Abstract
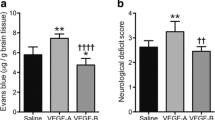
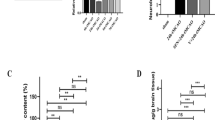
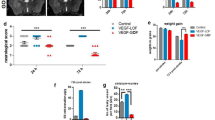
Recombinant human erythropoietin (rhEPO), a neurovascular protective agent, therapeutically supports angiogenesis after stroke by enhancing endogenous up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Increased VEGF expression has been characterized to negatively impact the integrity of the blood brain barrier (BBB), causing brain edema and secondary injury. The present study investigated the rhEPO-induced BBB protection after stroke and how it might be achieved by affecting VEGF pathway. rhEPO treatment (5,000 U/kg, i.p., 30 min before stroke and once a day for three days after stroke) reduced Evans blue leakage and brain edema after ischemia. The expression of the BBB integrity markers, occludin, α-catenin and β-catenin, in the brain was preserved in animals received rhEPO. rhEPO up-regulated VEGF expression; however, the expression of VEGF receptor-2 (fetal liver kinase receptor, Flk-1) was significantly reduced in rhEPO-treated animals three days after stroke. We propose that, disregarding increased VEGF levels, rhEPO protects against ischemia-induced BBB damage at least partly by down-regulating Flk-1 expression and the response to VEGF signaling in the acute phase after stroke.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hawkins BT, Davis TP (2005) The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev 57:173–185
Ballabh P, Braun A, Nedergaard M (2004) The blood-brain barrier: an overview: structure, regulation, and clinical implications. Neurobiol Dis 16:1–13
Dejana E, Corada M, Lampugnani MG (1995) Endothelial cell-to-cell junctions. Faseb J 9:910–918
Neuwelt EA (2004) Mechanisms of disease: the blood-brain barrier. Neurosurgery 54:131–140; discussion 141–132
Fischer S, Clauss M, Wiesnet M et al. (1999) Hypoxia induces permeability in brain microvessel endothelial cells via VEGF and NO. Am J Physiol 276:C812–C820
Fischer S, Wobben M, Marti HH et al. (2002) Hypoxia-induced hyperpermeability in brain microvessel endothelial cells involves VEGF-mediated changes in the expression of zonula occludens-1. Microvasc Res 63:70–80
Wang W, Dentler WL, Borchardt RT (2001) VEGF increases BMEC monolayer permeability by affecting occludin expression and tight junction assembly. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 280:H434–440
Chi OZ, Hunter C, Liu X et al (2007) Effects of anti-VEGF antibody on blood-brain barrier disruption in focal cerebral ischemia. Exp Neurol 204:283–287
Genc S, Koroglu TF, Genc K (2004) Erythropoietin as a novel neuroprotectant. Restorat Neurol Neurosci 22:105–119
Wang L, Zhang Z, Wang Y et al. (2004) Treatment of stroke with erythropoietin enhances neurogenesis and angiogenesis and improves neurological function in rats. Stroke; a J Cerebral Circul 35:1732–1737
Bartesaghi S, Marinovich M, Corsini E et al. (2005) Erythropoietin: a novel neuroprotective cytokine. Neurotoxicology 26:923–928
Li Y, Lu Z, Keogh CL et al. (2006) Erythropoietin-induced neurovascular protection, angiogenesis, and cerebral blood flow restoration after focal ischemia in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27(5):1043–1054
Wang W, Merrill MJ, Borchardt RT (1996) Vascular endothelial growth factor affects permeability of brain microvessel endothelial cells in vitro. Am J Physiol 271:C1973–1980
Dvorak HF, Brown LF, Detmar M et al. (1995) Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor, microvascular hyperpermeability, and angiogenesis. Am J Pathol146:1029–1039
Shalaby F, Rossant J, Yamaguchi TP et al. (1995) Failure of blood-island formation and vasculogenesis in Flk-1-deficient mice. Nature 376:62–66
Weis SM, Cheresh DA (2005) Pathophysiological consequences of VEGF–induced vascular permeability. Nature 437:497–504
Lafuente JV, Argandona EG, Mitre B (2006) VEGFR-2 expression in brain injury: its distribution related to brain-blood barrier markers. J Neural Transm 113:487–496
Hillman NJ, Whittles CE, Pocock TM et al. (2001) Differential effects of vascular endothelial growth factor-C and placental growth factor-1 on the hydraulic conductivity of frog mesenteric capillaries. J Vasc Res 38:176–186
