed functional expression of neuronal chemokine receptors following focal nerve demyelination in the rat: a mechanism for the development of chronic sensitization of peripheral nociceptors. Mol Pain 3:38. doi:10.1186/1744-8069-3-38
Shen W, Hu XM, Liu YN, Han Y, Chen LP, Wang CC, Song C (2014) CXCL12 in astrocytes contributes to bone cancer pain through CXCR4-mediated neuronal sensitization and glial activation in rat spinal cord. J Neuroinflamm 11:75. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-11-75
Cummins TR, Dib-Hajj SD, Black JA, Akopian AN, Wood JN, Waxman SG (1999) A novel persistent tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium current in SNS-null and wild-type small primary sensory neurons. J Neurosci 19(24):Rc43
Akopian AN, Souslova V, England S, Okuse K, Ogata N, Ure J, Smith A, Kerr BJ, McMahon SB, Boyce S, Hill R, Stanfa LC, Dickenson AH, Wood JN (1999) The tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel SNS has a specialized function in pain pathways. Nat Neurosci 2(6):541–548. doi:10.1038/9195
Rush AM, Cummins TR, Waxman SG (2007) Multiple sodium channels and their roles in electrogenesis within dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Physiol 579(Pt 1):1–14. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2006.121483
Blair NT, Bean BP (2002) Roles of tetrodotoxin (TTX)-sensitive Na+ current, TTX-resistant Na+ current, and Ca2+ current in the action potentials of nociceptive sensory neurons. J Neurosci 22(23):10277–10290
Renganathan M, Cummins TR, Waxman SG (2001) Contribution of Na(v)1.8 sodium channels to action potential electrogenesis in DRG neurons. J Neurophysiol 86(2):629–640
Herzog RI, Cummins TR, Waxman SG (2001) Persistent TTX-resistant Na+ current affects resting potential and response to depolarization in simulated spinal sensory neurons. J Neurophysiol 86(3):1351–1364
Neves SR, Ram PT, Iyengar R (2002) G protein pathways. Science (New York, NY) 296(5573):1636–1639. doi:10.1126/science.1071550
Belkouch M, Dansereau MA, Reaux-Le Goazigo A, Van Steenwinckel J, Beaudet N, Chraibi A, Melik-Parsadaniantz S, Sarret P (2011) The chemokine CCL2 increases Nav1.8 sodium channel activity in primary sensory neurons through a Gbetagamma-dependent mechanism. J Neurosci 31(50):18381–18390. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.3386-11.2011
Baker MD, Chandra SY, Ding Y, Waxman SG, Wood JN (2003) GTP-induced tetrodotoxin-resistant Na+ current regulates excitability in mouse and rat small diameter sensory neurones. J Physiol 548(Pt 2):373–382. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2003.039131
Kim DS, Kim YS, Bae WJ, Lee HJ, Chang SW, Kim WS, Kim EC (2014) The role of SDF-1 and CXCR4 on odontoblastic differentiation in human dental pulp cells. Int Endod J 47(6):534–541. doi:10.1111/iej.12182
Chen G, Chen SM, Wang X, Ding XF, Ding J, Meng LH (2012) Inhibition of chemokine (CXC motif) ligand 12/chemokine (CXC motif) receptor 4 axis (CXCL12/CXCR4)-mediated cell migration by targeting mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway in human gastric carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 287(15):12132–12141. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.302299
Jiang Z, Zhou W, Guan S, Wang J, Liang Y (2013) Contribution of SDF-1alpha/CXCR4 signaling to brain development and glioma progression. Neuro-Signals 21(3–4):240–258. doi:10.1159/000339091
Zou YR, Kottmann AH, Kuroda M, Taniuchi I, Littman DR (1998) Function of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in haematopoiesis and in cerebellar development. Nature 393(6685):595–599. doi:10.1038/31269
McGrath KE, Koniski AD, Maltby KM, McGann JK, Palis J (1999) Embryonic expression and function of the chemokine SDF-1 and its receptor, CXCR4. Dev Biol 213(2):442–456. doi:10.1006/dbio.1999.9405
Chen X, Zhang L, Kombian SB (2004) Dopamine-induced synaptic depression in the parabrachial nucleus is independent of CTX- and PTX-sensitive G-proteins, PKA and PLC signalling pathways. Brain Res 995(2):236–246
Tyrrell L, Renganathan M, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG (2001) Glycosylation alters steady-state inactivation of sodium channel Nav1.9/NaN in dorsal root ganglion neurons and is developmentally regulated. J Neurosci 21(24):9629–9637
