Abstract
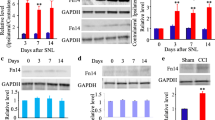
Neuropathic pain, caused by a lesion or dysfunction of the somatosensory nervous system, is a severe debilitating condition with which clinical treatment remains challenging. Jun activation domain-binding protein (JAB1) is a multifunctional protein that participates in several signaling pathways, controlling cell proliferation and apoptosis. However, the expression and possible function of JAB1 in the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain has not been elucidated. This study aimed to investigate the possible involvement of JAB1. Here, employing a neuropathic pain model induced by chronic constriction injury (CCI) on rats, we reported the role of JAB1 in the maintenance of neuropathic pain. By western blot, we found that CCI markedly up-regulated JAB1 expression in the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) and spinal cord. Immunofluorescent assay demonstrated that JAB1 was extensively localized in IB4-, CGRP- and NF200-positive neurons in the injured L5 DRG, and mainly co-localized with NeuN in spinal cord. In addition, we showed that CCI induced phosphorylation of p65 and JNK in vivo. Intrathecal injection of JAB1 siRNA significantly attenuated the CCI-induced JNK and p65 phosphorylation and alleviated both mechanical allodynia and heat hyperalgesia in rats. Taken together, these results suggested that JAB1 promotes neuropathic pain via positively regulating JNK and NF-κB activation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Treede RD, Jensen TS, Campbell JN, Cruccu G, Dostrovsky JO, Griffin JW, Hansson P, Hughes R, Nurmikko T, Serra J (2008) Neuropathic pain: redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology 70:1630–1635
Woolf CJ, Mannion RJ (1999) Neuropathic pain: aetiology, symptoms, mechanisms, and management. Lancet 353:1959–1964
Baron R (2006) Mechanisms of disease: neuropathic pain—a clinical perspective. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 2:95–106
Costigan M, Scholz J, Woolf CJ (2009) Neuropathic pain: a maladaptive response of the nervous system to damage. Annu Rev Neurosci 32:1–32
Wei N, Deng XW (2003) The COP9 signalosome. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 19:261–286
Huang X, Hetfeld BK, Seifert U, Kahne T, Kloetzel PM, Naumann M, Bech-Otschir D, Dubiel W (2005) Consequences of COP9 signalosome and 26S proteasome interaction. FEBS J 272:3909–3917
Chang EC, Schwechheimer C (2004) ZOMES III: the interface between signalling and proteolysis. Meeting on the COP9 signalosome, proteasome and eIF3. EMBO Rep 5:1041–1045
Wang J, Li C, Liu Y, Mei W, Yu S, Liu C, Zhang L, Cao X, Kimberly RP, Grizzle W, Zhang HG (2006) JAB1 determines the response of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts to tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Am J Pathol 169:889–902
Bae MK, Ahn MY, Jeong JW, Bae MH, Lee YM, Bae SK, Park JW, Kim KR, Kim KW (2002) Jab1 interacts directly with HIF-1alpha and regulates its stability. J Biol Chem 277:9–12
Boussiotis VA, Freeman GJ, Taylor PA, Berezovskaya A, Grass I, Blazar BR, Nadler LM (2000) p27kip1 functions as an anergy factor inhibiting interleukin 2 transcription and clonal expansion of alloreactive human and mouse helper T lymphocytes. Nat Med 6:290–297
Lyapina S, Cope G, Shevchenko A, Serino G, Tsuge T, Zhou C, Wolf DA, Wei N, Shevchenko A, Deshaies RJ (2001) Promotion of NEDD-CUL1 conjugate cleavage by COP9 signalosome. Science 292:1382–1385
Bech-Otschir D, Kraft R, Huang X, Henklein P, Kapelari B, Pollmann C, Dubiel W (2001) COP9 signalosome-specific phosphorylation targets p53 to degradation by the ubiquitin system. EMBO J 20:1630–1639
Cheng X, Zhou Z, Xu G, Zhao J, Wu H, Long L, Wen H, Gu X, Wang Y (2013) Dynamic changes of Jab1 and p27kip1 expression in injured rat sciatic nerve. J Mol Neurosci 51:148–158
