Abstract
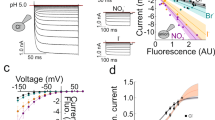
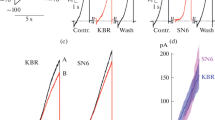
The Na+/H+ exchanger has been the only unequivocally demonstrated H+-transport mechanism in the synaptosomal preparation. We had previously suggested that a Cl−–H+ symporter (in its acidifying mode) is involved in cytosolic pH regulation in the synaptosomal preparation. Supporting this suggestion, we now show that: (1) when synaptosomes are transferred from PSS to either gluconate or sulfate solutions, the Fura-2 ratio remains stable instead of increasing as it does in 50 mM K solution. This indicates that these anions do not promote a plasma membrane depolarization. (2) Based in the recovery rate from the cytosolic alkalinization, the anionic selectivity of the Cl−–H+ symporter is NO −3 > Br− > Cl− >> I− = isethionate = sulfate = methanesulfonate = gluconate. (3) PCMB 10 μM inhibits the gluconate-dependent alkalinization by 30 ± 6%. (4) Neither Niflumic acid, 9AC, Bumetanide nor CCCP inhibits the recovery from the cytosolic alkalinization.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jean T, Frelin C, Vigne P, Barbry P, Lazdunski M (1985) Biochemical properties of the Na+/H+ exchange system in rat brain synaptosomes. J Biol Chem 260:9678–9684
Drapeau P, Nachshen DA (1988) Effects of lowering extracellular and cytosolic pH on calcium fluxes, cytosolic calcium levels, and transmitter release in presynaptic nerve terminals isolated from rat brain. J Gen Physiol 91:305–315
Sanchez-Armass S, Martinez-Zaguilan R, Martinez G, Gillies JR (1994) Regulation of pH in rat bain synaptosomes. I. Role of sodium, bicarbonate and potassium. J Neurophysiol 71:2236–2248
Sauvaigo S, Vigne P, Frelin C, Lazdunski M (1984) Identification of an amiloride sensitive Na+/H+ exchange system in brian synaptosomes. Brain Res 301:371–374
Martínez-Zaguilan R, Gillies JR, Sanchez-Armass S (1994) Regulation of pH in rat brain synaptosomes. II Role of chloride. J Neurophysiol 71:2249–2257
Boron WF (1986) Intracellular pH regulation in epithelial cell. Annu Rev Physiol 48:377–388
Chesler M (1987) pH regulation in the vertebrate central nervous system: microelectrode studies in the brain stem of the lamprey. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 65:986–993
Tonnessen TI, Sandvig K, Olsnes S (1990) Role of Na+/H+ and Cl−/HCO −3 antiports in the regulation of cytosolic pH near neutrality. Am J Physiol 258:C1117–C1126
Baxter KA, Church J (1996) Characterization of acid extrusion mechanisms in cultured fetal rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol 493:457–470
Ives HE, Chen PY, Verkman AS (1986) Mechanism of coupling between Cl− and OH− transport in renal brush-border membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 863:91–100
Karniski LP (1989) Activation of Cl−/OH− exchange by parachloromercuribenzoic acid in rabbit renal brush-border membranes. J Membr Biol 112:59–66
Alvarado F, Vasseur M (1998) Direct inhibitory effect of CCCP on the Cl−–H+ symporter of the guinea pig ileal brush border membrane. Am J Physiol 274:C481–C491
Vasseur M, Caüzac M, Frangne R, Alvarado F (1992) Trans-potassium effects on the chloride-proton symporter activity of guinea-pig ileal brush border membrane vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta 1107:150–158
Kongsamut S, Nachshen DA (1988) Measurement of the cytosolic sodium ion concentration in rat brain synaptosomes by a fluorescence method. Biochim Biophys Acta 940:241–246
Nagy A, Delgado-Escueta AV (1984) Rapid preparation of synaptosomes from mammalian brain using nontoxic isoosmotic grandient material (Percoll). J Neurochem 43:1114–1123
Dunkley PR, Heath JW, Harrison SM, Jarvie PE, Glenfield PJ, Rostas JAP (1988) A rapid Percoll gradient procedure for isolation of synaptosomes directly from an S1 fraction: homogeneity and morphology of subcellular fractions. Brain Res 441:59–71
Espinosa-Tanguma R, Guevara C, Gonzalez J, Ortega F, Ramírez-Zacarias JL, Hernández AE, Mandeville P, Sanchez-Armass S (2003) Changes in [Ca2+] in guinea pig tracheal smooth muscle cells in culture: effects of Na+ and ouabain. J Physiol Biochem 59:25–34
