Abstract
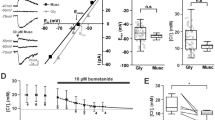
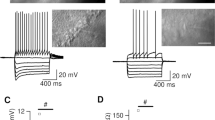
ATP is considered to impact on fast synaptic transmission in several regions of the CNS, including the CA1 and CA3 areas of the hippocampus. The existing paradigm suggests that ATP induces synaptic responses in CA3 pyramidal cells, and a fast ATP-mediated component is observed in cultured hippocampal slices mainly under conditions of a synchronous discharge from multiple presynaptic inputs. We confirmed the existence of a fast ATP-mediated component within electrically evoked EPSCs (eEPSCs) in CA3 neurons of acute slices of the rat hippocampus using a whole-cell patch-clamp recording mode. In approximately 50% of the examined cells, eEPSCs were not completely inhibited by co-applied glutamate receptor antagonists, NBQX (50 µM) and D-APV (25 µM). The residual current was sensitive to ionotropic P2X receptor antagonists, such as suramin (25 µM) and NF023 (2 µM). Known purinergic receptor modulators, ivermectin (10 µM) and PPADS (10 µM), practically did not affect EPSCs, whereas a nonhydrolyzable ATP analog, ATPγS (100 µM), slightly decreased the EPSC amplitude. Moreover, ATPγS (100 µM) at a holding potential of −70 mV generated a slow inward current in most recorded neurons, which was insensitive to glutamate receptor antagonists. This fact is indicative of the ionotropic P2X receptor activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Burnstock, “Purine and pyrimidine receptors,” Cell Mol. Life Sci., 64, 1471–1483 (2007).
B. P. Bean, C. A. Williams, and P. W. Ceelen, “ATP-activated channels in rat and bullfrog sensory neurons: current-voltage relation and single-channel behavior,” J. Neurosci., 10, 11–19 (1990).
R. J. Evans and V. Derkach, “ATP mediates fast synaptic transmission in mammalian neurons,” Nature, 357, 503–505 (1992).
L. A. Fieber and D. J. Adams, “Adenosine triphosphate-evoked currents in cultured neurons dissociated from rat parasympathetic cardiac ganglia,” J. Physiol., 434, 239–256 (1991).
O. A. Krishtal, S. M. Marchenko, and A. G. Obukhov, “Cationic channels activated by extracellular ATP in rat sensory neurons,” Neuroscience, 27, 995–1000 (1988).
A. Surprenant, G. Buell, and R. A. North, “P2x receptors bring new structure to ligand-gated ion channels,” Trends Neurosci., 18, 224–229 (1995).
F. A. Edwards, A. J. Gibb, and D. Colquhoun, “ATP receptor-mediated synaptic currents in the central nervous system,” Nature, 359, 144–147 (1992).
K. Nieber, W. Poelchen, and P. Illes, “Role of ATP in fast excitatory synaptic potentials in locus coeruleus neurones of the rat,” Br. J. Pharmacol., 122, 423–430 (1997).
S. Ueno, N. Harata, K. Inoue, and N. Akaike, “ATP-gated current in dissociated rat nucleus solitarii neurons,” J. Neurophysiol., 68, 778–785 (1992).
M. F. Ireland, P. G. Noakes, and M. C. Bellingham, “P2x7-like receptor subunits enhance excitatory synaptic transmission at central synapses by presynaptic mechanisms,” Neuroscience, 128, 269–280 (2004).
S. Boehm, “ATP stimulates sympathetic transmitter release via presynaptic P2x purinoceptors,” J. Neurosci., 19, 737–746 (1999).
J. W. Deitmer, J. Brockhaus, and D. Casel, “Modulation of synaptic activity in Purkinje neurons by ATP,” Cerebellum, 5, 49–54 (2006).
Y. Pankratov, U. Lalo, O. Krishtal, and A. Verkhratsky, “P2x receptor-mediated excitatory synaptic currents in somatosensory cortex,” Mol. Cell Neurosci., 24, 842–849 (2003).
Y. Pankratov, U. Lalo, E. Castro, et al., “ATP receptor-mediated component of the excitatory synaptic transmission in the hippocampus,” Prog. Brain Res., 120, 237–249 (1999).
Y. V. Pankratov, U. V. Lalo, and O. A. Krishtal, “Role for P2X receptors in long-term potentiation,” J. Neurosci., 22, No. 19, 8363–8369 (2002).
Y. Pankratov, U. Lalo, A. Verkhratsky, and R. A. North, “Quantal release of ATP in mouse cortex,” J. Gen. Physiol., 129, 257–265 (2007).
M. Mori, C. Heuss, B. H. Gahwiler, and U. Gerber, “Fast synaptic transmission mediated by P2x receptors in CA3 pyramidal cells of rat hippocampal slice cultures,” J. Physiol., 535, 115–123 (2001).
M. E. Rubio and F. Soto, “Distinct localization of P2x receptors at excitatory postsynaptic specializations,” J. Neurosci., 21, 641–653 (2001).
B. S. Khakh, W. B. Smith, C. S. Chiu, et al., “Activation-dependent changes in receptor distribution and dendritic morphology in hippocampal neurons expressing P2x2-green fluorescent protein receptors,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 5288–5293 (2001).
