Abstract
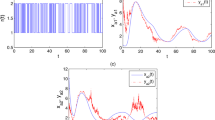
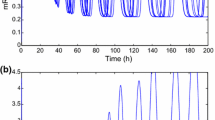
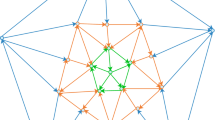
This paper investigates the global exponential synchronization problem of switching genetic oscillator networks with time-varying delays by using a newly-designed partial impulsive control scheme. This scheme is only required to control partial molecules of each gene node, different from the traditional pinning impulsive control scheme, in which all the molecules of the chosen nodes are assumed to be under control. Besides, both the number of controlled molecules and the impulsive strength of the presented control scheme are mode-dependent, either identical or different with respect to different topologies. Based on the Lyapunov stability theory and comparison principle, the sufficient criteria for guaranteeing the exponential synchronization of genetic oscillator networks with finite arbitrarily switching topologies are established. Finally, two illustrative examples are presented to verify the main results.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pandiselvi S, Raja R, Cao J, Rajchakit G (2019) Stabilization of switched stochastic genetic regulatory networks with leakage and impulsive effects. Neural Process Lett 49(2):593–610
Wang Y, Wang Z, Liang J, Li Y, Du M (2010) Synchronization of stochastic genetic oscillator networks with time delays and Markovian jumping parameters. Neurocomputing 73(13):2532–2539
Wan X, Wang Z, Wu M, Liu X (2018) State estimation for discrete time-delayed genetic regulatory networks with stochastic noises under the round-robin protocols. IEEE Trans Nanobiosci 17(2):145–154
Xiao M, Zheng WX, Jiang G (2018) Bifurcation and oscillatory dynamics of delayed cyclic gene networks including small RNAs. IEEE Trans Cybernetics 49(3):883–896
Ling G, Guan ZH, He DX, Liao RQ, Zhang XH (2014) Stability and bifurcation analysis of new coupled repressilators in genetic regulatory networks with delays. Neural Netw 60:222–231
McMillen D, Kopell N, Hasty J, Collins JJ (2002) Synchronizing genetic relaxation oscillators by intercell signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99(2):679–684
Shedden K, Cooper S (2002) Analysis of cell-cycle-specific gene expression in human cells as determined by microarrays and double-thymidine block synchronization. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99(7):4379–4384
Chu LF, Mamott D, Ni Z, Bacher R, Liu C, Swanson S, Thomson JA (2019) An in vitro human segmentation clock model derived from Embryonic stem cells. Cell Rep 28(9):2247–2255
Xu G, Bao H, Cao J (2020) Mean-square exponential input-to-state stability of stochastic gene regulatory networks with multiple time delays. Neural Process Lett 51(1):271–286
Qiu J, Sun K, Yang C, Chen X, Chen X, Zhang A (2017) Finite-time stability of genetic regulatory networks with impulsive effects. Neurocomputing 219:9–14
Syed Ali M, Vadivel R (2018) Decentralized event-triggered exponential stability for uncertain delayed genetic regulatory networks with Markov jump parameters and distributed delays. Neural Process Lett 47:1219–1252
Wan X, Xu L, Fang H, Yang F, Li X (2014) Exponential synchronization of switched genetic oscillators with time-varying delays. J Franklin Inst 351(8):4395–4414
Wang Y, Hori Y, Hara S, Doyle F (2014) Intercellular delay regulates the collective period of repressively coupled gene regulatory oscillator networks. IEEE Trans Autom Control 59(1):211–216
Li C, Chen L, Aihara K (2007) Stochastic synchronization of genetic oscillator networks. BMC Syst Biol 1(1):6
Zhou T, Chen L, Wang R (2005) A mechanism of synchronization in interacting multi-cell genetic systems. Phys. D 211(1–2):107–127
Zhang W, Tang Y, Fang JA, Zhu W (2011) Exponential cluster synchronization of impulsive delayed genetic oscillators with external disturbances. Chaos 21(4):043137
Mirollo RE, Strogatz SH (1990) Synchronization of pulse-coupled biological oscillators. SIAM J Appl Math 50(6):1645–1662
Garciaojalvo J, Elowitz MB, Strogatz SH (2004) Modeling a synthetic multicellular clock: repressilators coupled by quorum sensing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(30):10955–10960
Ling G, Guan ZH, Hu B, Lai Q, Wu Y (2017) Multistability and bifurcation analysis of inhibitory coupled cyclic genetic regulatory networks with delays. IEEE Trans Nanobiosci 16(3):216–225
Zhang W, Fang JA, Miao Q, Chen L, Zhu W (2013) Synchronization of Markovian jump genetic oscillators with nonidentical feedback delay. Neurocomputing 101:347–353
Qiu J, Cao J (2009) Global synchronization of delay-coupled genetic oscillators. Neurocomputing 72(16–18):3845–3850
Lu L, He B, Man C, Wang S (2015) Passive synchronization for Markov jump genetic oscillator networks with time-varying delays. Math Biosci 262:80–87
Zou C, Wang X (2020) Robust stability of delayed Markovian switching genetic regulatory networks with reaction–diffusion terms. Comput Math Appl 79(4):1150–1164
