Abstract
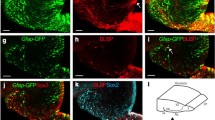
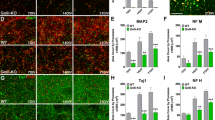
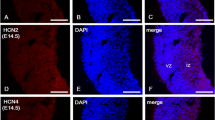
Previous work from our laboratory demonstrated that the RNA-binding protein HuD binds to and stabilizes the GAP-43 mRNA. In this study, we characterized the expression of HuD and GAP-43 mRNA in the hippocampus during two forms of neuronal plasticity. During post-natal development, maximal expression of both molecules was found at P5 and their levels steadily decreased thereafter. At P5, HuD was also present in the subventricular zone, where it co-localized with doublecortin. In the adult hippocampus, the basal levels of HuD and GAP-43 were lower than during development but were significantly increased in the dentate gyrus after seizures. The function of HuD in GAP-43 gene expression was confirmed using HuD-KO mice, in which the GAP-43 mRNA was significantly less stable than in wild type mice. Altogether, these results demonstrate that HuD plays a role in the post-transcriptional control of GAP-43 mRNA in dentate granule cells during developmental and adult plasticity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elliott RC, Miles MF, Lowenstein DH (2003) Overlapping microarray profiles of dentate gyrus gene expression during development and epilepsy-associated neurogenesis and axon outgrowth. J Neurosci 23:2218–2227
Represa A, Ben-Ari Y (1997) Molecular and cellular cascades in seizure-induced neosynapse formation. Adv Neurol 72:25–34
Benowitz LI, Routtenberg A (1997) GAP-43: an intrinsic determinant of neuronal development and plasticity. Trends Neurosci 20:84–91
Perrone-Bizzozero NI, Tanner DC (2006) GAP-43 in neural development and plasticity. In: Lajtha A (ed) Neuroactive proteins and peptides. Springer, Berlin, pp 316–329
Strittmatter SM, Fankhauser C, Huang PL, Mashimo H, Fishman MC (1995) Neuronal pathfinding is abnormal in mice lacking the neuronal growth cone protein GAP-43. Cell 80:445–452
Rekart JL, Meiri K, Routtenberg A (2005) Hippocampal-dependent memory is impaired in heterozygous GAP-43 knockout mice. Hippocampus 15:1–7
Aigner L, Arber S, Kapfhammer JP, Laux T, Schneider C, Botteri F, Brenner HR, Caroni P (1995) Overexpression of the neural growth-associated protein GAP-43 induces nerve sprouting in the adult nervous system of transgenic mice. Cell 83:269–278
Perrone-Bizzozero NI, Sower AC, Bird ED, Benowitz LI, Ivins KJ, Neve RL (1996) Levels of the growth-associated protein GAP-43 are selectively increased in association cortices in schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:14182–14187
Paz RD, Andreasen NC, Daoud SZ, Conley R, Roberts R, Bustillo J, Perrone-Bizzozero NI (2006) Increased expression of activity-dependent genes in cerebellar glutamatergic neurons of patients with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 163:1829–1831
Blennow K, Bogdanovic N, Gottfries CG, Davidsson P (1999) The growth-associated protein GAP-43 is increased in the hippocampus and in the gyrus cinguli in schizophrenia. J Mol Neurosci 13:101–109
Chambers JS, Thomas D, Saland L, Neve RL, Perrone-Bizzozero NI (2005) Growth-associated protein 43 (GAP-43) and synaptophysin alterations in the dentate gyrus of patients with schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 29:283–290
Eastwood SL, Harrison PJ (1998) Hippocampal and cortical growth-associated protein-43 messenger RNA in schizophrenia. Neuroscience 86:437–448
Sower AC, Bird ED, Perrone-Bizzozero NI (1995) Increased levels of GAP-43 protein in schizophrenic brain tissues demonstrated by a novel immunodetection method. Mol Chem Neuropathol 24:1–11
Weickert CS, Webster MJ, Hyde TM, Herman MM, Bachus SE, Bali G, Weinberger DR, Kleinman JE (2001) Reduced GAP-43 mRNA in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of patients with schizophrenia. Cereb Cortex 11:136–147
Tanner DC, Githinji AW, Young EA, Meiri K, Savage DD, Perrone-Bizzozero NI (2004) Fetal alcohol exposure alters GAP-43 phosphorylation and protein kinase C responses to contextual fear conditioning in the hippocampus of adult rat offspring. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 28:113–122
