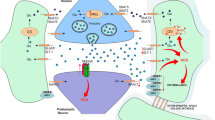
Abstract
Glutamine synthetase (GS, E.C. 6.3.1.2) is a ubiquitous and highly compartmentalized enzyme that is critically involved in several metabolic pathways in the brain, including the glutamine-glutamate-GABA cycle and detoxification of ammonia. GS is normally localized to the cytoplasm of most astrocytes, with elevated concentrations of the enzyme being present in perivascular endfeet and in processes close to excitatory synapses. Interestingly, an increasing number of studies have indicated that the expression, distribution, or activity of brain GS is altered in several brain disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia, depression, suicidality, and mesial temporal lobe epilepsy (MTLE). Although the metabolic and functional sequelae of brain GS perturbations are not fully understood, it is likely that a deficiency in brain GS will have a significant biological impact due to the critical metabolic role of the enzyme. Furthermore, it is possible that restoration of GS in astrocytes lacking the enzyme could constitute a novel and highly specific therapy for these disorders. The goals of this review are to summarize key features of mammalian GS under normal conditions, and discuss the consequences of GS deficiency in brain disorders, specifically MTLE.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elliott WH (1948) Adenosinetriphosphate in glutamine synthesis. Nature 161(4082):128
Speck JF (1949) The enzymatic synthesis of glutamine, a reaction utilizing adenosine triphosphate. J Biol Chem 179(3):1405–1426
Wu C (1963) Glutamine synthetase. I. A comparative study of its distribution in animals and its inhibition by Dl-Allo-Delta-Hydroxylysine. Comp Biochem Physiol 34:335–351
Albrecht J, Jones EA (1999) Hepatic encephalopathy: molecular mechanisms underlying the clinical syndrome. J Neurol Sci 170(2):138–146
Butterworth RF (2002) Pathophysiology of hepatic encephalopathy: a new look at ammonia. Metab Brain Dis 17(4):221–227
Choi DW, Hartley DM (1993) Calcium and glutamate-induced cortical neuronal death. In: Waxman SG (ed) Molecular and Cellular Approaches to the Treatment of Neurologic Disease. Raven Press, New York
Olney JW, Sharpe LG, Feigin RD (1972) Glutamate-induced brain damage in infant primates. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 31(3):464–488
Norenberg MD, Jayakumar AR, Rama Rao KV, Panickar KS (2007) New concepts in the mechanism of ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling. Metab Brain Dis 22(3–4):219–234
Haberle J, Gorg B, Rutsch F, Schmidt E, Toutain A, Benoist JF, Gelot A, Suc AL, Hohne W, Schliess F, Haussinger D, Koch HG (2005) Congenital glutamine deficiency with glutamine synthetase mutations. N Engl J Med 353(18):1926–1933. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa050456
Haberle J, Gorg B, Toutain A, Rutsch F, Benoist JF, Gelot A, Suc AL, Koch HG, Schliess F, Haussinger D (2006) Inborn error of amino acid synthesis: human glutamine synthetase deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis 29(2–3):352–358. doi:10.1007/s10545-006-0256-5
Hensley K, Hall N, Subramaniam R, Cole P, Harris M, Aksenov M, Aksenova M, Gabbita SP, Wu JF, Carney JM et al (1995) Brain regional correspondence between Alzheimer’s disease histopathology and biomarkers of protein oxidation. J Neurochem 65(5):2146–2156
Smith CD, Carney JM, Starke-Reed PE, Oliver CN, Stadtman ER, Floyd RA, Markesbery WR (1991) Excess brain protein oxidation and enzyme dysfunction in normal aging and in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88(23):10540–10543
Brusilow SW, Koehler RC, Traystman RJ, Cooper AJ (2010) Astrocyte glutamine synthetase: importance in hyperammonemic syndromes and potential target for therapy. Neurotherapeutics 7(4):452–470. doi:10.1016/j.nurt.2010.05.015
