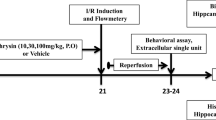
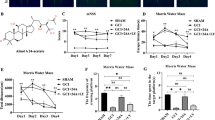
In our study, we investigated transient global cerebral ischemia (TGCI)-induced changes in spatial memory and motor activity together with apoptotic, oxidant, and NO/NOS signaling parameters in rats and the effects of treatment of animals with ghrelin. The TGCI-induced deficiencies of spatial memory and motor activity in the Y-maze and open field tests were attenuated by ghrelin treatment. Furthermore, ghrelin administration lowered the levels of caspase-3 and iNOS elevated by TGCI in the hippocampus. Thus, we conclude that ghrelin exerts a neuroprotective action against hippocampal TGCI injury via influencing apoptotic, oxidant, and/or NO/NOS pathways. If the underlying mechanisms of action of this agent are fully clarified, ghrelin might be a candidate drug for treatment of TGCI-induced memory impairments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Peskine, C. Picq, and P. Pradat-Diehl, “Cerebral anoxia and disability,” Brain Injury, 18, No. 12, 1243-1254 (2004).
Y. D. Cheng, L. Al-Khoury, and J. A. Zivin, “Neuroprotection for ischemic stroke: two decades of success and failure,” NeuroRx, 1, No. 1, 36-45 (2004).
J. L. Cummings, U. Tomiyasu, S. Read, et al., “Amnesia with hippocampal lesions after cardiopulmonary arrest,” Neurology, 34, No. 5, 679-681 (1984).
S. Zola-Morgan, L. R. Squire, and D. G. Amaral, “Human amnesia and the medial temporal region: enduring memory impairment following a bilateral lesion limited to field CA1 of the hippocampus,” J. Neurosci., 6, No. 10, 2950-2967 (1986).
C. K. Petito, E. Feldmann, W. A. Pulsinelli, et al., “Delayed hippocampal damage in humans following cardiorespiratory arrest,” Neurology, 37, No. 8, 1281-1286 (1987).
W. A. Pulsinelli, J. B. Brierley, and F. Plum, “Temporal profile of neuronal damage in a model of transient forebrain ischemia,” Ann. Neurol., 11, No. 5, 491-498 (1982).
“Recommendations for standards regarding preclinical neuroprotective and restorative drug development,” Stroke, 30, No. 12, 2752-2758 (1999).
I. Szabo and A. S. Tarnawski, “Apoptosis in the gastric mucosa: molecular mechanisms, basic and clinical implications,” J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 51, No. 1, 3-15 (2000).
J. Chandra, A. Samali, and S. Orrenius, “Triggering and modulation of apoptosis by oxidative stress,” Free Radical Biol. Med., 29, Nos. 3/4, 323-333 (2000).
I. Bohm and H. Schild, “Apoptosis: the complex scenario for a silent cell death,” Mol. Imag. Biol., 5, No. 1, 2-14 (2003).
G. M. Cohen, “Caspases: the executioners of apoptosis,” Biochem. J., 326, Part. 1, 1-16 (1997).
A. Rami, S. Jansen, I. Giesser, and J. Winckler, “Postischemic activation of caspase-3 in the rat hippocampus: evidence of an axonal and dendritic localization,” Neurochem. Int., 43, No. 3, 211-223 (2003).
M. Kaste, “Current therapeutic options for brain ischemia,” Neurology, 49, No. 5, Suppl. 4, S56-S59 (1997).
M. A. Moro, A. Cardenas, O. Hurtado, et al., “Role of nitric oxide after brain ischaemia,” Cell Calcium, 36, Nos. 3/4, 265-275 (2004).
L. J. Ignarro, G. M. Buga, K. S. Wood, et al., “Endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced and released from artery and vein is nitric oxide,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 84, No. 24, 9265-9269 (1987).
S. Moncada and J. P. Bolanos, “Nitric oxide, cell bioenergetics and neurodegeneration,” J. Neurochem., 97, No. 6, 1676-1689 (2006).
N. Panahian, T. Yoshida, P. L. Huang, et al., “Attenuated hippocampal damage after global cerebral ischemia in mice mutant in neuronal nitric oxide synthase,” Neuroscience, 72, No. 2, 343-354 (1996).
C. Iadecola, “Bright and dark sides of nitric oxide in ischemic brain injury,” Trends Neurosci., 20, No. 3, 132-139 (1997).