Perrone-Bizzozero NI, Isaacson TV, Keidan GM, Eriqat C, Meiri KF, Savage DD, Allan AM (1998) Prenatal ethanol exposure decreases GAP-43 phosphorylation and protein kinase C activity in the hippocampus of adult rat offspring. J Neurochem 71:2104–2111
Proper EA, Oestreicher AB, Jansen GH, Veelen CW, van Rijen PC, Gispen WH, de Graan PN (2000) Immunohistochemical characterization of mossy fibre sprouting in the hippocampus of patients with pharmaco-resistant temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 123:19–30
Rekart JL, Quinn B, Mesulam MM, Routtenberg A (2004) Subfield-specific increase in brain growth protein in postmortem hippocampus of Alzheimer’s patients. Neuroscience 126:579–584
Reinhard E, Nedivi E, Wegner J, Skene JH, Westerfield M (1994) Neural selective activation and temporal regulation of a mammalian GAP-43 promoter in zebrafish. Development 120:1767–1775
Vanselow J, Grabczyk E, Ping J, Baetscher M, Teng S, Fishman MC (1994) GAP-43 transgenic mice: dispersed genomic sequences confer a GAP-43-like expression pattern during development and regeneration. J Neurosci 14:499–510
Kinney WR, McNamara RK, Valcourt E, Routtenberg A (1996) Prolonged alteration in E-box binding after a single systemic kainate injection: potential relation to F1/GAP-43 gene expression. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 38:25–36
Chiaramello A, Neuman T, Peavy DR, Zuber MX (1996) The GAP-43 gene is a direct downstream target of the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors. J Biol Chem 271:22035–22043
Uittenbogaard M, Martinka DL, Chiaramello A (2003) The basic helix-loop-helix differentiation factor Nex1/MATH-2 functions as a key activator of the GAP-43 gene. J Neurochem 84:678–688
Perrone-Bizzozero NI, Neve RL, Irwin N, Lewis S, Fischer I, Benowitz LI (1991) Post-transcriptional regulation of GAP-43 mRNA levels during neuronal differentiation and nerve regeneration. Mol Cell Neurosci 2:402–409
Federoff HJ, Grabczyk E, Fishman MC (1988) Dual regulation of GAP-43 gene expression by nerve growth factor and glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem 263:19290–19295
Perrone-Bizzozero NI, Cansino VV, Kohn DT (1993) Posttranscriptional regulation of GAP-43 gene expression in PC12 cells through protein kinase C-dependent stabilization of the mRNA. J Cell Biol 120:1263–1270
Tsai KC, Cansino VV, Kohn DT, Neve RL, Perrone-Bizzozero NI (1997) Post-transcriptional regulation of the GAP-43 gene by specific sequences in the 3′ untranslated region of the mRNA. J Neurosci 17:1950–1958
Kohn DT, Tsai KC, Cansino VV, Neve RL, Perrone-Bizzozero NI (1996) Role of highly conserved pyrimidine-rich sequences in the 3′ untranslated region of the GAP-43 mRNA in mRNA stability and RNA-protein interactions. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 36:240–250
Perrone-Bizzozero N, Bolognani F (2002) Role of HuD and other RNA-binding proteins in neural development and plasticity. J Neurosci Res 68:121–126
Chung S, Eckrich M, Perrone-Bizzozero N, Kohn DT, Furneaux H (1997) The Elav-like proteins bind to a conserved regulatory element in the 3′-untranslated region of GAP-43 mRNA. J Biol Chem 272:6593–6598
Szabo A, Dalmau J, Manley G, Rosenfeld M, Wong E, Henson J, Posner JB, Furneaux HM (1991) HuD, a paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis antigen, contains RNA-binding domains and is homologous to Elav and sex-lethal. Cell 67:325–333
Anderson KD, Morin MA, Beckel-Mitchener A, Mobarak CD, Neve RL, Furneaux HM, Burry R, Perrone-Bizzozero NI (2000) Overexpression of HuD, but not of its truncated form HuD I+II, promotes GAP-43 gene expression and neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells in the absence of nerve growth factor. J Neurochem 75:1103–1114
Beckel-Mitchener AC, Miera A, Keller R, Perrone-Bizzozero NI (2002) Poly(A) tail length-dependent stabilization of GAP-43 mRNA by the RNA-binding protein HuD. J Biol Chem 277:27996–28002
