Abstract
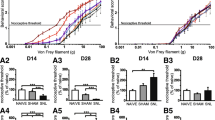
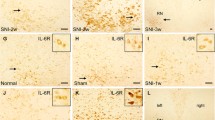
The present study investigated the expression patterns of glial cells and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) in the rat spinal cord after a surgical incision, which is closely related with clinical postoperative pain. Microglia and astrocytes became activated in the spinal cord following incision. Real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and immunohistochemisty showed that IL-1β mRNA and protein level in the spinal cord was transiently upregulated after surgical incision. The increased IL-1β-immunoreactivity (IR) was mainly localized in neurons but not the activated microglia or astrocytes. Although obvious increase in IL-1β-IR could be observed in the lumbar segments of the spinal cord ipsilateral to a hind paw incision, significant upregulation of IL-1β was not detected in the lumbar segments following thoracic incision. The present study indicated that surgical incision could induce glial activation and segmental upregulation of IL-1β in the spinal cord. The activated glial cells and upregulated IL-1β, in turn, may be involved in the incision-induced pain hypersensitivity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hunt SP, Mantyh PW (2001) The molecular dynamics of pain control. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:83–91
Ji RR, Woolf CJ (2001) Neuronal plasticity and signal transduction in nociceptive neurons: implications for the initiation and maintenance of pathological pain. Neurobiol Dis 8:1–10
Scholz J, Woolf CJ (2002) Can we conquer pain? Nat Neurosci 5(Suppl):1062–1067
DeLeo JA, Yezierski RP (2001) The role of neuroinflammation and neuroimmune activation in persistent pain. Pain 90:1–6
Watkins LR, Milligan ED, Maier SF (2001) Spinal cord glia: new players in pain. Pain 93:201–205
Watkins LR, Maier SF (2002) Beyond neurons: evidence that immune and glial cells contribute to pathological pain states. Physiol Rev 82:981–1011
Sweitzer SM, Colburn RW, Rutkowski M, DeLeo JA (1999) Acute peripheral inflammation induces moderate glial activation and spinal IL-1beta expression that correlates with pain behavior in the rat. Brain Res 829:209–221
Choi HS, Lee HJ, Jung CY, Ju JS, Park JS, Ahn DK (2003) Central cyclooxygenase-2 participates in interleukin-1 beta-induced hyperalgesia in the orofacial formalin test of freely moving rats. Neurosci Lett 352:187–190
Falchi M, Ferrara F, Gharib C, Dib B (2001) Hyperalgesic effect of intrathecally administered interleukin-1 in rats. Drugs Exp Clin Res 27:97–101
Reeve AJ, Patel S, Fox A, Walker K, Urban L (2000) Intrathecally administered endotoxin or cytokines produce allodynia, hyperalgesia and changes in spinal cord neuronal responses to nociceptive stimuli in the rat. Eur J Pain 4:247–257
Milligan ED, Twining C, Chacur M, Biedenkapp J, O’Connor K, Poole S, Tracey K, Martin D, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2003) Spinal glia and proinflammatory cytokines mediate mirror-image neuropathic pain in rats. J Neurosci 23:1026–1040
Brennan TJ, Vandermeulen EP, Gebhart GF (1996) Characterization of a rat model of incisional pain. Pain 64:493–501
Zahn PK, Brennan TJ (1998) Lack of effect of intrathecally administered N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists in a rat model for postoperative pain. Anesthesiology 88:143–156
Zahn PK, Umali E, Brennan TJ (1998) Intrathecal non-NMDA excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists inhibit pain behaviors in a rat model of postoperative pain. Pain 74:213–223
Ho ST, Wang JJ, Liaw WJ, Lee HK, Lee SC (1999) Surgical pain attenuates acute morphine tolerance in rats. Br J Anaesth 82:112–116
Budsberg SC, Cross AR, Quandt JE, Pablo LS, Runk AR (2002) Evaluation of intravenous administration of meloxicam for perioperative pain management following stifle joint surgery in dogs. Am J Vet Res 63:1557–1563
Zimmermann M (1983) Ethical guidelines for investigation of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain 16:109–110
Zhu X, Conklin D, Eisenach JC (2003) Cyclooxygenase-1 in the spinal cord plays an important role in postoperative pain. Pain 104:15–23
Fu D, Ng YK, Gan P, Ling EA (2004) Permanent occlusion of the middle cerebral artery upregulates expression of cytokines and neuronal nitric oxide synthase in the spinal cord and urinary bladder in the adult rat. Neuroscience 125:819–831
Muller PY, Janovjak H, Miserez AR, Dobbie Z (2002) Processing of gene expression data generated by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Biotechniques 32:1372–1379
Dai RP, Dheen ST, He BP, Tay SSW (2004) Differential Expression of Cytokines in the myocardium in response to sustained volume overload Eur J Heart Failure 6:693–703
Dai RP, He BP, Dheen ST, Tay SSW (2004) Acute cardiac injury induces glial cell response and activates extracellular signaling-regulated kinase-1 and -2 in the spinal cord. Neurosci Lett .366:34–38
Bursztajn S, Rutkowski MD, Deleo JA (2004) The role of the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor NR1 subunit in peripheral nerve injury-induced mechanical allodynia, glial activation and chemokine expression in the mouse Neuroscience 125:269–275
Zahn PK, Sluka KA, Brennan TJ (2002) Excitatory amino acid release in the spinal cord caused by plantar incision in the rat. Pain 100:65–76
Bao L, Zhu Y, Elhassan AM, Wu Q, Xiao B, Zhu J, Lindgren JU (2001) Adjuvant-induced arthritis: IL-1 beta, IL-6 and TNF-alpha are up-regulated in the spinal cord. Neuroreport 12:3905–3908
Pan JZ, Ni L, Sodhi A, Aguanno A, Young W, Hart RP (2002) Cytokine activity contributes to induction of inflammatory cytokine mRNAs in spinal cord following contusion. J Neurosci Res 68:315–322
Boddeke EW (2001) Involvement of chemokines in pain. Eur J Pharmacol 429:115–119
Mantyh PW, Clohisy DR, Koltzenburg M, Hunt SP (2002) Molecular mechanisms of cancer pain. Nat Rev Cancer 2:201–209
Bledsoe AW, Jackson CA, McPherson S, Morrow CD (2000) Cytokine production in motor neurons by poliovirus replicon vector gene delivery. Nat Biotechnol 18:964–969
Samad TA, Moore KA, Sapirstein A, Billet S, Allchorne A, Poole S, Bonventre JV, Woolf CJ (2001) Interleukin-1beta-mediated induction of Cox-2 in the CNS contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. Nature 410:471–475
Dolan S, Kelly JG, Huan M, Nolan AM (2003) Transient up-regulation of spinal cyclooxygenase-2 and neuronal nitric oxide synthase following surgical inflammation. Anesthesiogloy 98:170–180
Kroin JS, Ling ZD, Buvanendran A, Tuman KJ (2004) Upregulation of spinal cyclooxygenase-2 in rats after surgical incision. Anesthesiology 100:364–369
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, D., Guo, Q., Ai, Y. et al. Glial Activation and Segmental Upregulation of Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) in the Rat Spinal Cord after Surgical Incision. Neurochem Res 31, 333–340 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-9032-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-9032-4