Abstract
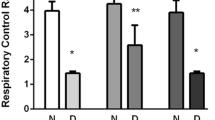
We studied the dynamics of modifications of the structure and architectonics in different zones of the pyramidal layer of the rat hippocampus within the early periods (3, 7, and 14 days) after induction of diabetes mellitus by streptozotocin. Using confocal immunofluorescence microscopy, we found neurons containing a specific protein, NeuN; a fluorescence dye, Hoechst 33258, allowed us to visualize the cell nuclei. The density of localization of neurons in the CA2 area decreased significantly on the 3rd day of development of diabetes. In the CA1 and CA3 areas, a significant decrease in this index was observed beginning from the 7th day. Within this time interval, we observed neurons with clear condensation of chromatin in the nuclei of these cells. The obtained data indicate that formation of appreciable neurodegenerative changes in the hippocampus occurs within the initial stages of development of experimental diabetes mellitus; this phenomenon can be a factor in the development of diabetic encephalopathy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. J. Biessels, “Cerebral complications of diabetes: clinical findings and pathogenetic mechanisms,” Neth. J. Med., 54, 35–45 (1999).
G. J. Biessels, L. P. van der Heide, A. Kamal, et al., “Ageing and diabetes: implications for brain function,” Eur. J. Pharmacol., 441, 1–14 (2002).
A. M. Brands, G. J. Biessels, L. J. Kappelle, et al., “Cognitive functioning and brain MRI in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a comparative study,” Dement. Geriat. Cogn. Disord., 23, 343–350 (2007).
G. J. Biessels and W. H. Gispen, “The impact of diabetes on cognition: what can be learned from rodent models?” Neurobiol. Aging, 26, 36–41 (2005).
C. M. Ryan and T. M. Williams, “Effects of insulin-dependent diabetes on learning and memory efficiency in adults,” J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol., 15, 685–700 (1993).
A. M. Wessels, S. A. Rombouts, P. L. Remijnse, et al., “Cognitive performance in type 1 diabetes patients is associated with cerebral white matter volume,” Diabetologia, 50, 1763–1769 (2007).
R. Prikryl, “Cognitive functions impairment in diabetes mellitus patients,” Cas. Lek. Cesk., 146, 434–437 (2007).
C. M. Ryan, “Diabetes, aging, and cognitive decline,” Neurobiol. Aging, 26, 21–25 (2005).
I. Tuma, “Diabetes mellitus and cognitive impairments,” Vnitr. Lek., 53, 486–488 (2007).
A. Kamal, G. J. Biessels, G. M. Ramakers, et al., “The effect of short duration streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus on the late phase and threshold of long-term potentiation induction in the rat,” Brain Res., 1053, 126–130 (2005).
A. Kamal, G. J. Biessels, I. J. Urban, et al., “Hippocampal synaptic plasticity in streptozotocin-diabetic rats: impairment of long-term potentiation and facilitation of long-term depression,” Neuroscience, 90, 737–745 (1999).
C. A. Grillo, G. G. Piroli, G. E. Wood, et al., “Immunocytochemical analysis of synaptic proteins provides new insights into diabetes-mediated plasticity in the rat hippocampus,” Neuroscience, 136, 477–486 (2005).
A. M. Magarinos and B. S. McEwen, “Experimental diabetes in rats causes hippocampal dendritic and synaptic reorganization and increased glucocorticoid reactivity to stress,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 97, 11056–11061 (2000).
Y. Revsin, F. Saravia, P. Roig, et al., “Neuronal and astroglial alterations in the hippocampus of a mouse model for type 1 diabetes,” Brain Res., 1038, 22–31 (2005).
M. A. Orlovsky, “Regularities of formation of hyperglycemia under conditions of experimental diabetes mellitus,” Patologiya, 1, 52–56 (2004).
G. Baydas, E. Sonkaya, M. Tuzcu, et al., “Novel role for gabapentin in neuroprotection of central nervous system in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats,” Acta Pharmacol. Sin., 4, 417–422 (2005).
R. J. Mullen, C. R. Buck, and A. M. Smith, “NeuN, a neuronal specific nuclear protein in vertebrates,” Development, 116, 201–211 (1992).
M. Saito, M. Kobayashi, S. Iwabuchi, et al., “DNA condensation monitoring after interaction with hoechst 33258 by atomic force microscopy and fluorescence spectroscopy,” J. Biochem., 6, 813–823 (2004).