Mobarak CD, Anderson KD, Morin M, Beckel-Mitchener A, Rogers SL, Furneaux H, King P, Perrone-Bizzozero NI (2000) The RNA-binding protein HuD is required for GAP-43 mRNA stability, GAP-43 gene expression, and PKC-dependent neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells. Mol Biol Cell 11:3191–3203
Robinow S, Campos AR, Yao KM, White K (1988) The Elav gene product of Drosophila, required in neurons, has three RNP consensus motifs. Science 242:1570–1572
Barami K, Iversen K, Furneaux H, Goldman SA (1995) Hu protein as an early marker of neuronal phenotypic differentiation by subependymal zone cells of the adult songbird forebrain. J Neurobiol 28:82–101
Bolognani F, Merhege MA, Twiss J, Perrone-Bizzozero NI (2004) Dendritic localization of the RNA-binding protein HuD in hippocampal neurons: association with polysomes and upregulation during contextual learning. Neurosci Lett 371:152–157
Okano HJ, Darnell RB (1997) A hierarchy of Hu RNA binding proteins in developing and adult neurons. J Neurosci 17:3024–3037
Anderson KD, Merhege MA, Morin M, Bolognani F, Perrone-Bizzozero NI (2003) Increased expression and localization of the RNA-binding protein HuD and GAP-43 mRNA to cytoplasmic granules in DRG neurons during nerve regeneration. Exp Neurol 183:100–108
Deschenes-Furry J, Mousavi K, Bolognani F, Neve RL, Parks RJ, Perrone-Bizzozero NI, Jasmin BJ (2007) The RNA-binding protein HuD binds acetylcholinesterase mRNA in neurons and regulates its expression after axotomy. J Neurosci 27:665–675
Akamatsu W, Fujihara H, Mitsuhashi T, Yano M, Shibata S, Hayakawa Y, Okano HJ, Sakakibara S, Takano H, Takano T, Takahashi T, Noda T, Okano H (2005) The RNA-binding protein HuD regulates neuronal cell identity and maturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:4625–4630
Akamatsu W, Okano HJ, Osumi N, Inoue T, Nakamura S, Sakakibara S, Miura M, Matsuo N, Darnell RB, Okano H (1999) Mammalian ELAV-like neuronal RNA-binding proteins HuB and HuC promote neuronal development in both the central and the peripheral nervous systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:9885–9890
Pascale A, Gusev PA, Amadio M, Dottorini T, Govoni S, Alkon DL, Quattrone A (2004) Increase of the RNA-binding protein HuD and posttranscriptional up-regulation of the GAP-43 gene during spatial memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:1217–1222
Quattrone A, Pascale A, Nogues X, Zhao W, Gusev P, Pacini A, Alkon DL (2001) Posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression in learning by the neuronal ELAV-like mRNA-stabilizing proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11668–11673
Bolognani F, Qiu S, Tanner DC, Paik J, Perrone-Bizzozero NI, Weeber EJ (2007) Associative and spatial learning and memory deficits in transgenic mice overexpressing the RNA-binding protein HuD. Neurobiol Learn Mem 87:635–643
Bolognani F, Tanner DC, Merhege M, Deschenes-Furry J, Jasmin B, Perrone-Bizzozero NI (2006) In vivo post-transcriptional regulation of GAP-43 mRNA by overexpression of the RNA-binding protein HuD. J Neurochem 96:790–801
Neve RL, Perrone-Bizzozero NI, Finklestein S, Zwiers H, Bird E, Kurnit DM, Benowitz LI (1987) The neuronal growth-associated protein GAP-43 (B-50, F1): neuronal specificity, developmental regulation and regional distribution of the human and rat mRNAs. Brain Res 388:177–183
Racine RJ (1972) Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation. II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 32:281–294
Ford LP, Wilusz J (1999) An in vitro system using HeLa cytoplasmic extracts that reproduces regulated mRNA stability. Methods 17:21–27
Brewer G, Ross J (1990) Messenger RNA turnover in cell-free extracts. Methods Enzymol 181:202–209
Bendotti C, Baldessari S, Pende M, Southgate T, Guglielmetti F, Samanin R (1997) Relationship between GAP-43 expression in the dentate gyrus and synaptic reorganization of hippocampal mossy fibres in rats treated with kainic acid. Eur J Neurosci 9:93–101