Klempan TA, Sequeira A, Canetti L, Lalovic A, Ernst C, ffrench-Mullen J, Turecki G (2009) Altered expression of genes involved in ATP biosynthesis and GABAergic neurotransmission in the ventral prefrontal cortex of suicides with and without major depression. Mol psychiatry 14(2):175–189. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4002110
Sequeira A, Mamdani F, Ernst C, Vawter MP, Bunney WE, Lebel V, Rehal S, Klempan T, Gratton A, Benkelfat C, Rouleau GA, Mechawar N, Turecki G (2009) Global brain gene expression analysis links glutamatergic and GABAergic alterations to suicide and major depression. PLoS ONE 4(8):e6585. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006585
Bruneau EG, McCullumsmith RE, Haroutunian V, Davis KL, Meador-Woodruff JH (2005) Increased expression of glutaminase and glutamine synthetase mRNA in the thalamus in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 75(1):27–34
Eid T, Ghosh A, Wang Y, Beckstrom H, Zaveri HP, Lee TS, Lai JC, Malthankar-Phatak GH, de Lanerolle NC (2008) Recurrent seizures and brain pathology after inhibition of glutamine synthetase in the hippocampus in rats. Brain 131(Pt 8):2061–2070
Eid T, Thomas MJ, Spencer DD, Runden-Pran E, Lai JC, Malthankar GV, Kim JH, Danbolt NC, Ottersen OP, de Lanerolle NC (2004) Loss of glutamine synthetase in the human epileptogenic hippocampus: possible mechanism for raised extracellular glutamate in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Lancet 363(9402):28–37
van der Hel WS, Notenboom RG, Bos IW, van Rijen PC, van Veelen CW, de Graan PN (2005) Reduced glutamine synthetase in hippocampal areas with neuron loss in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurology 64(2):326–333
Elliott WH (1951) Studies on the enzymic synthesis of glutamine. Biochem J 49(1):106–112
Fry BA (1955) Glutamine synthesis by Micrococcus pyogenes var. aureus. Biochem J 59(4):579–589
Elliott WH (1953) Isolation of glutamine synthetase and glutamotransferase from green peas. J Biol Chem 201(2):661–672
Tumani H, Shen GQ, Peter JB (1995) Purification and immunocharacterization of human brain glutamine synthetase and its detection in cerebrospinal fluid and serum by a sandwich enzyme immunoassay. J Immunol Methods 188(1):155–163
Kumada Y, Benson DR, Hillemann D, Hosted TJ, Rochefort DA, Thompson CJ, Wohlleben W, Tateno Y (1993) Evolution of the glutamine synthetase gene, one of the oldest existing and functioning genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(7):3009–3013
Wang Y, Kudoh J, Kubota R, Asakawa S, Minoshima S, Shimizu N (1996) Chromosomal mapping of a family of human glutamine synthetase genes: functional gene (GLUL) on 1q25, pseudogene (GLULP) on 9p13, and three related genes (GLULL1, GLULL2, GLULL3) on 5q33, 11p15, and 11q24. G. Genomics 37(2):195–199
Krajewski WW, Collins R, Holmberg-Schiavone L, Jones TA, Karlberg T, Mowbray SL (2008) Crystal structures of mammalian glutamine synthetases illustrate substrate-induced conformational changes and provide opportunities for drug and herbicide design. J Mol Biol 375(1):217–228
Gebhardt R, Mecke D (1983) Heterogeneous distribution of glutamine synthetase among rat liver parenchymal cells in situ and in primary culture. EMBO J 2(4):567–570
Blondet B, Hantaz-Ambroise D, Ait-Ikhlef A, Cambier D, Murawsky M, Rieger F (1995) Astrocytosis in wobbler mouse spinal cord involves a population of astrocytes which is glutamine synthetase-negative. Neurosci Lett 183(3):179–182
Norenberg MD (1979) Distribution of glutamine synthetase in the rat central nervous system. J Histochem Cytochem 27:756–762
Riepe RE, Norenberg MD (1978) Glutamine synthetase in the developing rat retina: an immunohistochemical study. Exp Eye Res 27(4):435–444