L. Stoppini, P. A. Buchs, and D. Muller, “A simple method for organotypic cultures of nervous tissue,” J. Neurosci. Method, 37, 173–182 (1991).
M. Bottlang, M. B. Sommers, T. A. Lusardi, et al., “Modeling neural injury in organotypic cultures by application of inertia-driven shear strain,” J. Neurotrauma, 24, 1068–1077 (2007).
H. B. Lee and M. D. Blaufox, “Blood volume in the rat,” J. Nucl. Med., 26, 72–76 (1985).
O. Chan, K. Inouye, M. C. Riddell, et al., “Diabetes and the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis,” Minerva Endocrinol., 28, 87–102 (2003).
T. Kovalenko, I. Osadchenko, A. Nikonenko, et al., “Ischemia-induced modifications in hippocampal CA1 stratum radiatum excitatory synapses,” Hippocampus, 16, 814–825 (2006).
G. G. Skibo, T. M. Kovalenko, I. O. Osadchenko, et al., “Structural changes in the hippocampus in experimental cerebral ischemia,” Ukr. Nevrol. Zh., 4, 38–44 (2006).
R. M. Sapolsky, “Potential behavioral modification of glucocorticoid damage to the hippocampus,” Behav. Brain Res., 57, 175–182 (1993).
R. M. Sapolsky, H. Uno, C. S. Rebert, et al., “Hippocampal damage associated with prolonged glucocorticoid exposure in primates,” J. Neurosci., 10, 2897–2902 (1990).
D. F. Swaab, A. M. Bao, and P. J. Lucassen, “The stress system in the human brain in depression and neurodegeneration,” Ageing Res. Rev., 4, 141–194 (2005).
P. J. Lucassen, V. M. Heine, M. B. Muller, et al., “Stress, depression and hippocampal apoptosis,” CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets, 5, 531–546 (2006).
S. Rossie, H. Jayachandran, and R. L. Meisel, “Cellular co-localization of protein phosphatase 5 and glucocorticoid receptors in rat brain,” Brain Res., 1111, 1–11 (2006).
M. P. Armanini, C. Hutchins, B. A. Stein, et al., “Glucocorticoid endangerment of hippocampal neurons is NMDA-receptor dependent,” Brain Res., 532, 7–12 (1990).
J. A. Van Eekelen and E. R. de Kloet, “Co-localization of brain corticosteroid receptors in the rat hippocampus,” Prog. Histochem. Cytochem., 26, 250–258 (1992).
G. Yang, M. F. Matocha, and S. I. Rapoport, “Localization of glucocorticoid receptor messenger ribonucleic acid in hippocampus of rat brain using in situ hybridization,” Mol. Endocrinol., 2, 682–685 (1988).
L. E. Haynes, M. R. Griffiths, R. E. Hyde, et al., “Dexamethasone induces limited apoptosis and extensive sublethal damage to specific subregions of the striatum and hippocampus: implications for mood disorders,” Neuroscience, 104, 57–69 (2001).
S. Kang, J. Song, H. Kang, et al., “Insulin can block apoptosis by decreasing oxidative stress via phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase-and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase-dependent signaling pathways in HepG2 cells,” Eur. J. Endocrinol., 148, 147–155 (2003).
F. Bertrand, A. Atfi, A. Cadoret, et al., “A role for nuclear factor kappaB in the antiapoptotic function of insulin,” J. Biol. Chem., 5, 2931–2938 (1998).
M. A. Orlovsky, F. Spiga, Y. V. Lebed, et al., “Early molecular events in the hippocampus of rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes,” Neurophysiology, 39, No. 6, 435–438 (2007).
F. Han, H. Ozawa, K. Matsuda, et al., “Colocalization of mineralocorticoid receptor and glucocorticoid receptor in the hippocampus and hypothalamus,” Neurosci. Res., 51, 371–381 (2005).
A. Mercer, H. L. Trigg, and A. M. Thomson, “Characterization of neurons in the CA2 subfield of the adult rat hippocampus,” J. Neurosci., 27, 7329–7338 (2007).
G. Buzsaki, “Theta rhythm of navigation: link between path integration and landmark navigation, episodic and semantic memory,” Hippocampus, 15, 827–840 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Neirofiziologiya/Neurophysiology, Vol. 40, No. 1, pp. 30–37, January–February, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lebed, Y.V., Orlovsky, M.A., Lushnikova, I.V. et al. Neurodegenerative changes in the hippocampus within the early period of experimental diabetes mellitus . Neurophysiology 40, 26–33 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-008-9019-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-008-9019-2