Sleeper AA, Cummins TR, Dib-Hajj SD, Hormuzdiar W, Tyrrell L, Waxman SG, Black JA (2000) Changes in expression of two tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channels and their currents in dorsal root ganglion neurons after sciatic nerve injury but not rhizotomy. J Neurosci 20(19):7279–7289
Qiu F, Jiang Y, Zhang H, Liu Y, Mi W (2012) Increased expression of tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channels Nav1.8 and Nav1.9 within dorsal root ganglia in a rat model of bone cancer pain. Neurosci Lett 512(2):61–66. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2012.01.069
Vlahos CJ, Matter WF, Hui KY, Brown RF (1994) A specific inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, 2-(4-morpholinyl)-8-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one (LY294002). J Biol Chem 269(7):5241–5248
Rush AM, Waxman SG (2004) PGE2 increases the tetrodotoxin-resistant Nav1.9 sodium current in mouse DRG neurons via G-proteins. Brain Res 2:264–271. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2004.07.042
Choi JI, Svensson CI, Koehrn FJ, Bhuskute A, Sorkin LS (2010) Peripheral inflammation induces tumor necrosis factor dependent AMPA receptor trafficking and Akt phosphorylation in spinal cord in addition to pain behavior. Pain 149(2):243–253. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2010.02.008
White FA, Wilson NM (2008) Chemokines as pain mediators and modulators. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 21(5):580–585. doi:10.1097/ACO.0b013e32830eb69d
Dubovy P, Klusakova I, Svizenska I, Brazda V (2010) Spatio-temporal changes of SDF1 and its CXCR4 receptor in the dorsal root ganglia following unilateral sciatic nerve injury as a model of neuropathic pain. Histochem Cell Biol 133(3):323–337. doi:10.1007/s00418-010-0675-0
Reaux-Le Goazigo A, Rivat C, Kitabgi P, Pohl M, Melik Parsadaniantz S (2012) Cellular and subcellular localization of CXCL12 and CXCR4 in rat nociceptive structures: physiological relevance. Eur J Neurosci 36(5):2619–2631. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2012.08179.x
Abbadie C, Lindia JA, Cumiskey AM, Peterson LB, Mudgett JS, Bayne EK, DeMartino JA, MacIntyre DE, Forrest MJ (2003) Impaired neuropathic pain responses in mice lacking the chemokine receptor CCR2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(13):7947–7952. doi:10.1073/pnas.1331358100
Tanaka T, Minami M, Nakagawa T, Satoh M (2004) Enhanced production of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in the dorsal root ganglia in a rat model of neuropathic pain: possible involvement in the development of neuropathic pain. Neurosci Res 48(4):463–469. doi:10.1016/j.neures.2004.01.004
White FA, Sun J, Waters SM, Ma C, Ren D, Ripsch M, Steflik J, Cortright DN, Lamotte RH, Miller RJ (2005) Excitatory monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 signaling is up-regulated in sensory neurons after chronic compression of the dorsal root ganglion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(39):14092–14097. doi:10.1073/pnas.0503496102
Hartmann TN, Grabovsky V, Pasvolsky R, Shulman Z, Buss EC, Spiegel A, Nagler A, Lapidot T, Thelen M, Alon R (2008) A crosstalk between intracellular CXCR7 and CXCR4 involved in rapid CXCL12-triggered integrin activation but not in chemokine-triggered motility of human T lymphocytes and CD34+ cells. J Leukoc Biol 84(4):1130–1140. doi:10.1189/jlb.0208088
Thelen M, Thelen S (2008) CXCR7, CXCR4 and CXCL12: an eccentric trio? J Neuroimmunol 198(1–2):9–13. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2008.04.020
Oh SB, Tran PB, Gillard SE, Hurley RW, Hammond DL, Miller RJ (2001) Chemokines and glycoprotein120 produce pain hypersensitivity by directly exciting primary nociceptive neurons. J Neurosci 21(14):5027–5035
Sun JH, Yang B, Donnelly DF, Ma C, LaMotte RH (2006) MCP-1 enhances excitability of nociceptive neurons in chronically compressed dorsal root ganglia. J Neurophysiol 96(5):2189–2199. doi:10.1152/jn.00222.2006
Priest BT (2009) Future potential and status of selective sodium channel blockers for the treatment of pain. Curr Opin Drug Discov Dev 12(5):682–692
Lampert A, O’Reilly AO, Reeh P, Leffler A (2010) Sodium channelopathies and pain. Pflugers Arch 460(2):249–263. doi:10.1007/s00424-009-0779-3
Zhuang ZY, Xu H, Clapham DE, Ji RR (2004) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activates ERK in primary sensory neurons and mediates inflammatory heat hyperalgesia through TRPV1 sensitization. J Neurosci 24(38):8300–8309. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.2893-04.2004