A. F. Samdani, T. M. Dawson, and V. L. Dawson, “Nitric oxide synthase in models of focal ischemia,” Stroke, 28, No. 6, 1283-1288 (1997).
N. Adachi, B. Lei, M. Soutani, and T. Arai, “Different roles of neuronal and endothelial nitric oxide synthases on ischemic nitric oxide production in gerbil striatum,” Neurosci. Lett., 288, No. 2, 151-154 (2000).
E. El Eter, A. Al Tuwaijiri, H. Hagar, and M. Arafa, “In vivo and in vitro antioxidant activity of ghrelin: Attenuation of gastric ischemic injury in the rat,” J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol., 22, No. 11, 1791-1799 (2007).
M. Kojima, H. Hosoda, Y. Date, et al., “Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach,” Nature, 402, No. 6762, 656-660 (1999).
N. Nagaya, M. Uematsu, M. Kojima, et al., “Chronic administration of ghrelin improves left ventricular dysfunction and attenuates development of cardiac cachexia in rats with heart failure,” Circulation, 104, No. 12, 1430-1435 (2001).
E. Ghigo, F. Broglio, E. Arvat, et al., “Ghrelin: more than a natural GH secretagogue and/or an orexigenic factor,” Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.), 62, No. 1, 1-17 (2005).
M. Kojima and K. Kangawa, “Ghrelin: structure and function,” Physiol. Rev., 85, No. 2, 495-522 (2005).
J. F. Davis, D. L. Choi, D. J. Clegg, and S. C. Benoit, “Signaling through the ghrelin receptor modulates hippocampal function and meal anticipation in mice,” Physiol. Behav., 103, No. 1, 39-43 (2011).
J. N. Cuellar and M. Isokawa, “Ghrelin-induced activation of cAMP signal transduction and its negative regulation by endocannabinoids in the hippocampus,” Neuropharmacology, 60, No. 6, 842-851 (2011).
S. Hwang, M. Moon, S. Kim, et al., “Neuroprotective effect of ghrelin is associated with decreased expression of prostate apoptosis response-4,” Endocrinol. J., 56, No. 4, 609-617 (2009).
H. Chung, E. Kim, D. H. Lee, et al., “Ghrelin inhibits apoptosis in hypothalamic neuronal cells during oxygenglucose deprivation,” Endocrinology, 148, No. 1, 148-159 (2007).
Y. Liu, L. Chen, X. Xu, et al., “Both ischemic preconditioning and ghrelin administration protect hippocampus from ischemia/reperfusion and upregulate uncoupling protein-2,” BMC Physiol., 9, 17 (2009).
W. A. Pulsinelli and J. B. Brierley, “A new model of bilateral hemispheric ischemia in the unanesthetized rat,” Stroke, 10, No. 3, 267-272 (1979).
O. Cheng, R. P. Ostrowski, B. Wu, et al., “Cyclooxygenase-2 mediates hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning in the rat model of transient global cerebral ischemia,” Stroke, 42, No. 2, 484-490 (2011).
W. R. Hawley, E. M. Grissom, and G. P. Dohanich, “The relationships between trait anxiety, place recognition memory, and learning strategy,” Behav. Brain Res., 216, No. 2, 525-530 (2011).
J. Zhao, Y. Zhao, W. Zheng, et al., “Neuroprotective effect of curcumin on transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats,” Brain Res., 1229, 224-232 (2008).
G. A. Donnan, M. Fisher, M. Macleod, and S. M. Davis, “Stroke,” Lancet, 371, No. 9624, 1612-1623 (2008).
W. T. Longstreth Jr. and S. S. Dikmen, “Outcomes after cardiac arrest,” Ann. Emerg. Med., 22, No. 1, 64-69 (1993).
P. S. Lagali, C. P. Corcoran, and D. J. Picketts, “Hippocampus development and function: role of epigenetic factors and implications for cognitive disease,” Clin. Genet., 78, No. 4, 321-333 (2010).
S. Diano, S. A. Farr, S. C. Benoit, et al., “Ghrelin controls hippocampal spine synapse density and memory performance,” Nat. Neurosci., 9, No. 3, 381-388 (2006).
M. Jászberényi, E. Bujdosó, Z. Bagosi, and G. Telegdy, “Mediation of the behavioral, endocrine and thermoregulatory actions of ghrelin,” Horm. Behav., 50, No. 2, 266-273 (2006).