W. Norenberg and P. Illes, “Neuronal P2x receptors: localisation and functional properties,” Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol., 362, 324–339 (2000).
S. J. Robertson, S. J. Ennion, R. J. Evans, and F. A. Edwards, “Synaptic P2x receptors,” Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 11, 378–386 (2001).
J. A. Sim, S. Chaumont, J. Jo, et al., “Altered hippocampal synaptic potentiation in P2x4 knock-out mice,” J. Neurosci., 26, 9006–9009 (2006).
A. De Simoni, C. B. Griesinger, and F. A. Edwards, “Development of rat CA1 neurons in acute versus organotypic slices: role of experience in synaptic morphology and activity,” J. Physiol., 550, Part 1, 135–147 (2003).
B. S. Khakh, D. Gittermann, D. A. Cockayne, and A. Jones, “ATP modulation of excitatory synapses onto interneurons,” J. Neurosci., 23, 7426–7437 (2003).
M. Ikeda, “Characterization of functional P2X(1) receptors in mouse megakaryocytes,” Thromb. Res., 119, 343–353 (2006).
Y. H. Jo and R. Schlichter, “Synaptic corelease of ATP and GABA in cultured spinal neurons,” Nat. Neurosci., 2, 241–245 (1999).
C. Kennedy, G. J. Mclaren, T. D. Westfall, and P. Sneddon, “ATP as a co-transmitter with noradrenaline in sympathetic nerves — function and fate,” CIBA Found. Symp., 198, 223–235 (1996).
I. von Kugelgen, C. Allgaier, A. Schobert, and K. Starke, “Co-release of noradrenaline and ATP from cultured sympathetic neurons,” Neuroscience, 61, 199–202 (1994).
A. Wieraszko, G. Goldsmith, and T. N. Seyfried, “Stimulation-dependent release of adenosine triphosphate from hippocampal slices,” Brain Res., 485, 244–250 (1989).
Y. Pankratov, U. Lalo, A. Verkhratsky, and R. A. North, “Vesicular release of ATP at central synapses,” Pflügers Arch., 452, 589–597 (2006).
G. R. Gordon, D. V. Baimoukhametova, S. A. Hewitt, et al., “Norepinephrine triggers release of glial ATP to increase postsynaptic efficacy,” Nat. Neurosci., 8, 1078–1086 (2005).
F. Soto, G. Lambrecht, P. Nickel, et al., “Antagonistic properties of the suramin analogue NF023 at heterologously expressed P2x receptors,” Neuropharmacology, 38, 141–149 (1999).
H. Shiokawa, T. Nakatsuka, H. Furue, et al., “Direct excitation of deep dorsal horn neurons in the rat spinal cord by the activation of postsynaptic P2x receptors,” J. Physiol., 573, 753–763 (2006).
G. Wollmann, C. Cuna-Goycolea, and A. N. Van Den Pol, “Direct excitation of hypocretin/orexin cells by extracellular ATP at P2x receptors,” J. Neurophysiol., 94, 2195–2206 (2005).
T. M. Egan, D. S. Samways, and Z. Li, “Biophysics of P2X receptors,” Pflügers Arch., 452, 501–512 (2006).
P. M. Dunn and A. G. Blakeley, “Suramin: a reversible P2-purinoceptor antagonist in the mouse vas deferens,” Br. J. Pharmacol., 93, 243–245 (1988).
H. Uneyama, C. Uneyama, S. Ebihara, and N. Akaike, “Suramin and reactive blue 2 are antagonists for a newly identified purinoceptor on rat megakaryocyte,” Br. J. Pharmacol., 111, 245–249 (1994).
A. Priel and S. D. Silberberg, “Mechanism of ivermectin facilitation of human P2x4 receptor channels,” J. Gen. Physiol., 123, 281–293 (2004).
B. S. Khakh, W. R. Proctor, T. V. Dunwiddie, et al., “Allosteric control of gating and kinetics at P2x(4) receptor channels,” J. Neurosci., 19, 7289–7299 (1999).
E. Toulme, F. Soto, M. Garret, and E. Boue-Grabot, “Functional properties of internalization-deficient P2x4 receptors reveal a novel mechanism of ligand-gated channel facilitation by ivermectin,” Mol. Pharmacol., 69, 576–587 (2006).
Y. Wang, J. Mackes, S. Chan, et al., “Impaired long-term depression in P2x3 deficient mice is not associated with a spatial learning deficit,” J. Neurochem., 99, 1425–1434 (2006).
R. A. Cunha, E. S. Vizi, J. A. Ribeiro, and A. M. Sebastiao, “Preferential release of ATP and its extracellular catabolism as a source of adenosine upon high-but not low-frequency stimulation of rat hippocampal slices,” J. Neurochem., 67, 2180–2187 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Neirofiziologiya/Neurophysiology, Vol. 40, No. 1, pp. 21–29, January–February, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kondratskaya, E., Nonaka, K. & Akaike, N. Influence of purinergic modulators on eEPSCs in rat CA3 hippocampal neurons: Contribution of ionotropic ATP receptors. Neurophysiology 40, 17–25 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-008-9011-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-008-9011-x