Abstract
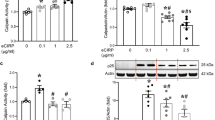
Gelsolin plays an important role in the regulation of amyloid beta-protein fibrillogenesis. We report here that calcium ionophore A23187 induces the expression of cytoplasmic gelsolin (c-gelsolin), and that protein kinase C (PKC) is involved in the up-regulation of c-gelsolin. In the presence of calcium, both SH-SY5Y and HEK-293 cells upon treatment with A23187 showed an increase in c-gelsolin expression in a concentration-dependent manner. Calcium-mediated up-regulation of c-gelsolin was inhibited by cycloheximide (a general inhibitor of protein synthesis). When cells were pretreated with staurosporine (an inhibitor of a variety of protein kinases including PKC), the up-regulation of c-gelsolin induced by A23187 was inhibited. Calphostin C, an inhibitor of PKC, blocked the up-regulation of c-gelsolin induced by A23187, while inhibitors of mitogen-activated protein kinases had no effect on c-gelsolin expression. In addition, phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate, an activator of PKC, up-regulated c-gelsolin expression. These results suggest that calcium mediates up-regulation of c-gelsolin in a PKC-dependent manner.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Aβ:
-
Amyloid beta-protein
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- APP:
-
β-amyloid precursor protein
- CHX:
-
Cycloheximide
- DAG:
-
Diacylglycerol
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium
- DMSO:
-
Dimethylsulfoxide
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- IP3 :
-
Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate
- JNK:
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase
- MAPKs:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- PLA2 :
-
Phospholipase A2
- PLC:
-
Phospholipase C
- PMA:
-
Phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate
References
Yin HL, Kwiatkowski DJ, Mole JE et al (1984) Structure and biosynthesis of cytoplasmic and secreted variants of gelsolin. J Biol Chem 259:5271–5276
Wen D, Corina K, Chow EP et al (1996) The plasma and cytoplasmic forms of human gelsolin differ in disulfide structure. Biochemistry 35:9700–9709
Witke W, Sharpe AH, Hartwig JH et al (1995) Hemostatic, inflammatory, and fibroblast responses are blunted in mice lacking gelsolin. Cell 81:41–51
Endres M, Fink K, Zhu J et al (1999) Neuroprotective effects of gelsolin during murine stroke. J Clin Invest 103:347–354
Yildirim F, Gertz K, Kronenberg G et al (2008) Inhibition of histone deacetylation protects wildtype but not gelsolin-deficient mice from ischemic brain injury. Exp Neurol 210:531–542
Asch HL, Head K, Dong Y et al (1996) Widespread loss of gelsolin in breast cancers of humans, mice, and rats. Cancer Res 56:4841–4845
Prasad SC, Thraves PJ, Dritschilo A et al (1997) Protein expression changes associated with radiation-induced neoplastic progression of human prostate epithelial cells. Electrophoresis 18:629–637
Dosaka-Akita H, Hommura F, Fujita H et al (1998) Frequent loss of gelsolin expression in non-small cell lung cancers of heavy smokers. Cancer Res 58:322–327
Maury CP, Sletten K, Totty N et al (1997) Identification of the circulating amyloid precursor and other gelsolin metabolites in patients with G654A mutation in the gelsolin gene (Finnish familial amyloidosis): pathogenetic and diagnostic implications. Lab Invest 77:299–304
Chauhan VP, Ray I, Chauhan A et al (1999) Binding of gelsolin, a secretory protein, to amyloid beta-protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 258:241–246
Hirko AC, Meyer EM, King MA et al (2007) Peripheral transgene expression of plasma gelsolin reduces amyloid in transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Ther 15:1623–1629
Ji L, Chauhan A, Chauhan V (2008) Cytoplasmic gelsolin in pheochromocytoma-12 cells forms a complex with amyloid beta-protein. Neuroreport 19:463–466