Derouiche A, Frotscher M (1991) Astroglial processes around identified glutamatergic synapses contain glutamine synthetase: evidence for transmitter degradation. Brain Res 552(2):346–350
Derouiche A, Ohm TG (1994) Glutamine synthetase immunoreactivity in the human hippocampus is lamina-specific. Neurosci Lett 165(1–2):179–182
Martinez-Hernandez A, Bell KP, Norenberg MD (1977) Glutamine synthetase: glial localization in brain. Science 195(4284):1356–1358
Chaudhry FA, Reimer RJ, Edwards RH (2002) The glutamine commute: take the N line and transfer to the A. Journal cell Biol 157(3):349–355. doi:10.1083/jcb.200201070
Jenstad M, Quazi AZ, Zilberter M, Haglerod C, Berghuis P, Saddique N, Goiny M, Buntup D, Davanger S, FM SH, Barnes CA, McNaughton BL, Ottersen OP, Storm-Mathisen J, Harkany T, Chaudhry FA (2009) System A transporter SAT2 mediates replenishment of dendritic glutamate pools controlling retrograde signaling by glutamate. Cereb Cortex 19(5):1092–1106. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhn151
Solbu TT, Bjorkmo M, Berghuis P, Harkany T, Chaudhry FA (2010) SAT1, a glutamine transporter, is preferentially expressed in GABAergic neurons. Front Neuroanat 4:1. doi:10.3389/neuro.05.001.2010
Kvamme E, Roberg B, Torgner IA (2001) Kinetics and localization of phosphate activated glutaminase. J Neurosci Res 66:951–958
Svenneby G (1970) Pig brain glutaminase: purification and identification of different enzyme forms. J Neurochem 17(11):1591–1599
Bellocchio EE, Hu H, Pohorille A, Chan J, Pickel VM, Edwards RH (1998) The localization of the brain-specific inorganic phosphate transporter suggests a specific presynaptic role in glutamatergic transmission. J Neurosci 18(21):8648–8659
Fremeau RT Jr, Burman J, Qureshi T, Tran CH, Proctor J, Johnson J, Zhang H, Sulzer D, Copenhagen DR, Storm-Mathisen J, Reimer RJ, Chaudhry FA, Edwards RH (2002) The identification of vesicular glutamate transporter 3 suggests novel modes of signaling by glutamate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(22):14488–14493. doi:10.1073/pnas.222546799
Fremeau RT Jr, Troyer MD, Pahner I, Nygaard GO, Tran CH, Reimer RJ, Bellocchio EE, Fortin D, Storm-Mathisen J, Edwards RH (2001) The expression of vesicular glutamate transporters defines two classes of excitatory synapse. Neuron 31(2):247–260
Takamori S, Malherbe P, Broger C, Jahn R (2002) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of human vesicular glutamate transporter 3. EMBO Rep 3(8):798–803. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kvf159
Danbolt NC (2001) Glutamate uptake. Prog Neurobiol 65:1–105
Bu DF, Erlander MG, Hitz BC, Tillakaratne NJ, Kaufman DL, Wagner-McPherson CB, Evans GA, Tobin AJ (1992) Two human glutamate decarboxylases, 65-kDa GAD and 67-kDa GAD, are each encoded by a single gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89(6):2115–2119
Jin H, Wu H, Osterhaus G, Wei J, Davis K, Sha D, Floor E, Hsu CC, Kopke RD, Wu JY (2003) Demonstration of functional coupling between γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) synthesis and vesicular GABA transport into synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(7):4293–4298. doi:10.1073/pnas.0730698100
Eulenburg V, Gomeza J (2010) Neurotransmitter transporters expressed in glial cells as regulators of synapse function. Brain Res Rev 63(1–2):103–112. doi:10.1016/j.brainresrev.2010.01.003
Richerson GB, Wu Y (2003) Dynamic equilibrium of neurotransmitter transporters: not just for reuptake anymore. J Neurophysiol 90(3):1363–1374. doi:10.1152/jn.00317.2003
Dennis SC, Lai JC, Clark JB (1977) Comparative studies on glutamate metabolism in synpatic and non-synaptic rat brain mitochondria. Biochem J 164(3):727–736
Albrecht J, Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz M, Zielinska M, Aschner M (2011) Roles of glutamine in neurotransmission. Neuron Glia Biol 6(4):263–276