Y. Liu, P. S. Wang, D. Xie, et al., “Ghrelin reduces injury of hippocampal neurons in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion,” Chin. J. Physiol., 49, No. 5, 244-250 (2006).
H. A. Awooda, M. F. Lutfi, G. M. Sharara, and A. M. Saeed, “Role of N-Nitro-L-Arginine-Methylester as anti-oxidant in transient cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in rats,” Exp. Trans. Stroke Med., 5, No. 1, 1 (2013).
M. Yaman, O. Eser, M. Cosar, et al., “Oral administration of avocado soybean unsaponifiables (ASU) reduces ischemic damage in the rat hippocampus,” Arch. Med. Res., 38, No. 5, 489-494 (2007).
P. H. Chan, “Reactive oxygen radicals in signaling and damage in the ischemic brain,” J. Cerebr. Blood Flow Metab., 21, No. 1, 2-14 (2001).
K. Zwirska-Korczala, M. Adamczyk-Sowa, P. Sowa, et al., “Role of leptin, ghrelin, angiotensin II and orexins in 3T3 L1 preadipocyte cells proliferation and oxidative metabolism,” J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 58, Suppl. 1, 53-64 (2007).
M. Suematsu, A. Katsuki, Y. Sumida, et al., “Decreased circulating levels of active ghrelin are associated with increased oxidative stress in obese subjects,” Eur. J. Endocrinol., 153, No. 3, 403-407 (2005).
M. A. Moro, A. Almeida, J. P. Bolaños, and I. Lizasoain, “Mitochondrial respiratory chain and free radical generation in stroke,” Free Radical Biol. Med., 39, No. 10, 1291-1304 (2005).
S. J. Heales, J. P. Bolaños, V. C. Stewart, et al., “Nitric oxide, mitochondria and neurological disease,” Biochim. Biophys. Acta., 1410, No. 2, 215-228 (1999).
B. Lei, N. Adachi, T. Nagaro, et al., “Nitric oxide production in the CA1 field of the gerbil hippocampus after transient forebrain ischemia: effects of 7-nitroindazole and NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester,” Stroke, 30, No. 3, 669-677 (1999).
J. S. Stamler, “Redox signaling: nitrosylation and related target interactions of nitric oxide,” Cell, 78, No. 6, 931-936 (1994).
B. Sekhon, C. Sekhon, M. Khan, et al., “N-Acetyl cysteine protects against injury in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia,” Brain Res., 971, No. 1, 1-8 (2003).
M. Willmot, C. Gibson, L. Gray, et al., “Nitric oxide synthase inhibitors in experimental ischemic stroke and their effects on infarct size and cerebral blood flow: a systematic review,” Free Radical Biol. Med., 39, No. 3, 412-425 (2005).
A. Aggarwal, V. Gaur, and A. Kumar, “Nitric oxide mechanism in the protective effect of naringin against post-stroke depression (PSD) in mice,” Life Sci., 86, Nos. 25/26, 928-935 (2010).
S. Murphy and C. L. Gibson, “Nitric oxide, ischaemia and brain inflammation,” Biochem. Soc. Trans., 35, Part 5, 1133-1137 (2007).
M. L. Holtz, S. D. Craddock, and L. C. Pettigrew, “Rapid expression of neuronal and inducible nitric oxide synthases during post-ischemic reperfusion in rat brain,” Brain Res., 898, No. 1, 49-60 (2001).
D. Y. Zhu, Q. Deng, H. H. Yao, et al., “Inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in the ischemic core and penumbra after transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice,” Life Sci., 71, No. 17, 1985-1996 (2002).
R. Greco, A. S. Mangione, D. Amantea, et al., “IkappaBalpha expression following transient focal cerebral ischemia is modulated by nitric oxide,” Brain Res., 1372, 145-151 (2011).
V. P. Carlini, M. F. Perez, E. Salde, et al., “Ghrelin induced memory facilitation implicates nitric oxide synthase activation and decrease in the threshold to promote LTP in hippocampal dentate gyrus,” Physiol. Behav., 101, No. 1, 117-123 (2010).
T. Brzozowski, P. C. Konturek, S. J. Konturek, et al., “Exogenous and endogenous ghrelin in gastroprotection against stress-induced gastric damage,” Regulat. Peptides, 120, Nos. 1/3, 39-51 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basaranlar, G., Derin, N., Tan, R. et al. Protective Actions of Ghrelin on Global Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Memory Deficits. Neurophysiology 46, 343–351 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-014-9454-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-014-9454-1