Abstract
Purpose
The updated Graded Prognostic Assessment for Lung Cancer Using Molecular Markers (lung-molGPA) index provide more accurate survival prediction for patients diagnose with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with brain metastases (BM). Given that the value of cranial radiotherapy (CRT) is still controversial for NSCLC patients with BM, this retrospective study aimed to evaluate the value of CRT and optimal timing in NSCLC patients with initial BM after stratified with lung-molGPA index.
Methods
This study screened NSCLC patients with initial BM in our cancer center from February 2012 to July 2018. The prognosis value of CRT and optimal timing was evaluated with Kaplan–Meier survival analysis and the patients were classified into lung-molGPA0–2 and lung-molGPA2.5–4 group. Upfront CRT was defined as received CRT within 3 months after initial diagnosis and without BM progression, other CRT was classified into deferred CRT.
Results
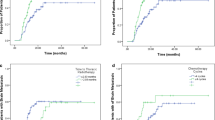
Overall, 288 patients were enrolled in our study, 156 patients received CRT. The median follow-up time was 47 months. In the entire cohort, the median PFS and OS were 9.2 and 17.0 months, respectively. In the lung-molGPA2.5–4 group, CRT can bring significantly overall survival benefit for NSCLC patients with initial BM (HR: 0.48, 95% CI: 0.34–0.68, P < 0.0001), and the upfront CRT can further expand this survival benefits compared with deferred CRT (HR: 0.49, 95% CI: 0.27–0.89, P = 0.0026). But this phenomenon was not observed in lung-molGPA0–2 group patients.
Conclusion
Upfront CRT could bring significantly overall survival benefit for these patients with lung-molGPA2.5–4 but not for patients with lung-molGPA0–2.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249
Zhang F, Zheng W, Ying L, Wu J, Wu S, Ma S, Su D (2016) A Nomogram to predict brain metastases of resected non-small cell lung cancer patients. Ann Surg Oncol 23(9):3033–3039
Park HS, Decker RH, Wilson LD, Yu JB (2015) Prophylactic cranial irradiation for patients with locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer at high risk for brain metastases. Clin Lung Cancer 16(4):292–297
Gaspar LE, Chansky K, Albain KS, Vallieres E, Rusch V, Crowley JJ, Livingston RB, Gandara DR (2005) Time from treatment to subsequent diagnosis of brain metastases in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer: a retrospective review by the Southwest Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 23(13):2955–2961
Stuschke M, Eberhardt W, Pottgen C, Stamatis G, Wilke H, Stuben G, Stoblen F, Wilhelm HH, Menker H, Teschler H et al (1999) Prophylactic cranial irradiation in locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer after multimodality treatment: long-term follow-up and investigations of late neuropsychologic effects. J Clin Oncol 17(9):2700–2709
Deng G, Zhang Y, Ke J, Wang Q, Qin H, Li J, Li Z (2021) Effect of brain radiotherapy strategies on prognosis of patients with EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma with brain metastasis. J Transl Med 19(1):486
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, Xu Z, Shanley R, Luo X, Sneed PK, Chao ST, Weil RJ, Suh J et al (2012) Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: an accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J Clin Oncol 30(4):419–425
Sperduto PW, Yang TJ, Beal K, Pan H, Brown PD, Bangdiwala A, Shanley R, Yeh N, Gaspar LE, Braunstein S et al (2017) Estimating survival in patients with lung cancer and brain metastases: an update of the graded prognostic assessment for lung cancer using molecular markers (lung-molGPA). JAMA Oncol 3(6):827–831
Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M, Asbell S, Phillips T, Wasserman T, McKenna WG, Byhardt R (1997) Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 37(4):745–751
Sperduto PW, Yang TJ, Beal K, Pan H, Brown PD, Bangdiwala A, Shanley R, Yeh N, Gaspar LE, Braunstein S et al (2016) The effect of gene alterations and tyrosine kinase inhibition on survival and cause of death in patients with adenocarcinoma of the lung and brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 96(2):406–413
Vogelbaum MA, Brown PD, Messersmith H, Brastianos PK, Burri S, Cahill D, Dunn IF, Gaspar LE, Gatson NTN, Gondi V et al (2021) Treatment for brain metastases: ASCO-SNO-ASTRO guideline. J Clin Oncol 40(5):492–516
Li J, Jing W, Zhai X, Jia W, Zhu H, Yu J (2021) Estimating survival in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and brain metastases: a verification of the graded prognostic assessment for lung cancer using molecular markers (lung-molGPA). Onco Targets Ther 14:1623–1631
Theelen W, Chen D, Verma V, Hobbs BP, Peulen HMU, Aerts J, Bahce I, Niemeijer ALN, Chang JY, de Groot PM et al (2021) Pembrolizumab with or without radiotherapy for metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: a pooled analysis of two randomised trials. Lancet Respir Med 9(5):467–475
Li Q, Hu C, Su S, Ma Z, Geng Y, Hu Y, Jin H, Li H, Lu B (2023) Impact of thoracic tumor radiotherapy on survival in non-small-cell lung cancer with malignant pleural effusion treated with targeted therapy: propensity score matching study. Cancer Med 12(14):14949–14959