Hertz L (2011) Astrocytic energy metabolism and glutamate formation–relevance for 13C-NMR spectroscopy and importance of cytosolic/mitochondrial trafficking. Magn Reson Imaging 29(10):1319–1329. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2011.04.013
Rothman DL, De Feyter HM, de Graaf RA, Mason GF, Behar KL (2011) 13C MRS studies of neuroenergetics and neurotransmitter cycling in humans. NMR Biomed 24(8):943–957. doi:10.1002/nbm.1772
Kirk E (1936) Amino acid metabolism in liver disease. Acta Med Scand Suppl 77:1–147
Gabuzda GJ Jr, Phillips GB, Davidson CS (1952) Reversible toxic manifestations in patients with cirrhosis of the liver given cation-exchange resins. N Engl J Med 246(4):124–130. doi:10.1056/NEJM195201242460402
Phillips GB, Schwartz R, Gabuzda GJ Jr, Davidson CS (1952) The syndrome of impending hepatic coma in patients with cirrhosis of the liver given certain nitrogenous substances. N Engl J Med 247(7):239–246. doi:10.1056/NEJM195208142470703
Cooper AJ, Plum F (1987) Biochemistry and physiology of brain ammonia. Physiol Rev 67(2):440–519
Haberle J, Shahbeck N, Ibrahim K, Hoffmann GF, Ben-Omran T (2011) Natural course of glutamine synthetase deficiency in a 3 years old patient. Mol Genet Metab 103(1):89–91. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2011.02.001
He Y, Hakvoort TB, Vermeulen JL, Lamers WH, Van Roon MA (2007) Glutamine synthetase is essential in early mouse embryogenesis. Dev Dyn 236(7):1865–1875. doi:10.1002/dvdy.21185
He Y, Hakvoort TB, Vermeulen JL, Labruyere WT, De Waart DR, Van Der Hel WS, Ruijter JM, Uylings HB, Lamers WH (2010) Glutamine synthetase deficiency in murine astrocytes results in neonatal death. Glia 58(6):741–754. doi:10.1002/glia.20960
Butterfield DA, Hensley K, Cole P, Subramaniam R, Aksenov M, Aksenova M, Bummer PM, Haley BE, Carney JM (1997) Oxidatively induced structural alteration of glutamine synthetase assessed by analysis of spin label incorporation kinetics: relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 68(6):2451–2457
Butterfield DA, Poon HF, St Clair D, Keller JN, Pierce WM, Klein JB, Markesbery WR (2006) Redox proteomics identification of oxidatively modified hippocampal proteins in mild cognitive impairment: insights into the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 22(2):223–232
Robinson SR (2000) Neuronal expression of glutamine synthetase in Alzheimer’s disease indicates a profound impairment of metabolic interactions with astrocytes. Neurochem Int 36(4–5):471–482
Robinson SR (2001) Changes in the cellular distribution of glutamine synthetase in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci Res 66(5):972–980
Choudary PV, Molnar M, Evans SJ, Tomita H, Li JZ, Vawter MP, Myers RM, Bunney WE Jr, Akil H, Watson SJ, Jones EG (2005) Altered cortical glutamatergic and GABAergic signal transmission with glial involvement in depression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(43):15653–15658. doi:10.1073/pnas.0507901102
Steffens M, Huppertz HJ, Zentner J, Chauzit E, Feuerstein TJ (2005) Unchanged glutamine synthetase activity and increased NMDA receptor density in epileptic human neocortex: implications for the pathophysiology of epilepsy. Neurochem Int 47(6):379–384
Spencer SS (2002) Neural networks in human epilepsy: evidence of and implications for treatment. Epilepsia 43(3):219–227
Gloor P (1991) Mesial temporal sclerosis: Historical background and an overview from a modern perspective. In: Luders H (ed) Epilepsy Surgery. Raven Press, New York, pp 689–703
Sommer W (1880) Erkrankung des Ammonshorns als aetiologisches Moment der Epilepsie. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr 10:631–675
Margerison JH, Corsellis JAN (1966) Epilepsy and the temporal lobes. Brain 89:499–530
Cavus I, Kasoff WS, Cassaday MP, Jacob R, Gueorguieva R, Sherwin RS, Krystal JH, Spencer DD, Abi-Saab WM (2005) Extracellular metabolites in the cortex and hippocampus of epileptic patients. Ann Neurol 57(2):226–235
