Abstract
Purpose
Glioblastoma is the most common primary malignant brain tumor in the adult, whose grim prognosis largely relates to the absence of effective treatment targets. Given its success in other cancers, immunotherapy has been trialed in glioblastoma and failed to demonstrate the expected benefit. Importantly, these disappointing results highlight the importance of understanding the unique and transforming biology of glioblastoma and its microenvironment. Our goal was to evaluate and characterize the expression of PD-L1 through immunohistochemistry in a large glioblastoma cohort. We further studied PD-L1 expression-associated prognosis and its correlation to systemic and neuropathological parameters.
Methods
A series of 352 glioblastoma specimens (313 initial resection, 39 matched recurrences) was collected, with a detailed characterization of tumor neuropathological characteristics, including the presence, density and location of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL). Two hematological markers, absolute lymphocyte count and neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio (NLR), were used to analyze and correlate with systemic inflammation and immunosuppression. Immunohistochemistry was performed to evaluate PD-L1 expression.
Results
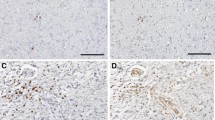
Membranous PD-L1 expression was identified in 31% (98/313) of newly diagnosed and 46% (18/39) of matched recurrent tumors. TIL were found in 26% (82/313) of primary tumors and both density and location were found to be significantly associated with PD-L1 expression (p < 0.001). Interestingly, PD-L1 expressing tumors had more frequently areas with sarcomatous differentiation (p < 0.001) and were significantly associated with lower lymphocyte count (p = 0.018) and higher NLR ratio (p = 0.004) upon diagnosis. Importantly, PD-L1 expression was an independent poor prognostic marker in our cohort.
Conclusion
Taken together, our data points to a putative role for PD-L1 expression in glioblastoma biology, which correlates to poor patient overall survival, as well as with a general systemic inflammatory status and immunosuppression.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ostrom QT, Cioffi G, Gittleman H, Patil N, Waite K, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan JS (2019) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2012–2016. Neuro Oncol 21(Suppl 5):v1–v100
Wen PY, Weller M, Lee EQ, Alexander BM, Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Barthel FP, Batchelor TT, Bindra RS, Chang SM, Chiocca EA et al (2020) Glioblastoma in adults: a Society for Neuro-Oncology (SNO) and European Society of Neuro-Oncology (EANO) consensus review on current management and future directions. Neuro Oncol 22(8):1073–1113
Dunn GP, Rinne ML, Wykosky J, Genovese G, Quayle SN, Dunn IF, Agarwalla PK, Chheda MG, Campos B, Wang A et al (2012) Emerging insights into the molecular and cellular basis of glioblastoma. Genes Dev 26(8):756–784
Chongsathidkiet P, Jackson C, Koyama S, Loebel F, Cui X, Farber SH, Woroniecka K, Elsamadicy AA, Dechant CA, Kemeny HR et al (2018) Sequestration of T cells in bone marrow in the setting of glioblastoma and other intracranial tumors. Nat Med 24(9):1459–1468
Woroniecka K, Chongsathidkiet P, Rhodin K, Kemeny H, Dechant C, Farber SH, Elsamadicy AA, Cui X, Koyama S, Jackson C et al (2018) T-cell exhaustion signatures vary with tumor type and are severe in glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 24(17):4175–4186
Woroniecka K, Fecci PE (2018) T-cell exhaustion in glioblastoma. Oncotarget 9(82):35287–35288
Grossman SA, Ye XB, Lesser G, Sloan A, Carraway H, Desideri S, Piantadosi S, Consortium NC (2011) Immunosuppression in patients with high-grade gliomas treated with radiation and temozolomide. Clin Cancer Res 17(16):5473–5480
Rahman R, Catalano PJ, Arvold ND, Aizer AA, Weiss SE, Pinnell N, Horvath MC, Christianson L, Reardon DA, Lee EQ et al (2016) Chemoradiation-related lymphopenia is common among glioblastoma patients and is associated with worse progression-free and overall survival. Int J Radiat Oncol 96(2):E123–E123
Aggarwal BB, Vijayalekshmi RV, Sung B (2009) Targeting inflammatory pathways for prevention and therapy of cancer: short-term friend, long-term foe. Clin Cancer Res 15(2):425–430
O’Callaghan DS, O’Donnell D, O’Connell F, O’Byrne KJ (2010) The role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 5(12):2024–2036
Liu D, Huang Y, Li L, Song J, Zhang L, Li W (2017) High neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratios confer poor prognoses in patients with small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 17(1):882
Zhou Y, Wei Q, Fan J, Cheng S, Ding W, Hua Z (2018) Prognostic role of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis containing 8252 patients. Clin Chim Acta 479:181–189
Lopes M, Carvalho B, Vaz R, Linhares P (2018) Influence of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in prognosis of glioblastoma multiforme. J Neuro-Oncol 136(1):173–180
Lei YY, Li YT, Hu QL, Wang J, Sui AX (2019) Prognostic impact of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in gliomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Surg Oncol 17(1):152
Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, Latchman Y, Bourque K, Brown JA, Boussiotis VA, Dorfman DM, Chernova T, Nishimura H et al (2000) Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7-family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation. Blood 96(11):810a–811a
Kuryk L, Bertinato L, Staniszewska M, Pancer K, Wieczorek M, Salmaso S, Caliceti P, Garofalo M (2020) From conventional therapies to immunotherapy: melanoma treatment in review. Cancers 12(10).