Ji L, Chauhan A, Chauhan V (2009) Role of gelsolin in Alzheimer’s disease. In: Sun M-K (ed) Research progress in Alzheimer’s disease and dementia, vol. 4. Nova Science Publishers, Inc., New York, pp 199–218
Ray I, Chauhan A, Wegiel J et al (2000) Gelsolin inhibits the fibrillization of amyloid beta-protein, and also defibrillizes its preformed fibrils. Brain Res 853:344–351
Glenner GG (1983) Alzheimer’s disease. The commonest form of amyloidosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 107:281–282
Tanaka J, Sobue K (1994) Localization and characterization of gelsolin in nervous tissues: gelsolin is specifically enriched in myelin-forming cells. J Neurosci 14:1038–1052
Matsuoka Y, Saito M, LaFrancois J et al (2003) Novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease by peripheral administration of agents with an affinity to beta-amyloid. J Neurosci 23:29–33
Antequera D, Vargas T, Ugalde C et al (2009) Cytoplasmic gelsolin increases mitochondrial activity and reduces Abeta burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 36:42–50
Azuma T, Koths K, Flanagan L et al (2000) Gelsolin in complex with phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate inhibits caspase-3 and -9 to retard apoptotic progression. J Biol Chem 275:3761–3766
Koya RC, Fujita H, Shimizu S et al (2000) Gelsolin inhibits apoptosis by blocking mitochondrial membrane potential loss and cytochrome c release. J Biol Chem 275:15343–15349
Kusano H, Shimizu S, Koya RC et al (2000) Human gelsolin prevents apoptosis by inhibiting apoptotic mitochondrial changes via closing VDAC. Oncogene 19:4807–4814
Obrig TG, Culp WJ, McKeehan WL et al (1971) The mechanism by which cycloheximide and related glutarimide antibiotics inhibit peptide synthesis on reticulocyte ribosomes. J Biol Chem 246:174–181
Toledo LM, Lydon NB (1997) Structures of staurosporine bound to CDK2 and Capk—new tools for structure-based design of protein kinase inhibitors. Structure 5:1551–1556
Ohori M, Kinoshita T, Okubo M et al (2005) Identification of a selective ERK inhibitor and structural determination of the inhibitor-ERK2 complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 336:357–363
Deng R, Li W, Guan Z et al (2006) Acetylcholinesterase expression mediated by c-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase pathway during anticancer drug-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 25:7070–7077
Su JH, Zhao M, Anderson AJ et al (2001) Activated caspase-3 expression in Alzheimer’s and aged control brain: correlation with Alzheimer pathology. Brain Res 898:350–357
LeBlanc A, Liu H, Goodyer C et al (1999) Caspase-6 role in apoptosis of human neurons, amyloidogenesis, and Alzheimer’s disease. J Biol Chem 274:23426–23436
Rohn TT, Rissman RA, Davis MC et al (2002) Caspase-9 activation and caspase cleavage of tau in the Alzheimer’s disease brain. Neurobiol Dis 11:341–354
Rissman RA, Poon WW, Blurton-Jones M et al (2004) Caspase-cleavage of tau is an early event in Alzheimer disease tangle pathology. J Clin Invest 114:121–130
Mouser PE, Head E, Ha KH et al (2006) Caspase-mediated cleavage of glial fibrillary acidic protein within degenerating astrocytes of the Alzheimer’s disease brain. Am J Pathol 168:936–946
Rohn TT, Head E, Su JH et al (2001) Correlation between caspase activation and neurofibrillary tangle formation in Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Pathol 158:189–198
Chauhan V, Chauhan A (2006) Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Pathophysiology 13:195–208
Chauhan V, Ji L, Chauhan A (2008) Anti-amyloidogenic, anti-oxidant and anti-apoptotic role of gelsolin in Alzheimer’s disease. Biogerontology 9:381–389
Granados MP, Salido GM, Gonzalez A et al (2006) Dose-dependent effect of hydrogen peroxide on calcium mobilization in mouse pancreatic acinar cells. Biochem Cell Biol 84:39–48
Korzets A, Chagnac A, Weinstein T et al (1999) H2O2 induces DNA repair in mononuclear cells: evidence for association with cytosolic Ca2+ fluxes. J Lab Clin Med 133:362–369