Cavus I, Pan JW, Hetherington HP, Abi-Saab W, Zaveri HP, Vives KP, Krystal JH, Spencer SS, Spencer DD (2008) Decreased hippocampal volume on MRI is associated with increased extracellular glutamate in epilepsy patients. Epilepsia 49(8):1358–1366
During MJ, Spencer DD (1993) Extracellular hippocampal glutamate and spontaneous seizure in the conscious human brain. Lancet 341(8861):1607–1610
Kim JH, Je S, Petroff OA, Spencer SS, Hwang JY, Spencer DD (2004) Hippocampal glial density in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 45(S7):S33–S34
Petroff OA, Cavus I, Kim JH, Spencer DD (2004) Interictal extracellular glutamate concentrations are increased in hippocampal sclerosis. Ann Neurol 56(S8):S43
Petroff OA, Errante LD, Kim JH, Spencer DD (2003) N-acetyl-aspartate, total creatine, and myo-inositol in the epileptogenic human hippocampus. Neurology 60(10):1646–1651
Ben-Ari Y (1985) Limbic seizure and brain damage produced by kainic acid: mechanisms and relevance to human temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroscience 14(2):375–403
Nadler J, Cuthbertson G (1980) Kainic acid neurotoxicity toward the hippocampal formation: dependence on specific excitatory pathways. Brain Res 195:47–56
Olney JW (1978) Neurotoxicity of excitatory amino acids. In: McGeer EG, Olney JW, McGeer PL (eds) Kainic Acid as a Tool in Neurobiology. Raven Press, New York, pp 37–70
Petroff OA, Errante LD, Rothman DL, Kim JH, Spencer DD (2002) Glutamate-glutamine cycling in the epileptic human hippocampus. Epilepsia 43(7):703–710
Perez E, Lauritzen F, Wang Y, Kang D, Ottersen OP, Eid T (2010) Ultrastructural distribution of glutamate in the glutamine-synthetase-deficient epileptogenic rat hippocampus. Neurosci Meet Plan 254:220
Wang Y, Zaveri HP, Lee TS, Eid T (2009) The development of recurrent seizures after continuous intrahippocampal infusion of methionine sulfoximine in rats: a video-intracranial electroencephalographic study. Exp Neurol 220(2):293–302
Bottcher T, Goiny M, Bering J, Domhof S, Nau R, Ungerstedt U (2003) Regional differences in glutamine synthetase inhibition by l-methionine sulfoximine: a microdialysis study in the rabbit brain. Exp Brain Res 150(2):194–200
Laake JH, Slyngstad TA, Haug FM, Ottersen OP (1995) Glutamine from glial cells is essential for the maintenance of the nerve terminal pool of glutamate: immunogold evidence from hippocampal slice cultures. J Neurochem 65(2):871–881
Fellin T, Pascual O, Gobbo S, Pozzan T, Haydon PG, Carmignoto G (2004) Neuronal synchrony mediated by astrocytic glutamate through activation of extrasynaptic NMDA receptors. Neuron 43(5):729–743
Hamilton NB, Attwell D (2010) Do astrocytes really exocytose neurotransmitters? Nat Rev Neurosci 11(4):227–238. doi:10.1038/nrn2803
Tian GF, Azmi H, Takano T, Xu Q, Peng W, Lin J, Oberheim N, Lou N, Wang X, Zielke HR, Kang J, Nedergaard M (2005) An astrocytic basis of epilepsy. Nat Med 11(9):973–981
McKenna MC, Sonnewald U, Huang X, Stevenson J, Zielke HR (1996) Exogenous glutamate concentration regulates the metabolic fate of glutamate in astrocytes. J Neurochem 66(1):386–393
Kvamme E, Roberg B, Torgner IA (2000) Glutamine transport in brain mitochondria. Neurochem Int 37(2–3):131–138
Paulsen RE, Fonnum F (1989) Role of glial cells for the basal and Ca2+-dependent K+-evoked release of transmitter amino acids investigated by microdialysis. J Neurochem 52(6):1823–1829
Rothstein JD, Tabakoff B (1984) Alteration of striatal glutamate release after glutamine synthetase inhibition. J Neurochem 43(5):1438–1446
Conti F, Minelli A (1994) Glutamate immunoreactivity in rat cerebral cortex is reversibly abolished by 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine (DON), an inhibitor of phosphate-activated glutaminase. J Histochem Cytochem 42(6):717–726
