Abstract
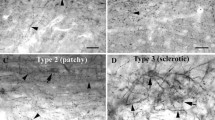
In the present study, we analyzed expressions of tandem of P domains in a Weak Inwardly rectifying K+ channel (TWIK)-related Acid-Sensitive K+ (TASK) channel-1 and -3 in the hippocampus of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) and in rat model. In the control human subjects, TASK-1, and -3 immunoreactivity was observed in pyramidal neurons and dentate granule cells. In TLE patients, TASK-1 and -3 immunoreactivity was rarely observed in neurons. However, TASK-1 immunoreactivity was observed in astrocytes, and TASK-3 immunoreactivity was detected in both astrocytes and microglia. In the rat hippocampus, TASK-1 immunoreactivity was observed in astrocytes within normal and epileptic hippocampus. The alterations in TASK-3 immunoreactivity in the rat hippocampus were similar to those in the human hippocampus. These findings reveal that TASK-1 and -3 are differentially expressed in the normal and epileptic hippocampus, and suggest that TASK channels may contribute to the properties of the epileptic hippocampus.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jan LY, Jan YN (1997) Cloned potassium channels from eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Annu Rev Neurosci 20:91–123
Hervieu GJ, Cluderay JE, Gray CW, Green PJ, Ranson JL, Randall AD (2001) Distribution and expression of TREK-1, a two-pore-domain potassium channel, in the adult rat CNS. Neuroscience 103(4):899–919
Chesler M, Kaila K (1992) Modulation of pH by neuronal activity. Trends Neurosci 15(10):396–402
Lindgren CA, Emery DG, Haydon PG (1997) Intracellular acidification reversibly reduces endoxytosis at the neuromuscular junction. J Neurosci 17(9):3074–3084
Ketchum KA, Joiner WJ, Sellers AJ, Kaczmarek LK, Goldstein SA (1995) A new family of outwardly rectifying potassium channel proteins with two pore domains in tandem. Nature 376(6542):690–695
Lesage F, Lazdunski M (2000) Molecular and functional properties of two-pore-domain potassium channels. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 279(5):F793–F801
Dingledine R, McBain CJ, McNamara JO (1990) Excitatory amino acid receptors in epilepsy. Trends Pharmacol Sci 11(8):334–338
Andrews RJ, Bringas JR, Alonzo G (1994) Cerebrospinal fluid pH and PCO2 rapidly follow arterial blood pH and PCO2 with changes in ventilation. Neurosurgery 34(3):466–470
Xiong ZQ, Stringer JL (2000) Extracellular pH responses in CA1 and the dentate gyrus during electrical stimulation, seizure discharges, and spreading depression. J Neurophysiol 83(6):3519–3524
Kim DS, Kim JE, Kwak SE, Choi HC, Song HK, Kimg YI (2007) Up-regulated astroglial TWIK-related acid-sensitive K+ channel-1 (TASK-1) in the hippocampus of seizure-sensitive gerbils: a target of anti-epileptic drugs. Brain Res 1185:346–358
Kim JE, Kwak SE, Choi SY, Kang TC (2008) Region-specific alterations in astroglial TWIK-related acid-sensitive K+-1 channel immunoreactivity in the rat hippocampal complex following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. J Comp Neurol 510(5):463–474
Wieser HG, Blume WT, Fish D, Goldensohn E, Hufnagel A, King D (2001) Commission on Neurosurgery of the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE). ILAE Commission Report. Proposal for a new classification of outcome with respect to epileptic seizures following epilepsy surgery. Epilepsia 42(2):282–286
Rau KK, Cooper BY, Johnson RD (2006) Expression of TWIK-related acid sensitive K+ channels in capsaicin sensitive and insensitive cells of rat dorsal root ganglia. Neuroscience 141(2):955–963
Millar JA, Barratt L, Southan AP, Page KM, Fyffe RE, Robertson B (2000) A functional role for the two-pore domain potassium channel TASK-1 in cerebellar granule neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(7):3614–3618
Kim DS, Kim JE, Kwak SE, Choi KC, Kim DW, Kwon OS (2008) Spatiotemporal characteristics of astroglial death in the rat hippocampo-entorhinal complex following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. J Comp Neurol 511(5):581–598
Yang P, Baker KA, Hagg T (2005) A disintegrin and metalloprotease 21 (ADAM21) is associated with neurogenesis and axonal growth in developing and adult rodent CNS. J Comp Neurol 490(2):163–179
Kang TC, Kim DS, Kwak SE, Kim JE, Won MH, Kim DW (2006) Epileptogenic roles of astroglial death and regeneration in the dentate gyrus of experimental temporal lobe epilepsy. Glia 54(4):258–271
Kindler CH, Pietruck C, Yost CS, Sampson ER, Gray AT (2000) Localization of the tandem pore domain K+ channel TASK-1 in the rat central nervous system. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 80(1):99–108
Talley EM, Lei Q, Sirois JE, Bayliss DA (2000) TASK-1, a two-pore domain K+ channel, is modulated by multiple neurotransmitters in motoneurons. Neuron 25(2):399–410
