Abstract
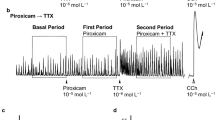
In strips of smooth muscles of the human colon, haloperidol (Hal) and clotrimazole (Clo), in contrast to pyridoxal-5′-phosphate (PP), suppressed spontaneous electrical and contractile activities of these strips and also post-inhibitory excitation developing after inhibitory synaptic potentials (ISPs). Haloperidol, Clo, PP, and PP applied against the background of the action of Nω-nitro-L-arginine noticeably changed the parameters of ISPs. The pattern of effect of Hal on synaptic inhibition in smooth muscles was preserved against the background of the action of PP, and that of PP was preserved against the background of the action of Hal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Gallego, P. Hernández, P. Clavé, and M. Jiménez, “P2Y1 receptors mediate inhibitory purinergic neuromuscular transmission in the human colon,” Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol., 291, G584–G594 (2006).
A. V. Romanenko and M. M. Grusha, “Synaptic inhibition of smooth muscles of the human colon: Effects of vitamin B6 and its derivatives,” Neurophysiology, 38, No. 4, 217–227 (2006).
A. V. Romanenko, M. M. Grusha, and P. D. Fomin, “Blocking effect of pyridoxal-5Γ-phosphate on non-adrenergic synaptic inhibition of smooth muscles of the human small intestine,” Fiziol. Zh., 52, No. 1, 62–70 (2006).
A. V. Romanenko and M. M. Grusha, “Effect of pyridoxal-5′-phosphate on synaptic inhibition of smooth muscles of the human intestine against the background of the action of isoniazid,” Éksp. Klin. Fiziol. Biokhim., 35, No. 3, 98–103 (2006).
V. Lerner, C. Miodownik, A. Kaptsan, et al., “Vitamin B6 in the treatment of tardive dyskinesia: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study,” Am. J. Phychiat., 158, No. 9, 1511–1514 (2001).
R. J. Baldessarini, “Drugs and the treatment of psychiatric disorders,” in: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, A. G. Gilman (ed.), Macmillan Co., London (1980), pp. 391–447.
T. Akamine, Y. Nisbimura, K. Ito, et al., “Effects of haloperidol on K+ currents in acutely isolated rat retinal ganglion cells,” Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci., 43, No. 4, 1257–1261 (2002).
J. D. McCann and M. J. Welsh, “Neuroleptics antagonize a calcium-activated potassium channel in airway smooth muscle,” J. Gen. Physiol., 89, No. 2, 339–352 (1987).
M. M. Shah, Z. Miscony, M. Javadzadeh-Tabatabaie, et al., “Clotrimazole analogues: effective blockers of the slow afterhyperpolarization in cultured rat hippocampal pyramidal neurons,” Br. J. Pharmacol., 132, 889–898 (2001).
R. A. Prokopenko, S. E. Mogilevich, A. I. Luik, et al., “Effects of haloperidol and chlorpromazine on smooth muscle contractility, platelet aggregation and neuronal calcium current,” Gen. Physiol. Biophys., 14, No. 4, 349–357 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Neirofiziologiya/Neurophysiology, Vol. 39, Nos. 4/5, pp. 408–411, July–October, 2007.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romanenko, A.V., Grusha, M.M. Effects of haloperidol, clotrimazole, and pyridoxal-5′-phosphate on synaptic transmission in smooth muscles of the human colon. Neurophysiology 39, 358–361 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-007-0057-y
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-007-0057-y