Papageorgiou IE, Gabriel S, Fetani AF, Kann O, Heinemann U (2011) Redistribution of astrocytic glutamine synthetase in the hippocampus of chronic epileptic rats. Glia 59(11):1706–1718. doi:10.1002/glia.21217
Sonnewald U, Westergaard N, Schousboe A, Svendsen JS, Unsgard G, Petersen SB (1993) Direct demonstration by [13C]NMR spectroscopy that glutamine from astrocytes is a precursor for GABA synthesis in neurons. Neurochem Int 22(1):19–29
Liang SL, Carlson GC, Coulter DA (2006) Dynamic regulation of synaptic GABA release by the glutamate-glutamine cycle in hippocampal area CA1. J Neurosci 26(33):8537–8548
Cremer CM, Bidmon HJ, Gorg B, Palomero-Gallagher N, Escobar JL, Speckmann EJ, Zilles K (2010) Inhibition of glutamate/glutamine cycle in vivo results in decreased benzodiazepine binding and differentially regulated GABAergic subunit expression in the rat brain. Epilepsia. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2010.02562.x
Silver ML, Johnson RE et al (1947) White bread and epilepsy in animals. J Am Med Assoc 135(12):757–760
Campbell PN, Work TS, Mellanby E (1951) The isolation of a toxic substance from agenized wheat flour. Biochem J 48(1):106–113
Bernard-Helary K, Ardourel MY, Hevor T, Cloix JF (2002) In vivo and in vitro glycogenic effects of methionine sulfoximine are different in two inbred strains of mice. Brain Res 929(2):147–155
Folbergrova J, Passonneau JV, Lowry OH, Schulz DW (1969) Glycogen, ammonia and related metabolities in the brain during seizures evoked by methionine sulphoximine. J Neurochem 16(2):191–203
Rowe WB, Meister A (1970) Identification of l-methionine-S-sulfoximine as the convulsant isomer of methionine sulfoximine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 66(2):500–506
Sellinger OZ, Azcurra JM, Ohlsson WG (1968) Methionine sulfoximine seizures. 8. The dissociation of the convulsant and glutamine synthetase inhibitory effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 164(1):212–222
Shaw CA, Bains JS (2002) Synergistic versus antagonistic actions of glutamate and glutathione: the role of excitotoxicity and oxidative stress in neuronal disease. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 48(2):127–136
Prigol M, Bruning CA, Nogueira CW, Zeni G (2011) The role of the glutathione system in seizures induced by diphenyl diselenide in rat pups. Chem Biol Interact 193(1):65–70. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2011.05.004
Folbergrova J (1973) Glycogen and glycogen phosphorylase in the cerebral cortex of mice under the influence of methionine sulphoximine. J Neurochem 20(2):547–557
Kam K, Nicoll R (2007) Excitatory synaptic transmission persists independently of the glutamate-glutamine cycle. J Neurosci 27(34):9192–9200. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1198-07.2007
Shaw CA, Bains JS, Pasqualotto BA, Curry K (1999) Methionine sulfoximine shows excitotoxic actions in rat cortical slices. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 77(11):871–877
Albrecht J, Norenberg MD (2006) Glutamine: a Trojan horse in ammonia neurotoxicity. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 44(4):788–794
Kimelberg HK, Goderie SK, Higman S, Pang S, Waniewski RA (1990) Swelling-induced release of glutamate, aspartate, and taurine from astrocyte cultures. J Neurosci 10:1583–1591
Laake JH, Takumi Y, Eidet J, Torgner IA, Roberg B, Kvamme E, Ottersen OP (1999) Postembedding immunogold labelling reveals subcellular localization and pathway-specific enrichment of phosphate activated glutaminase in rat cerebellum. Neurosci 88:1137–1151
Chapman AG, Evans MC (1983) Cortical GABA turnover during bicuculline seizures in rats. J Neurochem 41(3):886–889
Duffy TE, Howse DC, Plum F (1975) Cerebral energy metabolism during experimental status epilepticus. J Neurochem 24(5):925–934
