Abstract
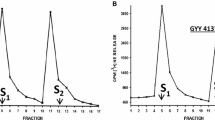
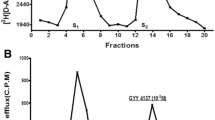
In the present study, we investigated the pharmacological action of hydrogen sulfide (H2S, using sodium hydrosulfide, NaHS, and/or sodium sulfide, Na2S as donors) on sympathetic neurotransmission from isolated, superfused porcine iris-ciliary bodies. We also examined the effect of H2S on norepinephrine (NE), dopamine and epinephrine concentrations in isolated porcine anterior uvea. Release of [3H]NE was triggered by electrical field stimulation and basal catecholamine concentrations was measured by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Both NaHS and Na2S caused a concentration-dependent inhibition of electrically evoked [3H]NE release from porcine iris-ciliary body without affecting basal [3H]NE efflux. The inhibitory action of H2S donors on NE release was attenuated by aminooxyacetic acid (AOA) and propargyglycine (PAG), inhibitors of cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) and cystathionine γ-lyase (CSE), respectively. With the exception of dopamine, NaHS caused a concentration-dependent reduction in endogenous NE and epinephrine concentrations in isolated iris-ciliary bodies. We conclude that H2S can inhibit sympathetic neurotransmission from isolated porcine anterior uvea, an effect that is dependent, at least in part, on intramural biosynthesis of this gas. Furthermore, the observed action of H2S donors on sympathetic transmission may be due to a direct action of this gas on neurotransmitter pools.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Erickson PF, Maxwell IH, Su LJ, Baumann M, Glode LM (1990) Sequence of cDNA for rat cystathionine gamma-lyase and comparison of deduced amino acid sequence with related Escherichia coli enzymes. Biochem J 269:335–340
Stipanuk MH, Beck PW (1982) Characterization of the enzymic capacity for cysteine desulphhydration in liver and kidney of the rat. Biochem J 206:267–277
Swaroop M, Bradley K, Ohura T, Tahara T, Roper MD, Rosenberg LE et al (1992) Rat cystathionine beta-synthase. Gene organization and alternative splicing. J Biol Chem 267:11455–11461
Hosoki R, Matsuki N, Kimura H (1997) The possible role of hydrogen sulfide as an endogenous smooth muscle relaxant in synergy with nitric oxide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 237:527–531. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.6878
Levonen AL, Lapatto R, Saksela M, Raivio KO (2000) Human cystathionine gamma-lyase: developmental and in vitro expression of two isoforms. Biochem J 347(Pt 1):291–295. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3470291
Lu Y, O’Dowd BF, Orrego H, Israel Y (1992) Cloning and nucleotide sequence of human liver cDNA encoding for cystathionine gamma-lyase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 189:749–758. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(92)92265-Y
Meier M, Janosik M, Kery V, Kraus JP, Burkhard P (2001) Structure of human cystathionine beta-synthase: a unique pyridoxal 5′-phosphate-dependent heme protein. EMBO J 20:3910–3916. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.15.3910
van der Molen EF, Hiipakka MJ, van Lith-Zanders H, Boers GH, van den Heuvel LP, Monnens LA et al (1997) Homocysteine metabolism in endothelial cells of a patient homozygous for cystathionine beta-synthase (CS) deficiency. Thromb Haemost 78:827–833
Yap S, Naughten ER, Wilcken B, Wilcken DE, Boers GH (2000) Vascular complications of severe hyperhomocysteinemia in patients with homocystinuria due to cystathionine beta-synthase deficiency: effects of homocysteine-lowering therapy. Semin Thromb Hemost 26:335–340. doi:10.1055/s-2000-8100
Persa C, Osmotherly K, Chao-Wei CK, Moon S, Lou MF (2006) The distribution of cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS) in the eye: implication of the presence of a trans-sulfuration pathway for oxidative stress defense. Exp Eye Res 83:817–823. doi:10.1016/j.exer.2006.04.001
Reiffenstein RJ, Hulbert WC, Roth SH (1992) Toxicology of hydrogen sulfide. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 32:109–134. doi:10.1146/annurev.pa.32.040192.000545
Watanabe M, Osada J, Aratani Y, Kluckman K, Reddick R, Malinow MR et al (1995) Mice deficient in cystathionine beta-synthase: animal models for mild and severe homocyst(e)inemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:1585–1589. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.5.1585
Moore PK, Bhatia M, Moochhala S (2003) Hydrogen sulfide: from the smell of the past to the mediator of the future? Trends Pharmacol Sci 24:609–611. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2003.10.007
Wang R (2002) Two’s company, three’s a crowd: can H2S be the third endogenous gaseous transmitter? FASEB J 16:1792–1798. doi:10.1096/fj.02-0211hyp
Boehning D, Snyder SH (2003) Novel neural modulators. Annu Rev Neurosci 26:105–131. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.26.041002.131047
Zhao W, Zhang J, Lu Y, Wang R (2001) The vasorelaxant effect of H(2)S as a novel endogenous gaseous K(ATP) channel opener. EMBO J 20:6008–6016. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.21.6008
Zhao W, Wang R (2002) H(2)S-induced vasorelaxation and underlying cellular and molecular mechanisms. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 283:H474–H480
Eto K, Ogasawara M, Umemura K, Nagai Y, Kimura H (2002) Hydrogen sulfide is produced in response to neuronal excitation. J Neurosci 22:3386–3391
Kimura H (2002) Hydrogen sulfide as a neuromodulator. Mol Neurobiol 26:13–19. doi:10.1385/MN:26:1:013