Meberg PJ, Routtenberg A (1991) Selective expression of protein F1/(GAP-43) mRNA in pyramidal but not granule cells of the hippocampus. Neuroscience 45:721–733
Steller U, Kohls S, Muller B, Soller R, Muller R, Schlender J, Blohm DH (1996) The RNA binding protein HuD: rat cDNA and analysis of the alternative spliced mRNA in neuronal differentiating cell lines P19 and PC12. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 35:285–296
Kempermann G, Gast D, Kronenberg G, Yamaguchi M, Gage FH (2003) Early determination and long-term persistence of adult-generated new neurons in the hippocampus of mice. Development 130:391–399
Francis F, Koulakoff A, Boucher D, Chafey P, Schaar B, Vinet MC, Friocourt G, McDonnell N, Reiner O, Kahn A, McConnell SK, Berwald-Netter Y, Denoulet P, Chelly J (1999) Doublecortin is a developmentally regulated, microtubule-associated protein expressed in migrating and differentiating neurons. Neuron 23:247–256
Clayton GH, Perez GM, Smith RL, Owens GC (1998) Expression of mRNA for the elav-like neural-specific RNA binding protein, HuD, during nervous system development. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 109:271–280
Deschenes-Furry J, Perrone-Bizzozero N, Jasmin BJ (2006) The RNA-binding protein HuD: a regulator of neuronal differentiation, maintenance and plasticity. Bioessays 28:822–833
Anderson KD, Sengupta J, Morin M, Neve RL, Valenzuela CF, Perrone-Bizzozero NI (2001) Overexpression of HuD accelerates neurite outgrowth and increases GAP-43 mRNA expression in cortical neurons and retinoic acid-induced embryonic stem cells in vitro. Exp Neurol 168:50–58
Namgung U, Routtenberg A (2000) Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of a brain growth protein: regional differentiation and regeneration induction of GAP-43. Eur J Neurosci 12:3124–3136
Deschenes-Furry J, Belanger G, Perrone-Bizzozero N, Jasmin BJ (2003) Post-transcriptional regulation of acetylcholinesterase mRNAs in nerve growth factor-treated PC12 cells by the RNA-binding protein HuD. J Biol Chem 278:5710–5717
Wakamatsu Y, Weston JA (1997) Sequential expression and role of Hu RNA-binding proteins during neurogenesis. Development 124:3449–3460
Cantallops I, Routtenberg A (1999) Activity-dependent regulation of axonal growth: posttranscriptional control of the GAP-43 gene by the NMDA receptor in developing hippocampus. J Neurobiol 41:208–220
Toba G, Qui J, Koushika SP, White K (2002) Ectopic expression of Drosophila ELAV and human HuD in Drosophila wing disc cells reveals functional distinctions and similarities. J Cell Sci 115:2413–2421
Kasashima K, Terashima K, Yamamoto K, Sakashita E, Sakamoto H (1999) Cytoplasmic localization is required for the mammalian ELAV-like protein HuD to induce neuronal differentiation. Genes Cells 4:667–683
Antic D, Keene JD (1998) Messenger ribonucleoprotein complexes containing human ELAV proteins: interactions with cytoskeleton and translational apparatus. J Cell Sci 111:183–197
Smith CL, Afroz R, Bassell GJ, Furneaux HM, Perrone-Bizzozero NI, Burry RW (2004) GAP-43 mRNA in growth cones is associated with HuD and ribosomes. J Neurobiol 61(2):222–235
Tenenbaum SA, Carson CC, Lager PJ, Keene JD (2000) Identifying mRNA subsets in messenger ribonucleoprotein complexes by using cDNA arrays. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:14085–14090
Acknowledgments
We dedicate this work to Dr. Naren Banik, in recognition to his outstanding achievements in multiple sclerosis and spinal cord injury research. This work was supported by NIH (NS30255) to NPB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Special issue in honor of Naren Banik.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bolognani, F., Tanner, D.C., Nixon, S. et al. Coordinated Expression of HuD and GAP-43 in Hippocampal Dentate Granule Cells During Developmental and Adult Plasticity. Neurochem Res 32, 2142–2151 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9388-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9388-8