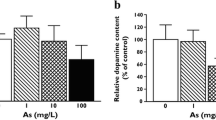
Abstract
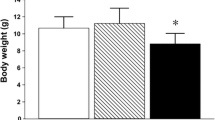
Chronic arsenic exposure is associated with nervous system damage, vascular disease, hepatic and renal damage as well as different types of cancer. Alterations of nitric oxide (NO) in the periphery have been detected after arsenic exposure, and we explored here NO production in the brain. Female Wistar rats were exposed to arsenite in drinking water (4–5 mg/kg/day) from gestation, lactation and until 4 months of age. NOS activity, NO metabolites content, reactive oxygen species production (ROS) and lipid peroxidation (LPx) were determined in vitro in the striatum, and NO production was estimated in vivo measuring citrulline by microdialysis. Exposed animals showed a significantly lower response to NMDA receptor stimulation, reduction of NOS activity and decreased levels of nitrites and nitrates in striatum. These markers of NO function were accompanied by significantly higher levels of LPx and ROS production. These results provide evidence of NO dysfunction in the rat brain associated with arsenic exposure.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calderón J, Navarro ME, Jiménez-Capdeville ME et al (2001) Exposure to arsenic and lead and neuropsychological development in Mexican children. Environ Res Sect A 85:69–76
Tsai SY, Chou HY, The HW et al (2003) The effects of chronic arsenic exposure from drinking water on the neurobehavioral development in adolescence. Neurotoxicology 24:747–753
Wasserman GA, Liu X, Parvez F et al (2004) Water arsenic exposure and children’s intellectual function in Araihazar, Bangladesh. Environ Health Perspect 112:1329–1333
Rodriguez VM, Jiménez-Capdeville ME, Giordano M (2003) The effects of arsenic exposure on the nervous system. Toxicol Lett 145:1–18
Chhuttani PN, Chopra JS (1979) Arsenic poisoning. In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds) Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Intoxications of the Nervous system, Part I, chapter 7, Vol. 36. Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, pp 199–216
Goebel HH, Schmidt PF, Bohl J et al (1990) Polyneuropathy due to acute arsenic intoxication: biopsy studies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 49:137–149
Styblo M, Drobná Z, Jaspers I et al (2002) The role of biomethylation in toxicity and carcinogenicity of arsenic: a research update. Environ Health Perspect 110S:767–771
Rodríguez VM, Carrizales L, Jiménez-Capdeville ME et al (2001) The effects of sodium arsenite exposure on behavioral parameters in the rat. Brain Res Bull 55:301–308
Rodríguez VM, Dufour L, Carrizales L et al (1998) Effects of oral exposure to mining waste on in vivo dopamine release from rat striatum. Environ Health Perspect 106:487–491
Flora SJS (1999) Arsenic-induced oxidative stress and its reversibility following combined administration of N-acetylcysteine and meso 2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 26:865–869
Waalkes MP, Ward JM, Liu J et al (2003) Transplacental carcinogenicity of inorganic arsenic in the drinking water: induction of hepatic, ovarian, pulmonary, and adrenal tumors in mice. Toxicol Appl Phamacol 186:116–126
Shen J, Wanibuchi H, Salim EI et al (2003) Liver tumorigenicity of trimethylarsine oxide in male Fischer 344 rats-association with oxidative DNA damage and enhanced cell proliferation. Carcinogen 24:1827–1835
García-Chavez E, Santamaría A, Díaz-Barriga F et al (2003) Arsenite-induced formation of hydroxyl radical in the striatum of awake rats. Brain Res 976:82–89
Chaudhuri AN, Basu S, Chattopadhyay S et al (1999) Effect of high arsenic content in drinking water on rat brain. Indian J Biochem Biophys 36:51–54
Pi J, Yamauchi H, Kumagai Y et al (2002) Evidence for induction of oxidative stress caused by chronic exposure of chinese residents to arsenic contained in drinking water. Environ Health Perspect 110:331–336
Kumagai Y, Pi J (2004) Molecular basis for arsenic-induced alteration in nitric oxide production and oxidative stress: implication of endothelial dysfunction. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 198:450–457
Pi J, Kumagai Y, Sun G et al (2000) Decreased serum concentrations of nitric oxide metabolites among Chinese in an endemic area of chronic arsenic poisoning in inner Mongolia. Free Rad Biol Med 28:1137–1142
Pi J, Yamauchi H, Sun G et al (2005) Vascular dysfunction in patients with chronic arsenosis can be reversed by reduction of arsenic exposure. Environ Health Perspect 113:339–341
Pi J, Horiguchi S, Sun Y et al (2003) A potential mechanism for the impairment of nitric oxide formation caused by prolonged oral exposure to arsenate in rabbits. Free Rad Biol Med 35:102–113
Lee MY, Jung BI, Chung SM et al (2003) Arsenic-induced dysfunction in relaxation of blood vessels. Environ Health Perspect 111:513–517
Tsou TC, Tsai FY, Hsieh YW et al (2005) Arsenite induces endotelial cytotoxicity by down-regulation of vascular endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 208:277–284
