Abstract
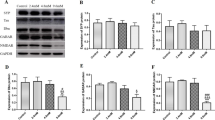
To investigate the mechanisms of the axonopathy induced by 2,5-hexanedione (2,5-HD), male Wistar rats were administered at a dosage of 400 mg/kg/day 2,5-HD (five times per week). The rats produced a slightly, moderately, or severely abnormal neurological changes, respectively, after 2, 4, or 8 weeks of treatment. The cerebrums were Triton-extracted and ultracentrifuged to yield a pellet fraction and a corresponding supernatant fraction. The relative levels of six cytoskeletal proteins (NF-L, NF-M, NF-H, α-tubulin, β-tubulin, and β-actin) in both fractions were determined by immunoblotting. The results showed that NFs content in HD-treated rats demonstrated a progressive decline as the intoxication of HD continued. As for microtubule proteins, the levels of α-tubulin and β-tubulin demonstrated some inconsistent changes. The content of α-tubulin kept unchangeable, while the content of β-tubulin increased significantly at the late stage of HD exposure. Furthermore, the content of β-actin in both fractions remained unaffected throughout the study. These findings suggest that HD intoxication resulted in a progressive decline of NFs, which was highly correlated with the development of HD-induced neuropathy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altenkirch H, Mager J, Stoltenburg G, Helmbrecht J (1977) Toxic polyneuropathies after sniffing a glue thinner. J Neurol 214:137–152
Spencer PS, Schaumburg HH, Sabri MI, Veronesi B (1980) The enlarging view of hexacarbon neurotoxicity. Crit Rev Toxicol 7:279–356
Cavanagh JB, Bennetts RJ (1981) On the pattern of changes in the rat nervous system produced by 2,5 hexanediol. A topographical study by light microscopy. Brain 104:297–318
Couri D, Milks M (1982) Toxicity and metabolism of the neurotoxic hexacarbons n-hexane, 2-hexanone, and 2,5-hexanedione. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 22:145–166
Lehning EJ, Dyer KS, Jortner BS, LoPachin RM (1995) Axonal atrophy is a specific component of 2,5-hexanedione peripheral neuropathy. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 135:58–66
Lehning EJ, Jortner BS, Fox JH, Arezzo JC, KitanoT, LoPachin RM (2000) Gamma-diketone peripheral neuropathy. I. Quality morphometric analyses of axonal atrophy and swelling. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 165:127–140
Opanashuk LA, He DK, Lehning EJ, Lopachin RM (2001) Diketone peripheral neuropathy III. Neurofilament gene expression. Neurotoxicology 22:215–220
DeCaprio AP, O’Neill EA (1985) Alterations in rat axonal cytoskeletal proteins induced by in vitro and in vivo 2,5-hexanedione exposure. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 78:235–247
Carden MJ, Lee VM, Schlaepfer WW (1986) 2,5-Hexanedione neuropathy is associated with the covalent crosslinking of neurofilament proteins. Neurochem Pathol 5:25–35
Lapadula DM, Suwita E, Abou-Donia MB (1988) Evidence for multiple mechanisms responsible for 2,5-hexanedione-induced neuropathy. Brain Res 458:123–131
LoPachin RM, He D, Reid ML, Opanashuk LA (2004) 2,5-Hexanedione-induced changes in monomeric neurofilament protein content of rat spinal cord fractions. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 198:61–73
LoPachin RM, He D, Reid ML (2005) 2,5-Hexanedione-induced changes in the neurofilament subunit pools of rat peripheral nerve. Neurotoxicology 26:229–240
Zhang T, Han X, Zhao X, Zhao L, Zhang C, Yu L, Yu S, Xie K (2005) 2,5-Hexanedione induced reduction in protein content and mRNA expression of neurofilament in rat cerebral cortex. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 20:92–98
LoPachin RM, Ross JF, Reid ML, Das S, Mansukhani S, Lehning EJ (2002) Neurological evaluation of toxic axonopathies in rats: acrylamide and 2,5-hexanedione. Neurotoxicology 23:95–110
Chiu FC, Norton WT (1982) Bulk preparation of CNS cytoskeleton and the separation of individual neurofilament proteins by gel filtration: dye-binding characteristics and amino acid compositions. J Neurochem 39:1252–1260
