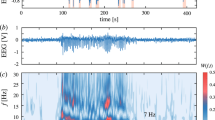
In this study, we investigated the presence of long-range correlation effects in the electrocortical activity of rats using the Hurst exponent (H) calculated by dispersion analysis (DA) and an aggregated variance method (AGV). A slow decline of the autocorrelation function during time expansion and the existence of a correlation between distant time points of electrocorticograms (ECoGs) were shown to be typical of various pathophysiological states. In these cases, the H values were within a 0.5 < H < 1 range. A particularly slow decay of the autocorrelation function is typical of a long-range dependence (LRD). We found that ECoGs after i.p. administrations of camphor essential oil or its main constituent, 1,8-cineole, included attacks of uncontrolled electrical discharges and showed the presence of long-range correlation effects. Such findings are in agreement with recent data obtained by other authors and suggest that initiation of seizures can be predicted by certain ECoG indices. We estimated the critical period where the H values for ECoGs containing uncontrolled electrical discharges continuously increased within a few minutes before the attack. We believe that the AGV demonstrates certain advantages over DA in calculations of the H.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. U. Acharya, O. Faust, N. Kannathal, et al., “Nonlinear analysis of EEG signals at various sleep stages,” Comp. Meth. Prog. Biomed. 80, 37-45 (2005).
T. Higuchi, “Approach to an irregular time series on the basis of the fractal theory,” Physica D, 31, 277-283 (1988).
H. E. Hurst, R. P. Black, and Y. M. Simaiki, Long-Term Storage: An Experimental Study, Constable, London (1965).
M. Kannathai, S. K. Puthusserypady, and L. C. Min, “Complex dynamics of epileptic EEG,” in: Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc., 26, 604-607 (2004).
N. Kannathai, U. R. Acharya, C. M. Lim, et al., “Characterization of EEG – A comparative study,” Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 80,17-23 (2005).
W. Klonowski, E. Olejarczyk and R. Stepien, “Nonlinear dynamics of EEG-signal reveals influence of magnetic field on the brain,” in: Proceedings of the 22nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE, 4, 2955-2958 (2000).
K. P. Indiradevi, E. Elias and P. S. Sathidevi, “Complexity analysis of electroencephalogram records of epileptic patients using Hurst exponent,” Int. J. Med. Eng. Inform., 1, 368-380 (2009).
F. Wendling, A. Hernandez, J. J. Bellanger, et al., “Interictal to ictal transition in human temporal lobe epilepsy: Insights from a computational model of intracerebral EEG,” J. Clin. Neurophysiol., 22, 343-356 (2005).
G. Grbić, M. Ćulić, Lj. Martać, et al., “Camphor oil poisoning-spectral analysis of rat brain activity,” Acta Physiol. Pharmacol. Serbica, 42, 233-238 (2006).
J. A. Gorter, E. A. Van Vliet, E. Aronica, et al., “Long-lasting increased excitability differs in dentate gyrus vs. CA1 in freely moving chronic epileptic rats after electrically induced status epilepticus,” Hippocampus, 12, 311-324 (2002).
M. Ćulić and G. Keković, “ Electrocortical activity of rat brain and cineole effect – spectral and continual wavelet analysis,” in: Abstracts of the IV Congress of Serbian Society for Neuroscience, September 11-14, 2008 [in Serbian], Kragujevac, p. 330 (2008).
M. Ćulić, G. Keković, G. Grbic, et al., “Wavelet and fractal analysis of rat brain activity in seizures evoked by camphor essential oil and 1,8-cineole,” Gen. Physiol. Biophys., Special Issue, 28, 33-40 (2009).
G. Grbic, M. Ćulić, M. L. Martac, et al., “Effect of camphor essential oil on rat cerebrocortical activity detected by changes in fractal dimension,” Arch. Biol. Sci., 60, 547-553 (2008).
G. Keković, G. Grbic, L. Martac, et al., “The nonlinear properties of EEG signals in acute model of epilepsy,” in: Proceedings of the NEUROMATH Workshop, Leuven, March 12-13, p. 52 (2009)
A. Carbone, “Algorithm to estimate the Hurst exponent of high-dimensional fractals,” Phys. Rev. E, 76, 056703 (2007).
I. Simonsen, A. Hansen, and O. M. Nes, “Determination of the Hurst exponent by use of wavelet transforms,” Phys. Rev. E, 58, 278-2787 (1998).
J. E. Bassignthwaighte and G. M.Raymond, “Evaluation of the dispersion analysis method for fractal time series,” Ann. Biomed. Eng., 23, 491-505 (1995).
P. Zhou, F. Li, W. Y. Liu, et al., “Fractal analysis in normal EEG and epileptic EEG of rats,” in: Proceedings of the World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2007), pp. 1266-1269
O. A. Rosso, S. Blanco, and A. Rabinowicz, “Wavelet analysis of generalized tonic-clonic epileptic seizures,” Signal Processing, 83, 1275-1289 (2003).
N. M. Barbaro, M. S. Berger, R. T. Canolty, et al., “High gamma power is phase-locked to theta oscillations in human neocortex,” Science, 313, 1626-1628 (2006).
R. Esteller, G. Vachtsevanos, J. Echauz, et al, “Fractal dimension characterizes seizure onset in epileptic patients,” in: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vol. 4, (1999), pp. 2343-2346.
M. Ćulić, G. Keković, L. Martac, et al., “Cerebellar role in brain injury and epilepsy: Linear and nonlinear analysis of electrocortical activity,” in: Proceedings of the VI Motor Control Conference, September 5-8, 2009, Varna (2009), pp. 39-40.
D. J. Davidson, “Functional mixed-effect models for electrophysiology responses,” Neurophysiology, 41, 79-87 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Neirofiziologiya/Neurophysiology, Vol. 42, No. 1, pp. 64-69, January-February, 2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ćulić, M., Stojadinović, G., Martać, L. et al. Use of the Hurst Exponent for Analysis of Electrocortical Epileptiform Activity Induced in Rats by Administration of Camphor Essential Oil or 1,8-Cineole. Neurophysiology 42, 57–62 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-010-9131-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-010-9131-y