Luscombe NM, Babu MM, Yu H, Snyder M, Teichmann SA, Gerstein M (2004) Genomic analysis of regulatory network dynamics reveals large topological changes. Nature 431(7006):308–312
Meng Q, Jiang H (2010) Robust stochastic stability analysis of Markovian switching genetic regulatory networks with discrete and distributed delays. Neurocomputing 74(1–3):362–368
Zhang D, Yu L (2011) Passivity analysis for stochastic Markovian switching genetic regulatory networks with time-varying delays. Commun Nonlinear Sci 16(8):2985–2992
Chen H, Shi P, Lim CC (2016) Exponential synchronization for Markovian stochastic coupled neural networks of neutral-type via adaptive feedback control. IEEE Trans Neur Net Lear 28(7):1618–1632
Yu T, Wang H, Cao J et al (2020) On impulsive synchronization control for coupled inertial neural networks with pinning control. Neural Process Lett 51:2195–2210
Guan ZH, Liu ZW, Feng G, Wang YW (2010) Synchronization of complex dynamical networks with time-varying delays via impulsive distributed control. IEEE Trans Circuits Inst 57(8):2182–2195
Wu X, Huang L (2019) Pinning adaptive and exponential synchronization of fractional-order uncertain complex neural networks with time-varying delays. Neural Process Lett 50:2373–2388
Suarez OJ, Vega CJ, Sanchez EN, Chen G, Elvira-Ceja JS, Rodriguez DI (2020) Neural sliding-mode pinning control for output synchronization for uncertain general complex networks. Automatica 112:108694
Li F, Sun J (2011) Stability analysis of a reduced model of the lac operon under impulsive and switching control. Nonlinear Anal Real 12(2):1264–1277
He DX, Ling G, Guan ZH, Hu B, Liao RQ (2018) Multisynchronization of coupled heterogeneous genetic oscillator networks via partial impulsive control. IEEE Trans Neur Net Lear 29(2):335–342
Lu J, Kurths J, Cao J, Mahdavi N, Huang C (2012) Synchronization control for nonlinear stochastic dynamical networks: pinning impulsive strategy. IEEE Trans Neur Net Lear 23(2):285–292
Pan L (2020) Stochastic quasi-synchronization of delayed neural networks: pinning impulsive scheme. Neural Process Lett 51(1):947–962
Tang Y, Gao H, Zhang W, Kurths J (2015) Leader-following consensus of a class of stochastic delayed multi-agent systems with partial mixed impulses. Automatica 53(53):346–354
Li C, Chen L, Aihara K (2006) Synchronization of coupled nonidentical genetic oscillators. Phys Biol 3(1):37
Wu X, Tang Y, Cao J (2019) Input-to-State stability of time-varying switched systems with time delays. IEEE Trans Automat Control 64(6):2537–2544
Pan L, Cao J (2012) Stochastic quasi-synchronization for delayed dynamical networks via intermittent control. Commun Nonlinear Sci 17(3):1332–1343
Zhang W, Tang Y, Miao Q, Du W (2013) Exponential synchronization of coupled switched neural networks with mode-dependent impulsive effects. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 24(8):1316–1326
Alwan M, Liu X, Xie W (2010) Existence, continuation, and uniqueness problems of stochastic impulsive systems with time delay. J Franklin I(347):1317–1333
Wang Y, Cao J, Hu J (2015) Stochastic synchronization of coupled delayed neural networks with switching topologies via single pinning impulsive control. Neural Comput Appl 26(7):1739–1749
Tang Y, Xing X, Karimi HR, Kocarev L, Jürgen K (2016) Tracking control of networked multi-agent systems under new characterizations of impulses and its applications in robotic systems. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 63(2):1299–1307
Zhao Y, Fu F, Wang J, Feng J, Zhang H (2018) Synchronization of hybrid-coupled delayed dynamical networks with noises by partial mixed impulsive control strategy. Phys A 492:1181–1193
Yi C, Feng J, Wang J, Xu C, Zhao Y (2017) Synchronization of delayed neural networks with hybrid coupling via partial mixed pinning impulsive control. Appl Math Comput 312:78–90
Li Y (2017) Impulsive synchronization of stochastic neural networks via controlling partial states. Neural Process Lett 46(1):59–69
Zhang G, Liu Z, Ma Z (2007) Synchronization of complex dynamical networks via impulsive control. Chaos 17(4):043126
Li F, Sun J (2010) Asymptotic stability of a genetic network under impulsive control. Phys Lett A 374(31–32):3177–3184
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to Fuyan Hu for helpful mathematics discussion, and also thank all reviewers and editors for their professional comments and valuable suggestions, which helped to improve the paper significantly.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 61503282 and 62073301, the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province of China under Grant 2019CFB559, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (WUT: 2019IB012, 2020IB003).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ling, G., Ge, MF., Tong, YH. et al. Exponential Synchronization of Delayed Switching Genetic Oscillator Networks via Mode-Dependent Partial Impulsive Control. Neural Process Lett 53, 1845–1863 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-021-10488-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-021-10488-9