Xu Q, Zhou F, Liu H, Jiang T, Li X, Xu Y, Zhou C (2018) Consolidative local ablative therapy improves the survival of patients with synchronous oligometastatic NSCLC harboring EGFR activating mutation treated with first-line EGFR-TKIs. J Thorac Oncol 13(9):1383–1392
Chang JY, Verma V (2022) Optimize local therapy for oligometastatic and oligoprogressive non-small cell lung cancer to enhance survival. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 20(5):531–539
Lock M, Chow E, Pond GR, Do V, Danjoux C, Dinniwell R, Lea J, Bezjak A (2004) Prognostic factors in brain metastases: can we determine patients who do not benefit from whole-brain radiotherapy? Clin Oncol 16(5):332–338
Nardone V, Romeo C, D’Ippolito E, Pastina P, D’Apolito M, Pirtoli L, Caraglia M, Mutti L, Bianco G, Falzea AC et al (2023) The role of brain radiotherapy for EGFR- and ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer with brain metastases: a review. Radiol Med 128(3):316–329
Merkin RD, Chiang VL, Goldberg SB (2023) Management of patients with brain metastases from NSCLC without a genetic driver alteration: upfront radiotherapy or immunotherapy? Ther Adv Med Oncol 15:17588359231175438
Mulvenna P, Nankivell M, Barton R, Faivre-Finn C, Wilson P, McColl E, Moore B, Brisbane I, Ardron D, Holt T et al (2016) Dexamethasone and supportive care with or without whole brain radiotherapy in treating patients with non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastases unsuitable for resection or stereotactic radiotherapy (QUARTZ): results from a phase 3, non-inferiority, randomised trial. Lancet 388(10055):2004–2014
Jiang T, Su C, Li X, Zhao C, Zhou F, Ren S, Zhou C, Zhang J (2016) EGFR TKIs plus WBRT demonstrated no survival benefit other than that of TKIs alone in patients with NSCLC and EGFR mutation and brain metastases. J Thorac Oncol 11(10):1718–1728
Magnuson WJ, Yeung JT, Guillod PD, Gettinger SN, Yu JB, Chiang VL (2016) Impact of deferring radiation therapy in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant non-small cell lung cancer who develop brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 95(2):673–679
Miyawaki E, Kenmotsu H, Mori K, Harada H, Mitsuya K, Mamesaya N, Kawamura T, Kobayashi H, Nakashima K, Omori S et al (2019) Optimal sequence of local and EGFR-TKI therapy for EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastases stratified by number of brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 104(3):604–613
Aoyama H, Tago M, Shirato H (2015) Stereotactic radiosurgery with or without whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases: secondary analysis of the JROSG 99-1 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol 1(4):457–464
Sperduto PW, Shanley R, Luo X, Andrews D, Werner-Wasik M, Valicenti R, Bahary JP, Souhami L, Won M, Mehta M (2014) Secondary analysis of RTOG 9508, a phase 3 randomized trial of whole-brain radiation therapy versus WBRT plus stereotactic radiosurgery in patients with 1–3 brain metastases; poststratified by the graded prognostic assessment (GPA). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 90(3):526–531
d’Avella D, Cicciarello R, Albiero F, Mesiti M, Gagliardi ME, Russi E, d’Aquino A, Tomasello F, d’Aquino S (1992) Quantitative study of blood-brain barrier permeability changes after experimental whole-brain radiation. Neurosurgery 30(1):30–34
Cao Y, Tsien CI, Shen Z, Tatro DS, Ten Haken R, Kessler ML, Chenevert TL, Lawrence TS (2005) Use of magnetic resonance imaging to assess blood-brain/blood-glioma barrier opening during conformal radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol 23(18):4127–4136
Bokobza SM, Jiang Y, Weber AM, Devery AM, Ryan AJ (2014) Short-course treatment with gefitinib enhances curative potential of radiation therapy in a mouse model of human non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 88(4):947–954
Li P-J, Lai S-Z, Jin T, Ying H-J, Chen Y-M, Zhang P, Hang Q-Q, Deng H, Wang L, Feng J-G et al (2023) Radiotherapy opens the blood-brain barrier and synergizes with anlotinib in treating glioblastoma. Radiother Oncol 183:109633
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant Number: 81972862 and 82030082]; CSCOPilot Cancer Research Fund [Grant Number: Y-2019AZZD-0352] and Shandong Province Natural Science Foundation innovation and development joint fund project [Grant Number: ZR2022LZL008].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Wenxiao Jia, Xiaoyang Zhai, Xuquan Jing and Qingdong Bao. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Wenxiao Jia, Xiaoyang Zhai and Shuhui Xu. Project administration, formal analysis and conceptualization was complete by Jinming Yu, Hui Zhu and Gang Wu. And all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval
This is a retrospectively observational study. The Shandong Cancer Hospital and Institute Ethics Committee has confirmed that no ethical approval is required.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, W., Zhai, X., Jing, X. et al. Prognostic value of cranial radiotherapy and optimal timing stratified by lung-molGPA for NSCLC patients with brain metastases. J Neurooncol 164, 321–330 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-023-04426-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-023-04426-z