Abe K, Kimura H (1996) The possible role of hydrogen sulfide as an endogenous neuromodulator. J Neurosci 16:1066–1071
Roth SH, Skrajny B, Reiffenstein RJ (1995) Alteration of the morphology and neurochemistry of the developing mammalian nervous system by hydrogen sulphide. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 22:379–380. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1681.1995.tb02024.x
Skrajny B, Hannah RS, Roth SH (1992) Low concentrations of hydrogen sulphide alter monoamine levels in the developing rat central nervous system. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 70:1515–1518
Opere CA, Monjok EM, Kaustubh KK, Zhao M, WeiDong Z, Ohia SE (2005) Regulation of [3H]-d-Aspartate release from mammalian isolated retinae by hydrogen sulfide. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:E-Abstract 2228
Ohia SE, Zeyssig R, Monjok EM, Kouamou GE, Opere CA (2006) Effect of hydrogen sulfide on catecholamin levels in mammalian ocular and brain tissues, in vitro. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47: E-Abstract 2611
Opere CA, Ohia SE (1997) Role of cyclic AMP in hydrogen peroxide-induced potentiation of sympathetic neurotransmission in the bovine iris. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther 13:261–268
Liu JHK (1992) Aqueous humor messengers in the transient decrease of intraocular pressure after ganglionectomy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 33:3181–3185
Lowicka E, Beltowski J (2007) Hydrogen sulfide (H2S)-the third gas of interest for pharmacologists. Pharmacol Rep 59:4–24
Beltowski J (2004) Hydrogen sulfide as a biologically active mediator in the cardiovascular system. Postepy Hig Med Dosw Online 58:285–291
Doeller JE, Isbell TS, Benavides G, Koenitzer J, Patel H, Patel RP, Lancaster JR Jr, rley-Usmar VM, Kraus DW (2005) Polarographic measurement of hydrogen sulfide production and consumption by mammalian tissues. Anal Biochem 341:40–51. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2005.03.024
Kimura H, Nagai Y, Umemura K, Kimura Y (2005) Physiological roles of hydrogen sulfide: synaptic modulation, neuroprotection, and smooth muscle relaxation. Antioxid Redox Signal 7:795–803. doi:10.1089/ars.2005.7.795
Eto K, Asada T, Arima K, Makifuchi T, Kimura H (2002) Brain hydrogen sulfide is severely decreased in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 293:1485–1488. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00422-9
Belardinelli MC, Chabli A, Chadefaux-Vekemans B, Kamoun P (2001) Urinary sulfur compounds in Down syndrome. Clin Chem 47:1500–1501
Chen YH, Yao WZ, Geng B, Ding YL, Lu M, Zhao MW et al (2005) Endogenous hydrogen sulfide in patients with COPD. Chest 128:3205–3211. doi:10.1378/chest.128.5.3205
Zanardo RC, Brancaleone V, Distrutti E, Fiorucci S, Cirino G, Wallace JL (2006) Hydrogen sulfide is an endogenous modulator of leukocyte-mediated inflammation. FASEB J 20:2118–2120. doi:10.1096/fj.06-6270fje
Bian JS, Yong QC, Pan TT, Feng ZN, Ali MY, Zhou S et al (2006) Role of hydrogen sulfide in the cardioprotection caused by ischemic preconditioning in the rat heart and cardiac myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 316:670–678. doi:10.1124/jpet.105.092023
Chunyu Z, Junbao D, Dingfang B, Hui Y, Xiuying T, Chaoshu T (2003) The regulatory effect of hydrogen sulfide on hypoxic pulmonary hypertension in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 302:810–816. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(03)00256-0
Collin M, Thiemermann C (2005) Hydrogen sulfide and sulfite: novel mediators in the pathophysiology of shock and inflammation. Shock 24:595–596. doi:10.1097/01.shk.0000188328.59770.25
Qu K, Chen CP, Halliwell B, Moore PK, Wong PT (2006) Hydrogen sulfide is a mediator of cerebral ischemic damage. Stroke 37:889–893. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000204184.34946.41
Beauchamp RO Jr, Bus JS, Popp JA, Boreiko CJ, Andjelkovich DA (1984) A critical review of the literature on hydrogen sulfide toxicity. Crit Rev Toxicol 13:25–97. doi:10.3109/10408448409029321
Collin M, Anuar FB, Murch O, Bhatia M, Moore PK, Thiemermann C (2005) Inhibition of endogenous hydrogen sulfide formation reduces the organ injury caused by endotoxemia. Br J Pharmacol 146:498–505. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp. 0706367
Fiorucci S, Antonelli E, Distrutti E, Rizzo G, Mencarelli A, Orlandi S et al (2005) Inhibition of hydrogen sulfide generation contributes to gastric injury caused by anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal drugs. Gastroenterology 129:1210–1224. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2005.07.060
Tamizhselvi R, Moore PK, Bhatia M (2007) Hydrogen sulfide acts as a mediator of inflammation in acute pancreatitis: in vitro studies using isolated mouse pancreatic acinar cells. J Cell Mol Med 11:315–326. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00024.x
Julian D, Statile JL, Wohlgemuth SE, Arp AJ (2002) Enzymatic hydrogen sulfide production in marine invertebrate tissues. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 133:105–115. doi:10.1016/S1095-6433(02)00122-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kulkarni, K.H., Monjok, E.M., Zeyssig, R. et al. Effect of Hydrogen Sulfide on Sympathetic Neurotransmission and Catecholamine Levels in Isolated Porcine Iris-Ciliary Body. Neurochem Res 34, 400–406 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-008-9793-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-008-9793-7