Abstract
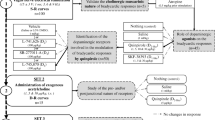
Our previous investigations have demonstrated that microinjection of acetylcholine (ACh) or muscarinic ACh receptor activation in the cerebellar cortex induces a systemic blood pressure depressor response. This study aimed to determine the role of muscarinic ACh receptor-2 (M2 receptor) in the cerebellar cortex in cardiovascular function regulation in rats. A nonselective muscarinic receptor agonist (oxotremorine M, OXO; 30 mM), a selective M2 receptor agonist (arecaidine but-2-ynyl ester tosylate, ABET; 3, 10, and 30 mM), 30 mM OXO mixed with a selective M2 receptor antagonist (methoctramine hydrate, MCT; 0.3, 1, and 3 mM), and normal saline (0.9 % NaCl) were separately microinjected (0.5 µl/5 s) into the cerebellar cortex (lobule VI) of anaesthetized rats. We measured the mean arterial pressure (MAP), maximum change in MAP, and reactive time (RT; the duration required for the blood pressure to return to basal levels), heart rate (HR) and the maximum change in HR during the RT in response to drug activation. The results demonstrated that ABET dose-dependently decreased MAP and HR, increased the maximum change in MAP and the maximum change in HR, and prolonged the RT. Furthermore, MCT dose-dependently blocked the OXO-mediated cardiovascular depressor response. This study provides the first evidence that M2 receptors in the cerebellar cortex are involved in cardiovascular regulation, the activation of which evokes significant depressor and bradycardic responses.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schweighofer N, Doya K, Kuroda S (2004) Cerebellar aminergic neuromodulation: towards a functional understanding. Brain Res Rev 44:103–116
Ito M (2012) The cerebellum: brain for an implicit self. FT Press, Upper Saddle River
Zhang Y, Kaneko R, Yanagawa Y, Saito Y (2014) The vestibulo- and preposito-cerebellar cholinergic neurons of a ChAT-tdTomato transgenic rat exhibit heterogeneous firing properties and the expression of various neurotransmitter receptors. Eur J Neurosci 39:1294–1313
Lan CT, Wen CY, Tan CK, Ling EA, Shieh JY (1995) Multiple origins of cerebellar cholinergic afferents from the lower brainstem in the gerbil. J Anat 186(Pt 3):549–561
Ojima H, Kawajiri S, Yamasaki T (1989) Cholinergic innervation of the rat cerebellum: qualitative and quantitative analyses of elements immunoreactive to a monoclonal antibody against choline acetyltransferase. J Comp Neurol 290:41–52
Graham A, Court J, Martin-Ruiz C, Jaros E, Perry R, Volsen S, Bose S, Evans N, Ince P, Kuryatov A (2002) Immunohistochemical localisation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits in human cerebellum. Neuroscience 113:493–507
Gotti C, Zoli M, Clementi F (2006) Brain nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: native subtypes and their relevance. Trends Pharmacol Sci 27:482–491
Levey AI, Kitt CA, Simonds WF, Price DL, Brann MR (1991) Identification and localization of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor proteins in brain with subtype-specific antibodies. J Neurosci 11:3218–3226
Tayebati SK, Vitali D, Scordella S, Amenta F (2001) Muscarinic cholinergic receptors subtypes in rat cerebellar cortex: light microscope autoradiography of age-related changes. Brain Res 889:256–259
Prestori F, Bonardi C, Mapelli L, Lombardo P, Goselink R, De Stefano ME, Gandolfi D, Mapelli J, Bertrand D, Schonewille M, De Zeeuw C, D’Angelo E (2013) Gating of long-term potentiation by nicotinic acetylcholine receptors at the cerebellum input stage. PLoS ONE 8:e64828
Rinaldo L, Hansel C (2013) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor activation blocks long-term potentiation at cerebellar parallel fiber-Purkinje cell synapses via cannabinoid signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:11181–11186
Zhou P, Zhu Q, Liu M, Li J, Wang Y, Zhang C, Hua T (2015) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in cerebellar cortex participates in acetylcholine-mediated blood depressor response in rats. Neurosci Lett 593:129–133