Sanchez-Armass S, Sennoune S, Ortega F, Martinez-Zaguilan R (2006) Spectral imaging microscopy demonstrate cytoplasmic pH heterogeneities in glioma cells. Am J Physiol 290:C524–C538
Simchowitz L, Roos A (1985) Regulaion of intracellular pH in human neutrophils. J Gen Physiol 85:443–470
R Development Core Team (2006) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org
Heiberger RM, Holland B (2004) Statistical analysis and data display: an intermediate course with examples in S-plus, R and SAS. Springer Texts in Statistics, Springer Science & Business Media Inc., New York, pp 111, 132–132, 148–150, 310
Thomas RC, Meech W (1982) Hydrogen ion currents and intracellular pH in depolarized voltage-clamped snail neurons. Nature 29:826–828
Byerly l, Meech RW (1984) Rapidly activated hydrogen ion currents in perfused neurons of the snail Limnea stagnalis. J Physiol 351:199–216
Kaila K, Viopio J (1987) Postsynaptic fall in intracellular pH induced by GABA-activated bicarbonate conductance. Nature (London) 330:163–165
Diamond JM, Wright EM (1969) Biological membranes: the physical basis of ion and nonelectrolyte selectivity. Annu Rev Physiol 31:581–646
Bryant SH, Morales-Aguilera A (1971) Chloride conductance in normal and myotonic muscle fibers and the action of monocarboxylic aromatic acids. J Physiol Lond 219:367–383
Drapeau P, Sanchez-Armass S (1988) Selection of postsynaptic serotonin receptors during reinnervation of an identified leech neuron in culture. J Neurosci 8:4718–4727
Ai T, Bompadre SG, Sohma Y, Wang X, Li M, Hwang TC (2004) Direct effects of 9-anthracene compounds on cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gating. Pflügers Arch 449:88–95
Large WA, Wang Q (1996) Characteristics and physiological role of the Ca2+-activated Cl− conductance in smooth muscle. Am J Physiol 271:C435–C454
Picollo A, Liantonio A, Babini E, Camerino DC, Pusch M (2007) Mechanism of Interaction of niflumic acid with heterologously expressed kidney CLC-K chloride channels. J Membr Biol 216:73–82
Babila T, Gottlieb Y, Lutz RA, Lichtstein D (1989) A bumetanide—sensitive, potassium carrier-mediated transport system in excitable tissues. Life Sci 44:1665–1675
Babila T, Atlan H, Fromer I, Schwalb H, Uretzki G, Lichtstein D (1990) Volume regulation of nerve terminals. J Neurochem 55:2058–2061
Pond BB, Berglund K, Kuner T, Feng G, Augustine GJ, Schwartz-Bloom RD (2006) The chloride transporter Na+–K+–Cl− cotransporter isoform-1 contributes to intracellular chloride increases after in vitro ischemia. J Neurosci 26:1396–1406
Colin W, Campbell B (1976) The Na+, K+, Cl− contents and derived membrane potentials of presynaptic nerve ending in vitro. Brain Res 101:594–599
Marchbanks RM (1975) The chloride content, anion deficit and volume of synaptosomes. J Neurochem 25:463–470
Blaustein MP, Goldring JM (1975) Membrane potentials in pinched-off presynaptic nerve terminals monitored with a fluorescent probe: evidence that synaptosomes have potassium diffusion potentials. J Physiol Lond 247:589–615
Sanchez-Armass S, Orrego F (1979) A major role for chloride in (3H)-Noradrenaline transport by rat heart adrenergic nerves. Life Sci 20:1829–1838
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by CONACyT (México) 29212-N and UASLP FAI-C05-FAI-10-3.24 to SSA; CONACyT (México) 62220 to RET, UM, SSA; M.L. Torres was a recipient of a M.Sc. degree fellowship from CONACyT (México). We are indebted to Ulises Meza for his critical reading and to Peter Mandeville and Omar Sanchez-Armass for the style correction of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special issue article in honor of Dr. Ricardo Tapia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torres, M.L., Ortega, F., Cuaranta, I. et al. Anionic Selectivity Sequence of the Cl−–H+ Symporter in the Synaptosomal Preparation from Rat Brain Cortex. Neurochem Res 33, 1574–1581 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-008-9685-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-008-9685-x