Folbergrova J, Ingvar M, Nevander G, Siesjo BK (1985) Cerebral metabolic changes during and following fluorothyl-induced seizures in ventilated rats. J Neurochem 44(5):1419–1426
Ingvar M, Soderfeldt B, Folbergrova J, Kalimo H, Olsson Y, Siesjo BK (1984) Metabolic, circulatory, and structural alterations in the rat brain induced by sustained pentylenetetrazole seizures. Epilepsia 25(2):191–204
Petroff OA, Prichard JW, Behar KL, Alger JR, Shulman RG (1984) In vivo phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in status epilepticus. Ann Neurol 16(2):169–177. doi:10.1002/ana.410160203
Young RS, Chen B, Petroff OA, Gore JC, Cowan BE, Novotny EJ Jr, Wong M, Zuckerman K (1989) The effect of diazepam on neonatal seizure: in vivo 31P and 1H NMR study. Pediatr Res 25(1):27–31
Voorhies TM, Ehrlich ME, Duffy TE, Petito CK, Plum F (1983) Acute hyperammonemia in the young primate: physiologic and neuropathologic correlates. Pediatr Res 17(12):970–975
Patel AB, de Graaf RA, Mason GF, Kanamatsu T, Rothman DL, Shulman GI, Behar KL (2004) Glutamatergic neurotransmission and neuronal glucose oxidation are coupled during intense neuronal activation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metabol 24(9):972–985. doi:00004647-200409000-00003
Pellerin L, Magistretti PJ (1994) Glutamate uptake into astrocytes stimulates aerobic glycolysis: a mechanism coupling neuronal activity to glucose utilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(22):10625–10629
Shulman RG, Hyder F, Rothman DL (2001) Cerebral energetics and the glycogen shunt: neurochemical basis of functional imaging. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(11):6417–6422. doi:10.1073/pnas.101129298
Sibson NR, Mason GF, Shen J, Cline GW, Herskovits AZ, Wall JE, Behar KL, Rothman DL, Shulman RG (2001) In vivo 13C NMR measurement of neurotransmitter glutamate cycling, anaplerosis and TCA cycle flux in rat brain during [2-13C] glucose infusion. J Neurochem 76(4):975–989
Swanson RA, Yu ACH, Chan PH, Sharp FR (1990) Glutamate increases glycogen content and reduces glucose utilization in primary astrocyte culture. J Neurochem 54:490–496
Brown AM, Ransom BR (2007) Astrocyte glycogen and brain energy metabolism. Glia 55(12):1263–1271
Gruetter R (2003) Glycogen: the forgotten cerebral energy store. J Neurosci Res 74(2):179–183. doi:10.1002/jnr.10785
Willard-Mack CL, Koehler RC, Hirata T, Cork LC, Takahashi H, Traystman RJ, Brusilow SW (1996) Inhibition of glutamine synthetase reduces ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling in rat. Neuroscience 71(2):589–599
Hevor TK, Delorme P, Beauvillain JC (1986) Glycogen synthesis and immunocytochemical study of fructose-1,6-biphosphatase in methionine sulfoximine epileptogenic rodent brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 6(3):292–297. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.1986.51
de Graaf RA, Mason GF, Patel AB, Rothman DL, Behar KL (2004) Regional glucose metabolism and glutamatergic neurotransmission in rat brain in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(34):12700–12705. doi:10.1073/pnas.0405065101
Sibson NR, Dhankhar A, Mason GF, Rothman DL, Behar KL, Shulman RG (1998) Stoichiometric coupling of brain glucose metabolism and glutamatergic neuronal activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(1):316–321
Seidel JL, Shuttleworth CW (2011) Contribution of astrocyte glycogen stores to progression of spreading depression and related events in hippocampal slices. Neuroscience 192:295–303. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.05.006
Badar-Goffer RS, Ben-Yoseph O, Bachelard HS, Morris PG (1992) Neuronal-glial metabolism under depolarizing conditions. A 13C-n.m.r. study. Biochem J 282(1):225–230