Gomeza J, Shannon H, Kostenis E, Felder C, Zhang L, Brodkin J, Grinberg A, Sheng H, Wess J (1999) Pronounced pharmacologic deficits in M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor knockout mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:1692–1697
Hong CM, Zheng QS, Liu XT, Shang FJ, Wang HT, Jiang WR (2009) Effects of autoantibodies against M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors on rabbit atria in vivo. Cardiology 112:180–187
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, Boston
Zhang WN, Bast T, Xu Y, Feldon J (2014) Temporary inhibition of dorsal or ventral hippocampus by muscimol: distinct effects on measures of innate anxiety on the elevated plus maze, but similar disruption of contextual fear conditioning. Behav Brain Res 262:47–56
Zhang C, Hua T, Zhu Z, Luo X (2006) Age-related changes of structures in cerebellar cortex of cat. J Biosci 31:55–60
Zhu Q, Zhou P, Wang S, Zhang C, Hua T (2015) A preliminary study on cerebellar acetylcholine-mediated blood pressure regulation in young and old rats. Exp Gerontol 63:76–80
Kumar NN, Ferguson J, Padley JR, Pilowsky PM, Goodchild AK (2009) Differential muscarinic receptor gene expression levels in the ventral medulla of spontaneously hypertensive and Wistar-Kyoto rats: role in sympathetic baroreflex function. J Hypertens 27:1001–1008
Deolindo MV, Pelosi GG, Busnardo C, Resstel LB, Correa FM (2011) Cardiovascular effects of acetylcholine microinjection into the ventrolateral and dorsal periaqueductal gray of rats. Brain Res 1371:74–81
Shafei MN, Niazmand S, Enayatfard L, Hosseini M, Daloee MH (2013) Pharmacological study of cholinergic system on cardiovascular regulation in the cuneiform nucleus of rat. Neurosci Lett 549:12–17
Aberger K, Chitravanshi VC, Sapru HN (2001) Cardiovascular responses to microinjections of nicotine into the caudal ventrolateral medulla of the rat. Brain Res 892:138–146
de Toro ED, Juíz JM, Smillie FI, Lindstrom J, Criado M (1997) Expression of α 7 neuronal nicotinic receptors during postnatal development of the rat cerebellum. Dev Brain Res 98:125–133
Jaarsma D, Ruigrok TJ, Caffe R, Cozzari C, Levey AI, Mugnaini E, Voogd J (1997) Cholinergic innervation and receptors in the cerebellum. Prog Brain Res 114:67–96
Nisimaru N (2004) Cardiovascular modules in the cerebellum. Jpn J Physiol 54:431–448
Jakubik J, Zimcik P, Randakova A, Fuksova K, El-Fakahany EE, Dolezal V (2014) Molecular mechanisms of methoctramine binding and selectivity at muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Mol Pharmacol 86:180–192
Fluckiger JP, Sonnay M, Boillat N, Atkinson J (1985) Attenuation of the baroreceptor reflex by general anesthetic agents in the normotensive rat. Eur J Pharmacol 109:105–109
Shimokawa A, Kunitake T, Takasaki M, Kannan H (1998) Differential effects of anesthetics on sympathetic nerve activity and arterial baroreceptor reflex in chronically instrumented rats. J Auton Nerv Syst 72:46–54
Alves FH, Crestani CC, Resstel LB, Correa FM (2007) Cardiovascular effects of carbachol microinjected into the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis of the rat brain. Brain Res 1143:161–168
Kruse AC, Kobilka BK, Gautam D, Sexton PM, Christopoulos A, Wess J (2014) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors: novel opportunities for drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 13:549–560
Haga T (2013) Molecular properties of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci 89:226–256
Larsell O (1952) The morphogenesis and adult pattern of the lobules and fissures of the cerebellum of the white rat. J Comp Neurol 97:281–356
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (No. 1308085MH127), Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Provincial Education Bureau (No. KJ2013B124), and the Scientific Foundations of Anqing Normal University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Sun, T., Zhou, P. et al. Role of Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor-2 in the Cerebellar Cortex in Cardiovascular Modulation in Anaesthetized Rats. Neurochem Res 41, 804–812 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1755-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1755-2