Giambelluca MS, Gende OA (2008) Hydrogen peroxide activates calcium influx in human neutrophils. Mol Cell Biochem 309:151–156
Sharma AK, Rohrer B (2004) Calcium-induced calpain mediates apoptosis via caspase-3 in a mouse photoreceptor cell line. J Biol Chem 279:35564–35572
Gordeeva AV, Zvyagilskaya RA, Labas YA (2003) Cross-talk between reactive oxygen species and calcium in living cells. Biochemistry (Mosc) 68:1077–1080
Maruyama J, Naguro I, Takeda K et al (2009) Stress-activated MAP kinase cascades in cellular senescence. Curr Med Chem 16:1229–1235
Kim J, Wong PK (2009) Oxidative stress is linked to ERK1/2-p16 signaling-mediated growth defect in ATM-deficient astrocytes. J Biol Chem 284:14396–14404
Liscovitch M, Cantley LC (1994) Lipid second messengers. Cell 77:329–334
Berridge MJ (1993) Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature 361:315–325
Cressman CM, Mohan PS, Nixon RA et al (1995) Proteolysis of protein kinase C: mM and microM calcium-requiring calpains have different abilities to generate, and degrade the free catalytic subunit, protein kinase M. FEBS Lett 367:223–227
Demuro A, Mina E, Kayed R et al (2005) Calcium dysregulation and membrane disruption as a ubiquitous neurotoxic mechanism of soluble amyloid oligomers. J Biol Chem 280:17294–17300
Chauhan A, Chauhan VP, Brockerhoff H et al (1991) Action of amyloid beta-protein on protein kinase C activity. Life Sci 49:1555–1562
Petersen RC, Smith GE, Ivnik RJ et al (1994) Memory function in very early Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 44:867–872
Bank B, DeWeer A, Kuzirian AM et al (1988) Classical conditioning induces long-term translocation of protein kinase C in rabbit hippocampal CA1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:1988–1992
Olds JL, Alkon DL (1993) Protein kinase C: a nexus in the biochemical events that underlie associative learning. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 53:197–207
Pascale A, Govoni S, Battaini F (1998) Age-related alteration of PKC, a key enzyme in memory processes: physiological and pathological examples. Mol Neurobiol 16:49–62
Cole G, Dobkins KR, Hansen LA et al (1988) Decreased levels of protein kinase C in Alzheimer brain. Brain Res 452:165–174
Govoni S, Bergamaschi S, Racchi M et al (1993) Cytosol protein kinase C downregulation in fibroblasts from Alzheimer’s disease patients. Neurology 43:2581–2586
Wang HY, Pisano MR, Friedman E (1994) Attenuated protein kinase C activity and translocation in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Neurobiol Aging 15:293–298
Kurumatani T, Fastbom J, Bonkale WL et al (1998) Loss of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor sites and decreased PKC levels correlate with staging of Alzheimer’s disease neurofibrillary pathology. Brain Res 796:209–221
Desdouits F, Buxbaum JD, Desdouits-Magnen J et al (1996) Amyloid alpha peptide formation in cell-free preparations. Regulation by protein kinase C, calmodulin, and calcineurin. J Biol Chem 271:24670–24674
Favit A, Grimaldi M, Nelson TJ et al (1998) Alzheimer’s-specific effects of soluble beta-amyloid on protein kinase C-alpha and -gamma degradation in human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:5562–5567
Pakaski M, Balaspiri L, Checler F et al (2002) Human amyloid-beta causes changes in the levels of endothelial protein kinase C and its alpha isoform in vitro. Neurochem Int 41:409–414
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by funds from the New York State Office of Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities, and by NIH Grant No. AG020992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, L., Chauhan, A. & Chauhan, V. Calcium Induces Expression of Cytoplasmic Gelsolin in SH-SY5Y and HEK-293 Cells. Neurochem Res 35, 1075–1082 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-010-0157-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-010-0157-8