Dalsgaard MK, Madsen FF, Secher NH, Laursen H, Quistorff B (2007) High glycogen levels in the hippocampus of patients with epilepsy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27(6):1137–1141
Phelps CH (1972) Barbiturate-induced glycogen accumulation in brain. An electron microscopic study. Brain Res 39(1):225–234
Kong J, Shepel PN, Holden CP, Mackiewicz M, Pack AI, Geiger JD (2002) Brain glycogen decreases with increased periods of wakefulness: implications for homeostatic drive to sleep. J Neurosci 22(13):5581–5587
Dienel GA, Ball KK, Cruz NF (2007) A glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor selectively enhances local rates of glucose utilization in brain during sensory stimulation of conscious rats: implications for glycogen turnover. J Neurochem 102(2):466–478. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04595.x
Orkand PM, Bracho H, Orkand RK (1973) Glial metabolism: alteration by potassium levels comparable to those during neural activity. Brain Res 55(2):467–471
Swanson RA (1992) Physiologic coupling of glial glycogen metabolism to neuronal activity in brain. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 70(Suppl):S138–S144
Swanson RA, Morton MM, Sagar SM, Sharp FR (1992) Sensory stimulation induces local cerebral glycogenolysis: demonstration by autoradiography. Neuroscience 51(2):451–461
Wender R, Brown AM, Fern R, Swanson RA, Farrell K, Ransom BR (2000) Astrocytic glycogen influences axon function and survival during glucose deprivation in central white matter. J Neurosci 20(18):6804–6810
DiNuzzo M, Maraviglia B, Giove F (2011) Why does the brain (not) have glycogen? BioEssays 33(5):319–326. doi:10.1002/bies.201000151
Rossi DJ, Brady JD, Mohr C (2007) Astrocyte metabolism and signaling during brain ischemia. Nat Neurosci 10(11):1377–1386
Tekkok SB, Brown AM, Westenbroek R, Pellerin L, Ransom BR (2005) Transfer of glycogen-derived lactate from astrocytes to axons via specific monocarboxylate transporters supports mouse optic nerve activity. J Neurosci Res 81(5):644–652. doi:10.1002/jnr.20573
Gibbs ME, Anderson DG, Hertz L (2006) Inhibition of glycogenolysis in astrocytes interrupts memory consolidation in young chickens. Glia 54(3):214–222. doi:10.1002/glia.20377
Gibbs ME, Lloyd HG, Santa T, Hertz L (2007) Glycogen is a preferred glutamate precursor during learning in 1-day-old chick: biochemical and behavioral evidence. J Neurosci Res 85(15):3326–3333. doi:10.1002/jnr.21307
Hertz L, O’Dowd BS, Ng KT, Gibbs ME (2003) Reciprocal changes in forebrain contents of glycogen and of glutamate/glutamine during early memory consolidation in the day-old chick. Brain Res 994(2):226–233
Bernard-Helary K, Lapouble E, Ardourel M, Hevor T, Cloix JF (2000) Correlation between brain glycogen and convulsive state in mice submitted to methionine sulfoximine. Life Sci 67(14):1773–1781
Cloix JF, Hevor T (2009) Epilepsy, regulation of brain energy metabolism and neurotransmission. Curr Med Chem 16(7):841–853
Acknowledgments
The authors are supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NINDS K08 NS058674 and R01 NS070824 to TE and NIMH R01 MH095104 to KB. This work was also made possible by CTSA Grant Number UL1 RR024139 from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS), a component of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and NIH roadmap for Medical Research. The contents of the publication are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official view of NCATS or NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special Issue: In Honor of Leif Hertz.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eid, T., Behar, K., Dhaher, R. et al. Roles of Glutamine Synthetase Inhibition in Epilepsy. Neurochem Res 37, 2339–2350 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0766-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0766-5