Wei L, Cui L, Snider BJ et al. (2005) Transplantation of embryonic stem cells overexpressing Bcl-2 promotes functional recovery after transient cerebral ischemia. Neurobiol Dis 19:183–193
Calapai G, Marciano MC, Corica F et al. (2000) Erythropoietin protects against brain ischemic injury by inhibition of nitric oxide formation. Eur J Pharmacol 401:349–356
Fandrey J (2004) Oxygen–dependent and tissue-specific regulation of erythropoietin gene expression. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 286:R977–988
Wei L, Han BH, Li Y et al. (2006) Cell death mechanism and protective effect of erythropoietin after focal ischemia in the whisker-barrel cortex of neonatal rats. J Pharmacol Experiment Therapeut 317:109–116
Bates DO, Hillman NJ, Williams B et al. (2002) Regulation of microvascular permeability by vascular endothelial growth factors. J Anat 200:581–597
Martinez-Estrada OM, Rodriguez-Millan E, Gonzalez-De Vicente E et al. (2003) Erythropoietin protects the in vitro blood-brain barrier against VEGF-induced permeability. Eur J Neurosci 18:2538–2544
Uzum G, Sarper Diler A, Bahcekapili N et al. (2006) Erythropoietin prevents the increase in blood-brain barrier permeability during pentylentetrazol induced seizures. Life Sci 78:2571–2576
Bahcekapili N, Uzum G, Gokkusu C et al. (2007) The relationship between erythropoietin pretreatment with blood-brain barrier and lipid peroxidation after ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Life Sci 80:1245–1251
Andras IE, Deli MA, Veszelka S et al. (2007) The NMDA and AMPA/KA receptors are involved in glutamate-induced alterations of occludin expression and phosphorylation in brain endothelial cells. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab
Hawkins BT, Lundeen TF, Norwood KM et al. (2007) Increased blood-brain barrier permeability and altered tight junctions in experimental diabetes in the rat: contribution of hyperglycaemia and matrix metalloproteinases. Diabetologia 50:202–211
Neufeld G, Cohen T, Gengrinovitch S et al. (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptors. Faseb J 13:9–22
Park JE, Chen HH, Winer J et al. (1994) Placenta growth factor. Potentiation of vascular endothelial growth factor bioactivity, in vitro and in vivo, and high affinity binding to Flt-1 but not to Flk-1/KDR. J Biolog Chem 269:25646–25654
Joukov V, Pajusola K, Kaipainen A et al. (1996) A novel vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF-C, is a ligand for the Flt4 (VEGFR-3) and KDR (VEGFR-2) receptor tyrosine kinases. EMBO J 15:290–298
Bauters C, Asahara T, Zheng LP et al. (1995) Site-specific therapeutic angiogenesis after systemic administration of vascular endothelial growth factor. J Vasc Surg 21:314–324; discussion 324–315
Brogi E, Schatteman G, Wu T et al. (1996) Hypoxia-induced paracrine regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor expression. J Clin Investig 97:469–476
Shibuya M (2006) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-Receptor2: its biological functions, major signaling pathway, and specific ligand VEGF-E. Endothelium 13:63–69
Board RE, Thistlethwaite FC, Hawkins RE (2007) Anti-angiogenic therapy in the treatment of advanced renal cell cancer. Cancer Treatt Rev 33:1–8
Takagi H, King GL, Ferrara N et al. (1996) Hypoxia regulates vascular endothelial growth factor receptor KDR/Flk gene expression through adenosine A2 receptors in retinal capillary endothelial cells. Investig Ophthalmol Visual Science 37:1311–1321
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by NIH grants NS 37372, NS 045155, and NS 045810. The work was also supported by NIH C06 RR015455 from the Extramural Research Facilities Program of the National Center for Research Resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Lu, ZY., Ogle, M. et al. Erythropoietin Prevents Blood Brain Barrier Damage Induced by Focal Cerebral Ischemia in Mice. Neurochem Res 32, 2132–2141 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9387-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9387-9