Tsuda M, Tashiro T, Komiya Y (1997) Increased solubility of highmolecular-mass neurofilament subunit by suppression of dephosphorylation: its relation to axonal transport. J Neurochem 68:2558–2565
Lee MK, Cleveland DW (1996) Neuronal intermediate filaments. Annu Rev Neurosci 19:187–217
Lee MK, Xu Z, Wong PC, Cleveland DW (1993) Neurofilaments are obligate heteropolymers in vivo. J Cell Biol 122:1337–1350
Cleveland DW, Monteiro MJ, Wong PC, Gill SR, Gearhart JD, Hoffman PN (1991) Involvement of neurofilaments in the radial growth of axons. J Cell Sci Suppl 15:85–95
Lee MK, Cleveland DW (1994) Neurofilament function and dysfunction: involvement in axonal growth and neuronal disease. Curr Opin Cell Biol 6:34–40
Micheva KD, Vallee A, Beaulieu C, Herman IM, Leclerc N (1998) Beta-actin is confined to structures having high capacity of remodeling in developing and adult rat cerebellum. Eur J Neurosci 10:3785–3798
Shea TB, Dahl DC, Nixon RA, Fischer I (1997) Triton-soluble phosphovariants of the heavy neurofilament subunit in developing and mature mouse central nervous system. J Neurosci Res 48:515–523
Shea TB, Sihag RK, Nixon RA (1990) Dynamics of phosphorylation and assembly of the high molecular weight neurofilament subunit in NB2a/d1 neuroblastoma. J Neurochem 55:1784–1792
Cohlberg JA, Hajarian H, Tran T, Alipourjeddi P, Noveen A (1995) Neurofilament protein heterotetramers as assembly intermediates. J Biol Chem 270:9334–9339
Arbuthnott ER, Boyd IA, Kalu KU (1980) Ultrastructural dimensions of myelinated peripheral nerve fibers in the cat and their relation to conduction velocity. J Physiol 308:125–137
Sakaguchi T, Okada M, Kitamura T, Kawasaki K (1993) Reduced diameter and conduction velocity of myelinated fibers in the sciatic nerve of a neurofilament-deficient mutant quail. Neurosci Lett 153:65–68
Banik NL, Hogan EL, Powers JM, Whetstine LJ (1982) Degradation of cytoskeletal proteins in spinal cord injury. Neurochem Res 7:1465–1475
Banik NL, Matzelle DC, Gantt-Wilford G, Osborne A, Hogan EL (1997) Increased calpain content and progressive degradation of neurofilament protein in spinal cord injury. Brain Res 752:301–306
Ray SK, Hogan EL, Banik NL (2003) Calpain in the pathophysiology of spinal cord injury: neuroprotection with calpain inhibitors. Brain Res Rev 42:169–185
Guo-Ross S, Yang E, Bondy SC (1998) Elevation of cerebral proteases after systemic administration of aluminum. Neurochem Int 33(3):277–282
Gupta RP, Abou-Donia MB (1996) Alterations in the neutral proteinase activities of central and peripheral nervous systems of acrylamide-, carbon disulfide-, or 2,5-hexanedione-treated rats. Mol Chem Neuropathol 29:53–66
Rao MV, Houseweart MK, Williamson TL, Crawford TO, Folmer J, Cleveland DW (1998) Neurofilament-dependent radial growth of motor axons and axonal organization of neurofilaments does not require the neurofilament heavy subunit (NF-H) or its phosphorylation. J Cell Biol 143:171–181
Moskowitz PF, Smith R, Pickett J, Frankfurter A, Oblinger MM (1993) Expression of the class III β-tubulin gene during axonal regeneration of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Neurosci Res 34:129–134
Song FY, Yu SF, Zhao XL, Zhang CL, Xie KQ (2006) Carbon disulfide-induced changes in cytoskeleton protein content of rat cerebral cortex. Neurochem Res 31:71–79
Yagihashi S, Kamijo M, Watanabe K (1990) Reduced myelinated fiber size correlates with loss of axonal neurofilaments in peripheral nerve of chronically streptozotocin rats. Am J Pathol 136:1365–1373
Liuzzi FJ, Bufton SM, Vinik AI (1998) Streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus causes changes in primary sensory neuronal cytoskeletal mRNA levels that mimic those caused by axotomy. Exp Neurol 154:381–388
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (No.2002CB512907), and National Natural Science Fund of China (No. 271138).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, F., Zhang, C., Yu, S. et al. Time-dependent Alteration of Cytoskeletal Proteins in Cerebral Cortex of Rat During 2,5-Hexanedione-induced Neuropathy. Neurochem Res 32, 1407–1414 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9325-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9325-x