Abstract
Purpose
Following surgical resection of brain metastases (BMs), adjuvant stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) has become the standard of care post-operative cavity irradiation. Recent studies, however, have demonstrated that with the current sequence of surgery and radiation, risk of leptomeningeal disease (LMD) and radiation necrosis (RN) remains high. Pre-operative, or neoadjuvant, SRS (nSRS) has been proposed as an alternative treatment strategy which not only minimizes local recurrence (LR) but also LMD and RN. It is thought that nSRS sterilizes the tumor, allowing for minimal spillage of viable tumor cells during resection, creating less favorable conditions for LMD. Furthermore, nSRS allows for easier contouring and decreased margin irradiation during planning and treatment, respectively, diminishing the risk of symptomatic RN. While nSRS has already been adopted for treating other extra-cranial tumors, its role in treating BMs is yet to be defined. We aim to summarize recent studies in nSRS usage for BMs and the rationale of this treatment strategy.
Methods
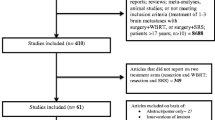
We performed a search for articles regarding nSRS for BMs published in PubMed from 2018 to 2022 using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) method. We summarized a total of 14 retrospective reviews, case series, dose/timing studies, and ongoing Phase II & III clinical trials.
Conclusion
In this review, we describe the findings of current studies and identify prospective clinical trials with the aim of understanding the efficacy of nSRS over current treatment standards. Herein, we also discuss the theoretical advantages and limitations of nSRS (both biologic and clinical) to help guide future clinical investigations.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Sloan AE, Davis FG, Vigneau FD, Lai P, Sawaya RE (2004) Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973–2001) in the metropolitan Detroit cancer surveillance system. J Clin Oncol 22(14):2865–2872. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2004.12.149
Arvold ND, Lee EQ, Mehta MP et al (2016) Updates in the management of brain metastases. Neuro Oncol 18(8):1043–1065. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/now127
Mahajan A, Ahmed S, McAleer MF et al (2017) Post-operative stereotactic radiosurgery versus observation for completely resected brain metastases: a single-centre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 18(8):1040–1048. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30414-X
Brown PD, Ballman KV, Cerhan JH et al (2017) Postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery compared with whole brain radiotherapy for resected metastatic brain disease (NCCTG N107C/CEC·3): a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 18(8):1049–1060. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30441-2
Suh JH, Kotecha R, Chao ST, Ahluwalia MS, Sahgal A, Chang EL (2020) Current approaches to the management of brain metastases. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 17(5):279–299. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-019-0320-3
Nabors LB, Portnow J, Ahluwalia M et al (2020) Central nervous system cancers, version 3.2020, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 18(11):1537–1570. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2020.0052
Gondi V, Bauman G, Bradfield L et al (2022) Radiation therapy for brain metastases: an ASTRO clinical practice guideline. Pract Radiat Oncol 12(4):265–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prro.2022.02.003
Tewarie IA, Jessurun CAC, Hulsbergen AFC, Smith TR, Mekary RA, Broekman MLD (2021) Leptomeningeal disease in neurosurgical brain metastases patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuro-Oncol Adv 3(1):162. https://doi.org/10.1093/noajnl/vdab162
Foreman PM, Jackson BE, Singh KP et al (2018) Postoperative radiosurgery for the treatment of metastatic brain tumor: evaluation of local failure and leptomeningeal disease. J Clin Neurosci 49:48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2017.12.009
Suki D, Abouassi H, Patel AJ, Sawaya R, Weinberg JS, Groves MD (2008) Comparative risk of leptomeningeal disease after resection or stereotactic radiosurgery for solid tumor metastasis to the posterior fossa. J Neurosurg 108(2):248–257. https://doi.org/10.3171/JNS/2008/108/2/0248
Suki D, Hatiboglu MA, Patel AJ et al (2009) Comparative risk of leptomeningeal dissemination of cancer after surgery or stereotactic radiosurgery for a single supratentorial solid tumor metastasis. Neurosurgery 64(4):664–674. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000341535.53720.3E
Cagney DN, Lamba N, Sinha S et al (2019) Association of neurosurgical resection with development of pachymeningeal seeding in patients with brain metastases. JAMA Oncol 5(5):703–709. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.7204
Minniti G, Clarke E, Lanzetta G et al (2011) Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: analysis of outcome and risk of brain radionecrosis. Radiat Oncol 6:48. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717X-6-48
Kohutek ZA, Yamada Y, Chan TA et al (2015) Long-term risk of radionecrosis and imaging changes after stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases. J Neurooncol 125(1):149–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1881-3
Sauer R, Becker H, Hohenberger W et al (2004) Preoperative versus postoperative chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer. N Engl J Med 351(17):1731–1740. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa040694
Lazarev S, McGee H, Moshier E, Ru M, Demicco EG, Gupta V (2017) Preoperative vs postoperative radiation therapy in localized soft tissue sarcoma: nationwide patterns of care and trends in utilization. Pract Radiat Oncol 7(6):e507–e516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prro.2017.04.010
van Hagen P, Hulshof MCCM, van Lanschot JJB et al (2012) Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N Engl J Med 366(22):2074–2084. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1112088
Versteijne E, Suker M, Groothuis K et al (2020) Preoperative chemoradiotherapy versus immediate surgery for resectable and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: results of the Dutch randomized phase III PREOPANC trial. J Clin Oncol 38(16):1763–1773. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.19.02274