Guo CJ, Douglas SD, Gao Z, Wolf BA, Grinspan J, Lai JP, Riedel E, Ho WZ (2004) Interleukin-1beta upregulates functional expression of neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R) via NF-κB in astrocytes. Glia 48:259–266
Kim HK, Park SK, Zhou JL, Taglialatela G, Chung K, Coggeshall RE, Chung JM (2004) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) play an important role in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Pain 111:116–124
Sakaue G, Shimaoka M, Fukuoka T, Hiroi T, Inoue T, Hashimoto N, Sakaguchi T, Sawa Y, Morishita R, Kiyono H, Noguchi K, Mashimo T (2001) NF-κB decoy suppresses cytokine expression and thermal hyperalgesia in a rat neuropathic pain model. NeuroReport 12:2079–2084
Xu YQ, Jin SJ, Liu N, Li YX, Zheng J, Ma L, Du J, Zhou R, Zhao CJ, Niu Y, Sun T, Yu JQ (2014) Aloperine attenuated neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury via anti-oxidation activity and suppression of the nuclear factor kappa B pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 451:568–573
Pan YD, Guo QL, Wang E, Ye Z, He ZH, Zou WY, Cheng ZG, Wang YJ (2010) Intrathecal infusion of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate for the prevention and reversal of neuropathic pain in rats using a sciatic chronic constriction injury model. Reg Anesth Pain Med 35:231–237
Zhuang ZY, Wen YR, Zhang DR, Borsello T, Bonny C, Strichartz GR, Decosterd I, Ji RR (2006) A peptide c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitor blocks mechanical allodynia after spinal nerve ligation: respective roles of JNK activation in primary sensory neurons and spinal astrocytes for neuropathic pain development and maintenance. J Neurosci 26:3551–3560
Ji RR, Kawasaki Y, Zhuang ZY, Wen YR, Decosterd I (2006) Possible role of spinal astrocytes in maintaining chronic pain sensitization: review of current evidence with focus on bFGF/JNK pathway. Neuron Glia Biol 2:259–269
Obata K, Noguchi K (2004) MAPK activation in nociceptive neurons and pain hypersensitivity. Life Sci 74:2643–2653
Zimmermann M (1983) Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain 16:109–110
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53:55–63
Hylden JL, Wilcox GL (1980) Intrathecal morphine in mice: a new technique. Eur J Pharmacol 67:313–316
Jensen TS, Baron R, Haanpaa M, Kalso E, Loeser JD, Rice AS, Treede RD (2011) A new definition of neuropathic pain. Pain 152:2204–2205
von Hehn CA, Baron R, Woolf CJ (2012) Deconstructing the neuropathic pain phenotype to reveal neural mechanisms. Neuron 73:638–652
Pollock J, McFarlane SM, Connell MC, Zehavi U, Vandenabeele P, MacEwan DJ, Scott RH (2002) TNF-alpha receptors simultaneously activate Ca2+ mobilisation and stress kinases in cultured sensory neurones. Neuropharmacology 42:93–106
Gupta S, Barrett T, Whitmarsh AJ, Cavanagh J, Sluss HK, Derijard B, Davis RJ (1996) Selective interaction of JNK protein kinase isoforms with transcription factors. EMBO J 15:2760–2770
Gao YJ, Ji RR (2008) Activation of JNK pathway in persistent pain. Neurosci Lett 437:180–183
Acknowledgments
This work were supported by National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, No. 2012CB822104); National Natural Science Foundation of China (31500647, 31170766); the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (15KJA310003); the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20150408); the Six Talent Peaks Project in Jiangsu Province (YY-050); A Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yan Chen and Xiangdong Chen contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Chen, X., Yu, J. et al. JAB1 is Involved in Neuropathic Pain by Regulating JNK and NF-κB Activation After Chronic Constriction Injury. Neurochem Res 41, 1119–1129 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1802-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1802-z