Abstract
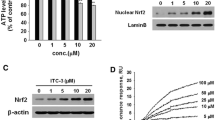
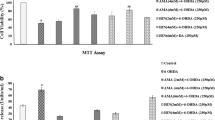
In this study, we investigated whether tanshinone I (T-I) has therapeutic effects in cellular and animal model of Parkinson’s disease (PD), and explore its possible mechanism. For this purpose, human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells were cultured and exposed to 100 μM 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) in the absence or presence of T-I (1, 2.5 and 5 μM). The results revealed that 6-OHDA-induced cell death was reduced by T-I pretreatment as measured by MTT assay, lactate dehydrogenase release and flow cytomety analysis of cell apoptosis. The increase in the reactive oxygen species caused by 6-OHDA treatment was also attenuated by T-I in SH-SY5Y cells. T-I pretreatment was also shown to result in an increase in nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) protein levels and its transcriptional activity as well as the upregulation of Nrf2-dependent genes encoding the antioxidant enzymes heme oxygenase-1, glutathione cysteine ligase regulatory subunit and glutathione cysteine ligase modulatory subunit in SH-SY5Y cells. Moreover, in the in vivo experiment, T-I treatment significantly attenuated 6-OHDA-induced striatal oxidative stress and ameliorated dopaminergic neurotoxicity in 6-OHDA-lesioned mice, as evidenced by western blot analysis of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and TH immunostaining of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and the striatum. Taken together, the results suggest that T-I may be beneficial for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases like PD.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Savitt JM, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2006) Diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease: molecules to medicine. J Clin Invest 116:1744–1754
Hwang O (2013) Role of oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurobiol 22:11–17
Burton NC, Kensler TW, Guilarte TR (2006) In vivo modulation of the Parkinsonian phenotype by Nrf2. Neurotoxicology 27:1094–1100
Jakel RJ, Townsend JA, Kraft AD, Johnson JA (2007) Nrf2-mediated protection against 6-hydroxydopamine. Brain Res 1144:192–201
Rojo AI, Innamorato NG, Martin-Moreno AM, De Ceballos ML, Yamamoto M, Cuadrado A (2010) Nrf2 regulates microglial dynamics and neuroinflammation in experimental Parkinson’s disease. Glia 58:588–598
Chen PC, Vargas MR, Pani AK, Smeyne RJ, Johnson DA, Kan YW, Johnson JA (2009) Nrf2-mediated neuroprotection in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: critical role for the astrocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:2933–2938
Jazwa A, Rojo AI, Innamorato NG, Hesse M, Fernandez-Ruiz J, Cuadrado A (2011) Pharmacological targeting of the transcription factor Nrf2 at the basal ganglia provides disease modifying therapy for experimental parkinsonism. Antioxid Redox Signal 14:2347–2360
Kaidery NA, Banerjee R, Yang L, Smirnova NA, Hushpulian DM, Liby KT, Williams CR, Yamamoto M, Kensler TW, Ratan RR, Sporn MB, Beal MF, Gazaryan IG, Thomas B (2013) Targeting Nrf2-mediated gene transcription by extremely potent synthetic triterpenoids attenuate dopaminergic neurotoxicity in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 18:139–157
Lou H, Jing X, Wei X, Shi H, Ren D, Zhang X (2014) Naringenin protects against 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity via activation of the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Neuropharmacology 79:380–388
Lee JC, Park JH, Park OK, Kim IH, Yan BC, Ahn JH, Kwon SH, Choi JH, Kim JD, Won MH (2013) Neuroprotective effects of tanshinone I from Danshen extract in a mouse model of hypoxia-ischemia. Anat Cell Biol 46:183–190
Tao S, Zheng Y, Lau A, Jaramillo MC, Chau BT, Lantz RC, Wong PK, Wondrak GT, Zhang DD (2013) Tanshinone I activates the Nrf2-dependent antioxidant response and protects against As(III)-induced lung inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Antioxid Redox Signal 19:1647–1661
Rahman I, Kode A, Biswas SK (2006) Assay for quantitative determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide levels using enzymatic recycling method. Nat Protoc 1:3159–3165
Jing X, Ren D, Wei X, Shi H, Zhang X, Perez RG, Lou H (2013) Eriodictyol-7-O-glucoside activates Nrf2 and protects against cerebral ischemic injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 273:672–679
Cuadrado A, Moreno-Murciano P, Pedraza-Chaverri J (2009) The transcription factor Nrf2 as a new therapeutic target in Parkinson’s disease. Expert Opin Ther Targets 13:319–329
Chong CM, Zhou ZY, Razmovski-Naumovski V, Cui GZ, Zhang LQ, Sa F, Hoi PM, Chan K, Lee SM (2013) Danshensu protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced damage of PC12 cells in vitro and dopaminergic neurons in zebrafish. Neurosci Lett 543:121–125
Wang S, Jing H, Yang H, Liu Z, Guo H, Chai L, Hu L (2015) Tanshinone I selectively suppresses pro-inflammatory genes expression in activated microglia and prevents nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J Ethnopharmacol 164:247–255
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81274124, 81200982) and Shandong Province Science and Technology Program (No. 2014GSF118038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jing, X., Wei, X., Ren, M. et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Tanshinone I Against 6-OHDA-Induced Oxidative Stress in Cellular and Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease Through Upregulating Nrf2. Neurochem Res 41, 779–786 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1751-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1751-6