Patel KR, Burri SH, Boselli D et al (2017) Comparing pre-operative stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) to post-operative whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) for resectable brain metastases: a multi-institutional analysis. J Neurooncol 131(3):611–618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2334-3
Patel KR, Burri SH, Asher AL et al (2016) Comparing preoperative with postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery for resectable brain metastases: a multi-institutional analysis. Neurosurgery 79(2):279–285. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000001096
Prabhu RS, Dhakal R, Vaslow ZK et al (2021) Preoperative radiosurgery for resected brain metastases: the PROPS-BM multicenter cohort study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 111(3):764–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.05.124
Palmer JD, Perlow HK, Matsui JK et al (2022) Fractionated pre-operative stereotactic radiotherapy for patients with brain metastases: a multi-institutional analysis. J Neuro-Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04073-w
Udovicich C, Ng SP, Tange D, Bailey N, Haghighi N (2022) From postoperative to preoperative: a case series of hypofractionated and single-fraction neoadjuvant stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases. Oper Neurosurg 22(4):208–214. https://doi.org/10.1227/ONS.0000000000000101
Deguchi S, Mitsuya K, Yasui K et al (2022) Neoadjuvant fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy followed by piecemeal resection of brain metastasis: a case series of 20 patients. Int J Clin Oncol 27(3):481–487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-021-02083-8
Patel AR, Nedzi L, Lau S et al (2018) Neoadjuvant stereotactic radiosurgery before surgical resection of cerebral metastases. World Neurosurg 120:e480–e487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.08.107
Kotecha R, Tonse R, Menendez MAR et al (2022) Evaluation of the impact of pre-operative stereotactic radiotherapy on the acute changes in histopathologic and immune marker profiles of brain metastases. Sci Rep 12(1):4567. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-08507-3
Steverink JG, Willems SM, Philippens MEP et al (2018) Early tissue effects of stereotactic body radiation therapy for spinal metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 100(5):1254–1258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.01.005
Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Shuto T et al (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): a multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol 15(4):387–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70061-0
El Shafie RA, Tonndorf-Martini E, Schmitt D et al (2019) Pre-operative versus post-operative radiosurgery of brain metastases—volumetric and dosimetric impact of treatment sequence and margin concept. Cancers (Basel) 11(3):294. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030294
Walker AJ, Ruzevick J, Malayeri AA et al (2014) Postradiation imaging changes in the CNS: how can we differentiate between treatment effect and disease progression? Future Oncol 10(7):1277–1297. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon.13.271
Murphy ES, Yang K, Suh JH et al (2019) Prospective phase I dose escalation study for neoadjuvant radiosurgery for large brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 105(1):S10–S11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.06.399
Routman DM, Yan E, Vora S et al (2018) Preoperative stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases. Front Neurol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2018.00959
Asher AL, Burri SH, Wiggins WF et al (2014) A new treatment paradigm: neoadjuvant radiosurgery before surgical resection of brain metastases with analysis of local tumor recurrence. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 88(4):899–906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.12.013
Marcrom SR, Foreman PM, Colvin TB et al (2020) Focal management of large brain metastases and risk of leptomeningeal disease. Adv Radiat Oncol 5(1):34–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adro.2019.07.016
Ahn JH, Lee SH, Kim S et al (2012) Risk for leptomeningeal seeding after resection for brain metastases: implication of tumor location with mode of resection: clinical article. J Neurosurg 116(5):984–993. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.1.JNS111560
Soliman H, Myrehaug S, Tseng CL et al (2019) Image-guided, linac-based, surgical cavity-hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy in 5 daily fractions for brain metastases. Neurosurgery 85(5):E860–E869. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyz162
DePaoli B, Gozal YM, Pater LE et al (2019) Ventricular violation increases the risk of leptomeningeal disease in cavity-directed radiosurgery treated patients. J Radiat Oncol 8(1):23–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13566-018-0368-1
Prabhu RS, Turner BE, Asher AL et al (2021) Leptomeningeal disease and neurologic death after surgical resection and radiosurgery for brain metastases: a multi-institutional analysis. Adv Radiat Oncol 6(2):100644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adro.2021.100644
Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Regine WF et al (1998) Postoperative radiotherapy in the treatment of single metastases to the brain: a randomized trial. J Am Med Assoc 280(17):1485–1489. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.280.17.1485
Scharl S, Kirstein A, Kessel KA et al (2019) Stereotactic irradiation of the resection cavity after surgical resection of brain metastases—when is the right timing? Acta Oncol 58(12):1714–1719. https://doi.org/10.1080/0284186X.2019.1643917
Gray LH, Conger AD, Ebert M, Hornsey S, Scott OCA (1953) The concentration of oxygen dissolved in tissues at the time of irradiation as a factor in radiotherapy. BJR 26(312):638–648. https://doi.org/10.1259/0007-1285-26-312-638
Udovicich C, Phillips C, Kok DL et al (2019) Neoadjuvant stereotactic radiosurgery: a further evolution in the management of brain metastases. Curr Oncol Rep 21(8):73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-019-0817-z
Lehrer EJ, Peterson JL, Zaorsky NG et al (2019) Single versus multifraction stereotactic radiosurgery for large brain metastases: an international meta-analysis of 24 trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 103(3):618–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.10.038