Lesage F, Guillemare E, Fink M, Duprat F, Lazdunski M, Romey G (1996) TWIK-1, a ubiquitous human weakly inward rectifying K+ channel with a novel structure. EMBO J 15(5):1004–1011
Lesage F, Lauritzen I, Duprat F, Reyes R, Fink M, Heurteaux C (1997) The structure, function and distribution of the mouse TWIK-1K+ channel. FEBS Lett 402(1):28–32
Duprat F, Lesage F, Fink M, Reyes R, Heurteaux C, Lazdunski M (1997) TASK, a human background K+ channel to sense external pH variations near physiological pH. EMBO J 16(17):5464–5471
Leonoudakis D, Gray AT, Winegar BD, Kindler CH, Harada M, Taylor DM (1998) An open rectifier potassium channel with two pore domains in tandem cloned from rat cerebellum. J Neurosci 18(3):868–877
Fink M, Duprat F, Lesage F, Reyes R, Romey G, Heurteaux C (1996) Cloning, functional expression and brain localization of a novel unconventional outward rectifier K+ channel. EMBO J 15(24):6854–6862
Meadows HJ, Benham CD, Cairns W, Gloger I, Jennings C, Medhurst AD (2000) Cloning, localisation and functional expression of the human orthologue of the TREK-1 potassium channel. Pflugers Arch 439(6):714–722
Sheng M, Liao YJ, Jan YN, Jan LY (1993) Presynaptic A-current based on heteromultimeric K+ channels detected in vivo. Nature 365(6441):72–75
Wang H, Kunkel DD, Martin TM, Schwartzkroin PA, Tempel BL (1993) Heteromultimeric K+ channels in terminal and juxtaparanodal regions of neurons. Nature 365(6441):75–79
Wang H, Kunkel DD, Schwartzkroin PA, Tempel BL (1994) Localization of Kv1.1 and Kv1.2, two K channel proteins, to synaptic terminals, somata, and dendrites in the mouse brain. J Neurosci 14(8):4588–4599
Rhodes KJ, Keilbaugh SA, Barrezueta NX, Lopez KL, Trimmer JS (1995) Association and colocalization of K+ channel alpha- and beta-subunit polypeptides in rat brain. J Neurosci 15(7 Pt 2):5360–5371
Bittner S, Budde T, Wiendl H, Meuth SG (2010) From the background to the spotlight: TASK channels in pathological conditions. Brain Pathol 20(6):999–1009
Brickley SG, Aller MI, Sandu C, Veale EL, Alder FG, Sambi H (2007) TASK-3 two-pore domain potassium channels enable sustained high-frequency firing in cerebellar granule neurons. J Neurosci 27(35):9329–9340
Doherty J, Dingledine R (2001) Reduced excitatory drive onto interneurons in the dentate gyrus after status epilepticus. J Neurosci 21(6):2048–2057
Kobayashi M, Buckmaster PS (2003) Reduced inhibition of dentate granule cells in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurosci 23(6):2440–2452
Cohen AS, Lin DD, Quirk GL, Coulter DA (2003) Dentate granule cell GABA(A) receptors in epileptic hippocampus: enhanced synaptic efficacy and altered pharmacology. Eur J Neurosci 17(8):1607–1616
Leroy C, Poisbeau P, Keller AF, Nehlig A (2004) Pharmacological plasticity of GABA(A) receptors at dentate gyrus synapses in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Physiol 557(Pt 2):473–487
Kwak SE, Kim JE, Kim DS, Won MH, Lee HJ, Choi SY (2006) Differential paired-pulse responses between the CA1 region and the dentate gyrus are related to altered CLC-2 immunoreactivity in the pilocarpine-induced rat epilepsy model. Brain Res 1115(1):162–168
Wu K, Leung LS (2003) Increased dendritic excitability in hippocampal ca1 in vivo in the kainic acid model of temporal lobe epilepsy: a study using current source density analysis. Neuroscience 116(2):599–616
Wozny C, Gabriel S, Jandova K, Schulze K, Heinemann U, Behr J (2005) Entorhinal cortex entrains epileptiform activity in CA1 in pilocarpine-treated rats. Neurobiol Dis 19(3):451–460
Gabriel S, Kivi A, Eilers A, Kovács R, Heinemann U (1998) Effects of barium on stimulus-induced rises in [K+]o in juvenile rat hippocampal area CA1. Neuroreport 9(11):583–587
Schilling T, Eder C (2007) Ion channel expression in resting and activated microglia of hippocampal slices from juvenile mice. Brain Res 1186:21–28
Schilling T, Nitsch R, Heinemann U, Haas D, Eder C (2001) Astrocyte-released cytokines induce ramification and outward K+ channel expression in microglia via distinct signalling pathways. Eur J Neurosci 14(3):463–473
Ince C, Coremans JM, Ypey DL, Leijh PC, Verveen AA, van Furth R (1997) Phagocytosis by human macrophages is accompanied by changes in ionic channel currents. J Cell Biol 106(6):1873–1878
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Research Foundation of Korea; Contract grant number: 2010K000808 and 2009-0093812.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JE., Yeo, SI., Ryu, H.J. et al. Changes in TWIK-related Acid Sensitive K+-1 and -3 Channel Expressions from Neurons to Glia in the Hippocampus of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Patients and Experimental Animal Model. Neurochem Res 36, 2155–2168 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-011-0540-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-011-0540-0