Rosen GM, Tsai P, Weaver J et al (2002) The role of tetrahydrobiopterin in the regulation of neuronal nitric-oxide synthase-generated superoxide. J Biol Chem 277:40275–40280
Xia Y, Tsai AL, Berka V et al (1998) Superoxide generation from endothelial nitric-oxide synthase. J Biol Chem 274:25804–25808
Gally JA, Montague PR, Reeke GN Jr et al (1990) The NO hypothesis: possible effects of a short-lived, rapidly diffusible signal in the development and function of the nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:3547–3551
Edelman GM, Gally JA (1992) Nitric oxide: linking space and time in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:11651–11652
Bliss TVP, Collingridge GL (1993) A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361:31–39
Bredt DS, Snyder SH (1989) Nitric oxide mediates glutamate-linked enhancement of cGMP levels in the cerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:9030–9033
Bredt DS, Snyder SH (1990) Isolation of nitric oxide synthase, a calmodulin-requiring enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:682–685
Guidelines for the Care and Use of Mammals in Neuroscience and Behavioral Research (2003) National research council of the national academies. The National Academies Press, Washington DC
Santamaria A, Rios C (1993) MK-801, an N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist, blocks quinolinic acid-induced lipid peroxidation in rat corpus striatum. Neurosci Lett 159:51–54
Ali SF, LeBel CP, Bondy SC (1992) Reactive oxygen species formation as a biomarker of methylmercury and trimethyltin neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 13:637–648
Horwitz W (1982) Evaluation of analytical methods used for regulation of foods and drugs. Anal Chem 54:67–76
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr L et al (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Miranda KM, Espey MG, Wink DA (2001) A rapid, simple spectrophotometric method for simultaneous detection of nitrate and nitrite. Nitric Oxide: Biol Chem 5:62–71
Tenorio FA, del Valle L, Pastelín G (2005) Validación de un método analítico espectrofotométrico para la cuantificación de metabolitos estables de óxido nítrico en fluidos biológicos. Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Farmacéuticas 36:31–41
Pérez-Severiano F, Escalante B, Vergara P et al (2002) Age-dependent changes in nitric oxide synthase activity and protein expression in striata of mice transgenic for the Huntington’s disease mutation. Brain Res 951:36–42
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press Inc., San Diego
Castillo CG, Montante M, Dufour L et al (2002) Behavioral effects of exposure to endosulfan and methyl parathion in adult rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol 24:797–804
Armitage P, Berry G (1997) Estadística para la investigación biomedical, 3rd edn. Harcourt Brace, Madrid, pp 359–363
Hagioka S, Takeda Y, Zhang S et al (2005) Effects of 7-nitroindazole and N-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester on changes in cerebral blood flow and nitric oxide production preceding development of hyperbaric oxygen-induced seizures in rats. Neuroscience Lett 382:206–210
Morris SM Jr (2000) Regulation of arginine availability and its impact on NO synthesis. In: Ignarro LJ (ed) Nitric oxide, biology and pathobiology. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 187–197
Kamada Y, Jenkins GJ, Lau M et al (2005) Tetrahydrobiopterin depletion and ubiquitylation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 142:19–27
Mejía JJ, Díaz-Barriga F, Calderón J et al (1997) Effects of lead–arsenic combined exposure on central monoaminergic systems. Neurotoxicol Teratol 19:489–497
Rodriguez VM, Carrizales L, Mendoza MS et al (2002) Effects of sodium arsenite exposure on development and behavior in the rat. Neurotoxicol Teratol 24:743–750
Ahmad S, Kitchin KT, Cullen WR (2000) Arsenic species that cause release of iron from ferritin and generation of activated oxygen. Arch Biochem Biophys 382:195–202
Yamanka K, Hoshino M, Okamoto M et al (1990) Induction of DNA damage by dimethylarsine, a metabolite of inorganic arsenic, is for the major part likely due to its peroxyl radical. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 168:58–64
Bernstam L, Nriagu J (2000) Molecular aspects of arsenic stress. J Toxicol Environ Health 3:293–322
Shila S, Kokilavani V, Subathra M et al (2005) Brain regional responses in antioxidant system to α-lipoic acid in arsenic intoxicated rat. Toxicology 210:25–36
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grants 40627-M from Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACYT), Programa Integral de Fortalecimiento a la Investigación (PIFI 3.1), and a CONACYT fellowship (186322) to S.Z. The authors thank Paula Vergara and Melissa Bocanegra for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zarazúa, S., Pérez-Severiano, F., Delgado, J.M. et al. Decreased Nitric Oxide Production in the Rat Brain after Chronic Arsenic Exposure. Neurochem Res 31, 1069–1077 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-006-9118-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-006-9118-7