Akanda ZZ, Hong W, Nahavandi S, Haghighi N, Phillips C, Kok DL (2020) Post-operative stereotactic radiosurgery following excision of brain metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiother Oncol 142:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2019.08.024
Jhaveri J, Chowdhary M, Zhang X et al (2018) Does size matter? Investigating the optimal planning target volume margin for postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery to resected brain metastases. J Neurosurg 130(3):797–803. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.9.JNS171735
Patel RA, Lock D, Helenowski IB et al (2018) Postsurgical cavity evolution after brain metastasis resection: how soon should postoperative radiosurgery follow? World Neurosurg 110:e310–e314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.10.159
Shah JK, Potts MB, Sneed PK, Aghi MK, McDermott MW (2016) Surgical cavity constriction and local progression between resection and adjuvant radiosurgery for brain metastases. Cureus 8(4):e575. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.575
Soliman H, Ruschin M, Angelov L et al (2018) Consensus contouring guidelines for postoperative completely resected cavity stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 100(2):436–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.09.047
Yang R, Duan C, Yuan L et al (2018) Inhibitors of HIF-1α and CXCR4 mitigate the development of radiation necrosis in mouse brain. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 100(4):1016–1025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.12.257
Carnevale JA, Imber BS, Winston GM et al (2021) Risk of tract recurrence with stereotactic biopsy of brain metastases: an 18-year cancer center experience. J Neurosurg 136(4):1045–1051. https://doi.org/10.3171/2021.3.JNS204347
Schödel P, Jünger ST, Wittersheim M et al (2020) Surgical resection of symptomatic brain metastases improves the clinical status and facilitates further treatment. Cancer Med 9(20):7503–7510. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.3402
Minniti G, Lanzetta G, Capone L et al (2021) Leptomeningeal disease and brain control after postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery with or without immunotherapy for resected brain metastases. J Immunother Cancer 9(12):e003730. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2021-003730
Wegner R. A phase II study of pre-op SRS followed by surgical resection for brain metastases. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT05341739. Updated April 22, 2022. Accessed September 29, 2022. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05341739
Yu M. Preop fSRS for resectable brain metastases. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT05267587. Updated March 4, 2022. Accessed September 29, 2022. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05267587
Brun L. Preoperative stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases (STEP). ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04503772. Updated April 8, 2022. Accessed September 29, 2022. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04503772
Agarwal N. Pre-operative stereotactic radiosurgery followed by resection for patients with brain metastases. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03398694. Updated June 9, 2022. Accessed September 29, 2022. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03398694
Clump D. Preoperative stereotactic radiosurgery followed by resection for brain metastases. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT02514195. Updated April 13, 2021. Accessed September 29, 2022. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02514195
Yeboa D. Pre-operative SRS or post-operative SRS in treating cancer patients with brain metastases. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03741673. Updated June 13, 2022. Accessed September 29, 2022. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03741673
Huhammud F. Pre-versus post-operative SRS for resectable brain metastases. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04474925. Updated September 29, 2021. Accessed September 29, 2022. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04474925
Yan E. Pre-operative or post-operative stereotactic radiosurgery in treating patients with operative metastatic brain tumors. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03750227. Updated February 14, 2022. Accessed September 29, 2022. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03750227
Rogers S. Trial of preoperative radiosurgery versus postoperative stereotactic radiotherapy for resectable brain metastases (PREOP-2). ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT05124236. Updated September 10, 2022. Accessed September 29, 2022. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05124236
Burri S. Comparing the addition of radiation either before or after surgery for patients with brain metastases. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT05438212. Updated August 29, 2022. Accessed September 29, 2022. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05438212
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Sarah Carey, MS, Jade Chang, and Jacalyn Newman, PhD, of Allegheny Health Network’s Health System Publication Support Office (HSPSO) for their assistance in editing and formatting the manuscript. The HSPSO is funded by Highmark Health (Pittsburgh, PA, United States of America) and all work was done in accordance with Good Publication Practice (GPP3) guidelines (http://www.ismpp.org/gpp3).
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the content of the review. Material preparation and literature review was performed by all authors. The first draft of the manuscript was written by SR, and all authors commented on subsequent versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
Rodney Wegner, MD has received grant funding from Elekta (not in support of this study). No other authors have declared financial interests.
Ethical approval
This is a literature and topic review. The Allegheny Health Network ethics committee has verified that no ethics approval is required.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rajkumar, S., Liang, Y., Wegner, R.E. et al. Utilization of neoadjuvant stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of brain metastases requiring surgical resection: a topic review. J Neurooncol 160, 691–705 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04190-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04190-6