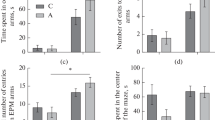
In a chronic experiment on rats with induced alcohol addiction, it was shown that chronic alcoholization leads to decreases in the levels of cortisol and testosterone in the hypothalamus, amygdalar complex, and blood serum. Functional changes in the hippocampus and nucl. accumbens are believed to play a leading role in the formation of the alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Under these conditions, the level of NO metabolites in the above structures decreases against the background of increased BDNF concentrations in blood serum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. P. Anokhina, N. L. Vekshina, and A. G. Veretinskaya, “Central mechanisms of predisposition to the dependence on psychoactive agents,”Korsakov Zh. Neurol. Psikhiatr., 12, 83-86 (1997).
T. M. Vorob’yova, “Neurobiology of secondary acquired motivations,” Mezhdunar. Med. Zh., Nos. 1/2, 211-217 (2002).
J. Bures, M. Petran, and I. Zachar, Electrophysiological Methods in Biological Research, Publ. House Foreign Lit., Moscow (1962).
P. P. Golikov and N. Yu. Nikolayeva, “Methods of measurement of nitric oxide (NOx) in the cerebrospinal liquid of neurosurgical patients,” Neirokhirurgiya, No. 3, 35-37 (2003).
R. Ward, “Biochemical and neurotransmitter changes implicated in alcohol-induced brain damage in chronic or ‘binge drinking’ alcohol abuse,” Alcohol Alcohol, 44, No. 2, 128-135 (2009).
E. P. Hayden, R. E. Wiegand, E. T. Meyer, et al., “Patterns of regional brain activity in alcohol-dependent subjects,” Alcoholism: Clin. Exp. Res., 30, No. 12, 1986-1991 (2006).
P. Coutin-Сhurchman and R. Moreno, “Intracranial current density (LORETA) differences in QEEG frequency bands between depressed and non-depressed alcoholic patients,” Clin. Neurophysiol., 119, No. 4, 948-958 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berchenko, O.G., Titkova, A.M., Veselovs’ka, O.V. et al. Electrical Activity of the Cerebral Structures and Regulatory Effects of NO, Steroid Hormones, and BDNF in Rats with Experimental Alcohol Addiction. Neurophysiology 49, 234–236 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-017-9668-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-017-9668-0