Abstract
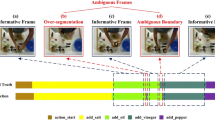
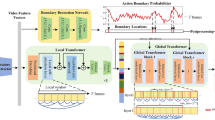
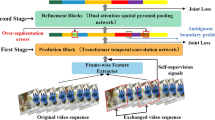
Segmenting human actions in long untrimmed videos is challenging due to the complicated temporal correlations between actions and over-segmentation errors. Although Transformer architectures have advanced correlations exploration for action recognition, they are not designed for action segmentation, which would face heavy computational cost and temporal redundancy. In this paper, we propose a Multi-Stage Dilated Transformer Network (MSDTN) to deal with these challenges. Specifically, we construct Transformer between frames of different time spans to capture short- and long-term relationships in videos. Furthermore, to alleviate over-segmentation errors in action segmentation, we propose to generate more stable and distinguishable features via temporal context aggregation at local scales. Especially, our method, termed as Feature Aggregation Module (FAM), is a general module, and can be integrated into existing architectures seamlessly with negligible overheads for action segmentation. We evaluate our proposed MSDTN and FAM on three challenging datasets (GTEA, 50Salads and Breakfast). Experimental results validate the effectiveness of our method on all three datasets.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carreira J, Zisserman A (2017) Quo vadis, action recognition? A new model and the kinetics dataset. In: CVPR, pp 6299–6308
Arnab A, Dehghani M, Heigold G, Sun C, Lučić M, Schmid C (2021) Vivit: a video vision transformer. In: ICCV, pp 6836–6846
Feichtenhofer C, Fan H, Malik J, He K (2019) Slowfast networks for video recognition. In: ICCV, pp 6202–6211
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. arXiv:1406.2199
Wang L, Xiong Y, Wang Z, Qiao Y, Lin D, Tang X, Van Gool L (2016) Temporal segment networks: towards good practices for deep action recognition. In: ECCV, pp 20–36
Qiu Z, Yao T, Mei T (2017) Learning spatio-temporal representation with pseudo-3d residual networks. In: ICCV, pp 5533–5541
Collins RT, Lipton AJ, Kanade T (2000) Introduction to the special section on video surveillance. TPAMI 22(8):745–746. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2000.868676
Vishwakarma S, Agrawal A (2013) A survey on activity recognition and behavior understanding in video surveillance. Vis Comput 29(10):983–1009
Lee YJ, Ghosh J, Grauman K (2012) Discovering important people and objects for egocentric video summarization. In: CVPR, pp 1346–1353
Ma Y-F, Hua X-S, Lu L, Zhang H-J (2005) A generic framework of user attention model and its application in video summarization. TMM 7(5):907–919
Feichtenhofer C, Pinz A, Wildes RP (2017) Spatiotemporal multiplier networks for video action recognition. In: CVPR, pp 4768–4777
Wang X, Girshick R, Gupta A, He K (2018) Non-local neural networks. In: CVPR, pp 7794–7803
Rohrbach M, Amin S, Andriluka M, Schiele B (2012) A database for fine grained activity detection of cooking activities. In: CVPR, pp 1194–1201
Karaman S, Seidenari L, Del Bimbo A (2014) Fast saliency based pooling of fisher encoded dense trajectories. In: ECCV THUMOS workshop, p 5
Oneata D, Verbeek J, Schmid C (2014) The lear submission at thumos 2014. In: ECCV THUMOS challenge
Kuehne H, Gall J, Serre T (2016) An end-to-end generative framework for video segmentation and recognition. In: WACV, pp 1–8
Kuehne H, Arslan A, Serre T (2014) The language of actions: recovering the syntax and semantics of goal-directed human activities. In: CVPR, pp 780–787
Lea C, Reiter A, Vidal R, Hager GD (2016) Segmental spatiotemporal cnns for fine-grained action segmentation. In: ECCV, pp 36–52
Singh B, Marks TK, Jones M, Tuzel O, Shao M (2016) A multi-stream bi-directional recurrent neural network for fine-grained action detection. In: CVPR, pp 1961–1970
Farha YA, Gall J (2019) Ms-tcn: multi-stage temporal convolutional network for action segmentation. In: CVPR, pp 3575–3584
Li S-J, AbuFarha Y, Liu Y, Cheng M-M, Gall J (2020) Ms-tcn++: multi-stage temporal convolutional network for action segmentation. TPAMI
Wang Z, Gao Z, Wang L, Li Z, Wu G (2020) Boundary-aware cascade networks for temporal action segmentation. In: ECCV, pp 34–51
Huang Y, Sugano Y, Sato Y (2020) Improving action segmentation via graph-based temporal reasoning. In: CVPR
Wang D, Hu D, Li X, Dou D (2021) Temporal relational modeling with self-supervision for action segmentation. In: AAAI, vol 35, pp 2729–2737