Bonnington JK, McNaughton PA (2003) Signalling pathways involved in the sensitisation of mouse nociceptive neurones by nerve growth factor. J Physiol 551(Pt 2):433–446. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2003.039990
Kao DJ, Li AH, Chen JC, Luo RS, Chen YL, Lu JC, Wang HL (2012) CC chemokine ligand 2 upregulates the current density and expression of TRPV1 channels and Nav1.8 sodium channels in dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Neuroinflamm 9:189. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-9-189
Knerlich-Lukoschus F, von der Ropp-Brenner B, Lucius R, Mehdorn HM, Held-Feindt J (2011) Spatiotemporal CCR1, CCL3(MIP-1alpha), CXCR4, CXCL12(SDF-1alpha) expression patterns in a rat spinal cord injury model of posttraumatic neuropathic pain. J Neurosurg Spine 14(5):583–597. doi:10.3171/2010.12.spine10480
Luo Y, Lathia J, Mughal M, Mattson MP (2008) SDF1alpha/CXCR4 signaling, via ERKs and the transcription factor Egr1, induces expression of a 67-kDa form of glutamic acid decarboxylase in embryonic hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem 283(36):24789–24800. doi:10.1074/jbc.M800649200
Rivat C, Sebaihi S, Van Steenwinckel J, Fouquet S, Kitabgi P, Pohl M, Melik Parsadaniantz S, Reaux-Le Goazigo A (2014) Src family kinases involved in CXCL12-induced loss of acute morphine analgesia. Brain Behav Immun 38:38–52. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2013.11.010
Murphy PM (1996) Chemokine receptors: structure, function and role in microbial pathogenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 7(1):47–64
Maingret F, Coste B, Padilla F, Clerc N, Crest M, Korogod SM, Delmas P (2008) Inflammatory mediators increase Nav1.9 current and excitability in nociceptors through a coincident detection mechanism. J Gen Physiol 131(3):211–225. doi:10.1085/jgp.200709935
Ostman JA, Nassar MA, Wood JN, Baker MD (2008) GTP up-regulated persistent Na+ current and enhanced nociceptor excitability require NaV1.9. J Physiol 586(4):1077–1087. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2007.147942
Zheng J, Thylin MR, Ghorpade A, Xiong H, Persidsky Y, Cotter R, Niemann D, Che M, Zeng YC, Gelbard HA, Shepard RB, Swartz JM, Gendelman HE (1999) Intracellular CXCR4 signaling, neuronal apoptosis and neuropathogenic mechanisms of HIV-1-associated dementia. J Neuroimmunol 98(2):185–200
Kelly A, Lynch MA (2000) Long-term potentiation in dentate gyrus of the rat is inhibited by the phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor, wortmannin. Neuropharmacology 39(4):643–651
Lin CH, Yeh SH, Lin CH, Lu KT, Leu TH, Chang WC, Gean PW (2001) A role for the PI-3 kinase signaling pathway in fear conditioning and synaptic plasticity in the amygdala. Neuron 31(5):841–851
Sanna PP, Cammalleri M, Berton F, Simpson C, Lutjens R, Bloom FE, Francesconi W (2002) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is required for the expression but not for the induction or the maintenance of long-term potentiation in the hippocampal CA1 region. J Neurosci 22(9):3359–3365
Tan M, Groszer M, Tan AM, Pandya A, Liu X, Xie CW (2003) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase cascade facilitates mu-opioid desensitization in sensory neurons by altering G-protein-effector interactions. J Neurosci 23(32):10292–10301
Radeff-Huang J, Seasholtz TM, Matteo RG, Brown JH (2004) G protein mediated signaling pathways in lysophospholipid induced cell proliferation and survival. J Cell Biochem 92(5):949–966. doi:10.1002/jcb.20094
Acknowledgments
The project was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (Grant 30901398). The authors thank Yue-Juan Li and Fang Li for all the helpful suggestions during the revision of original manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We don’t have any actual or potential conflict of interest including any financial, personal or other relationships with other people or organizations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, F., Li, Y., Fu, Q. et al. Stromal Cell-Derived Factor 1 Increases Tetrodotoxin-Resistant Sodium Currents Nav1.8 and Nav1.9 in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons via Different Mechanisms. Neurochem Res 41, 1587–1603 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1873-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1873-5