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, Kaiser L, Polosukhin I (2017) Attention is all you need. In: NeurIPS
Bertasius G, Wang H, Torresani L (2021) Is space-time attention all you need for video understanding? In: ICML
Yi F, Wen H, Jiang T (2021) Asformer: transformer for action segmentation. arXiv:2110.08568
Ishikawa Y, Kasai S, Aoki Y, Kataoka H (2021) Alleviating over-segmentation errors by detecting action boundaries. In: WACV, pp 2322–2331
Stein S, McKenna SJ (2013) Combining embedded accelerometers with computer vision for recognizing food preparation activities. In: UbiComp, pp 729–738
Fathi A, Ren X, Rehg JM (2011) Learning to recognize objects in egocentric activities. In: CVPR, pp 3281–3288
Fathi A, Rehg JM (2013) Modeling actions through state changes. In: CVPR, pp 2579–2586
Cheng Y, Fan Q, Pankanti S, Choudhary A (2014) Temporal sequence modeling for video event detection. In: CVPR, pp 2227–2234
Richard A, Gall J (2016) Temporal action detection using a statistical language model. In: CVPR, pp 3131–3140
Ding L, Xu C (2018) Weakly-supervised action segmentation with iterative soft boundary assignment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 6508–6516
Richard A, Kuehne H, Gall J (2017) Weakly supervised action learning with RNN based fine-to-coarse modeling. In: CVPR, pp 754–763
Fayyaz M, Gall J (2020) Sct: set constrained temporal transformer for set supervised action segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 501–510
Zhang J, Cao Y, Wu Q (2021) Vector of locally and adaptively aggregated descriptors for image feature representation. Pattern Recogn 116:107952
Ishihara K, Nakano G, Inoshita T (2022) Mcfm: Mutual cross fusion module for intermediate fusion-based action segmentation. In: 2022 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP). IEEE, pp 1701–1705
van den Oord A, Dieleman S, Zen H, Simonyan K, Vinyals O, Graves A, Kalchbrenner N, Senior A, Kavukcuoglu K (2016) Wavenet: A generative model for raw audio. In: 9th ISCA Speech Synthesis Workshop
Lea C, Flynn MD, Vidal R, Reiter A, Hager GD (2017) Temporal convolutional networks for action segmentation and detection. In: CVPR, pp 156–165
Lei P, Todorovic S (2018) Temporal deformable residual networks for action segmentation in videos. In: CVPR, pp 6742–6751
Gao S-H, Han Q, Li Z-Y, Peng P, Wang L, Cheng M-M (2021) Global2local: efficient structure search for video action segmentation. In: CVPR
Ishikawa Y, Kasai S, Aoki Y, Kataoka H (2021) Alleviating over-segmentation errors by detecting action boundaries. In: WACV, pp 2322–2331
Ahn H, Lee D (2021) Refining action segmentation with hierarchical video representations. In: ICCV, pp 16302–16310
Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, Weissenborn D, Zhai X, Unterthiner T, Dehghani M, Minderer M, Heigold G, Gelly S, Uszkoreit J, Houlsby N (2021) An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. In: ICLR
Yu J, Li J, Yu Z, Huang Q (2019) Multimodal transformer with multi-view visual representation for image captioning. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 30(12):4467–4480
Kitaev N, Kaiser L, Levskaya A (2020) Reformer: the efficient transformer. In: ICLR
Ridley J, Coskun H, Tan DJ, Navab N, Tombari F (2022) Transformers in action: weakly supervised action segmentation. arXiv:2201.05675
Li M, Chen L, Duan Y, Hu Z, Feng J, Zhou J, Lu J (2022) Bridge-prompt: towards ordinal action understanding in instructional videos. In: CVPR, pp 19880–19889
Chen M-H, Li B, Bao Y, AlRegib G, Kira Z (2020) Action segmentation with joint self-supervised temporal domain adaptation. In: CVPR, pp 9454–9463
Ahn H, Lee D (2021) Refining action segmentation with hierarchical video representations. In: ICCV, pp 16302–16310
Rohrbach M, Rohrbach A, Regneri M, Amin S, Andriluka M, Pinkal M, Schiele B (2016) Recognizing fine-grained and composite activities using hand-centric features and script data. Int J Comput Vis 119(3):346–373
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NSFC under Grant 62031023.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Du, Z., Wang, Q. Dilated Transformer with Feature Aggregation Module for Action Segmentation. Neural Process Lett 55, 6181–6197 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-022-11133-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-022-11133-9