Rizvi NA, Hellmann MD, Snyder A, Kvistborg P, Makarov V, Havel JJ, Lee W, Yuan JD, Wong P, Ho TS et al (2015) Mutational landscape determines sensitivity to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Science 348(6230):124–128
Samstein RM, Lee CH, Shoushtari AN, Hellmann MD, Shen RL, Janjigian YY, Barron DA, Zehir A, Jordan EJ, Omuro A et al (2019) Tumor mutational load predicts survival after immunotherapy across multiple cancer types. Nat Genet 51(2):202
Le DT, Durham JN, Smith KN, Wang H, Bartlett BR, Aulakh LK, Lu S, Kemberling H, Wilt C, Luber BS et al (2017) Mismatch repair deficiency predicts response of solid tumors to PD-1 blockade. Science 357(6349):409–413
Topalian SL, Drake CG, Pardoll DM (2012) Targeting the PD-1/B7-H1(PD-L1) pathway to activate anti-tumor immunity. Curr Opin Immunol 24(2):207–212
Sampson JH, Omuro AMP, Preusser M, Lim M, Butowski NA, Cloughesy TF, Strauss LC, Latek RR, Paliwal P, Weller M et al (2016) A randomized, phase 3, open-label study of nivolumab versus temozolomide (TMZ) in combination with radiotherapy (RT) in adult patients (pts) with newly diagnosed, O-6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase (MGMT)-unmethylated glioblastoma (GBM): CheckMate-498. J Clin Oncol 34(15_suppl):TPS2079-TPS2079.
Bristol Myers Squibb Announces Update on Phase 3 CheckMate -548 Trial Evaluating Patients with Newly Diagnosed MGMT-Methylated Glioblastoma Multiforme. https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20201223005025/en/
Reardon DA, Brandes AA, Omuro A, Mulholland P, Lim M, Wick A, Baehring J, Ahluwalia MS, Roth P, Bahr O et al (2020) Effect of nivolumab vs bevacizumab in patients with recurrent glioblastoma the checkmate 143 phase 3 randomized clinical trial. Jama Oncol 6(7):1003–1010
Parsa AT, Waldron JS, Panner A, Crane CA, Parney IF, Barry JJ, Cachola KE, Murray JC, Tihan T, Jensen MC et al (2007) Loss of tumor suppressor PTEN function increases B7–H1 expression and immunoresistance in glioma. Nat Med 13(1):84–88
Rutledge WC, Kong J, Gao JJ, Gutman DA, Cooper LAD, Appin C, Park Y, Scarpace L, Mikkelsen T, Cohen ML et al (2013) Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in glioblastoma are associated with specific genomic alterations and related to transcriptional class. Clin Cancer Res 19(18):4951–4960
Zhao JF, Chen AX, Gartrell RD, Silverman AM, Aparicio L, Chu T, Bordbar D, Shan D, Samanamud J, Mahajan A et al (2019) Immune and genomic correlates of response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in glioblastoma (vol 25, pg 462, 2019). Nat Med 25(6):1022–1022
Dahlin AM, Henriksson ML, Van Guelpen B, Stenling R, Oberg A, Rutegard J, Palmqvist R (2011) Colorectal cancer prognosis depends on T-cell infiltration and molecular characteristics of the tumor. Modern Pathol 24(5):671–682
Berghoff AS, Kiesel B, Widhalm G, Rajky O, Ricken G, Wohrer A, Dieckmann K, Filipits M, Brandstetter A, Weller M et al (2015) Programmed death ligand 1 expression and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol 17(8):1064–1075
Holzl D, Hutarew G, Zellinger B, Schlicker HU, Schwartz C, Winkler PA, Sotlar K, Kraus TFJ (2021) Integrated analysis of programmed cell death ligand 1 expression reveals increased levels in high-grade glioma. J Cancer Res Clin 147(8):2271–2280
Topalian SL, Taube JM, Pardoll DM (2020) Neoadjuvant checkpoint blockade for cancer immunotherapy. Science 367(6477).
Zhang JY, Yan YY, Li JJ, Adhikari R, Fu LW (2020) PD-1/PD-L1 based combinational cancer therapy: icing on the cake. Front Pharmacol 11:722
Garber ST, Hashimoto Y, Weathers SP, Xiu J, Gatalica Z, Verhaak RG, Zhou S, Fuller GN, Khasraw M, de Groot J et al (2016) Immune checkpoint blockade as a potential therapeutic target: surveying CNS malignancies. Neuro Oncol 18(10):1357–1366
Xue S, Hu M, Li P, Ma J, Xie L, Teng F, Zhu Y, Fan B, Mu D, Yu J (2017) Relationship between expression of PD-L1 and tumor angiogenesis, proliferation, and invasion in glioma. Oncotarget 8(30):49702–49712
Zhang Y, Pan C, Wang J, Cao J, Liu Y, Wang Y, Zhang L (2017) Genetic and immune features of resectable malignant brainstem gliomas. Oncotarget 8(47):82571–82582
Berghoff AS, Kiesel B, Widhalm G, Wilhelm D, Rajky O, Kurscheid S, Kresl P, Wohrer A, Marosi C, Hegi ME et al (2017) Correlation of immune phenotype with IDH mutation in diffuse glioma. Neuro Oncol 19(11):1460–1468
Hodges TR, Ott M, Xiu J, Gatalica Z, Swensen J, Zhou S, Huse JT, de Groot J, Li S, Overwijk WW et al (2017) Mutational burden, immune checkpoint expression, and mismatch repair in glioma: implications for immune checkpoint immunotherapy. Neuro Oncol 19(8):1047–1057
Heiland DH, Haaker G, Delev D, Mercas B, Masalha W, Heynckes S, Gabelein A, Pfeifer D, Carro MS, Weyerbrock A et al (2017) Comprehensive analysis of PD-L1 expression in glioblastoma multiforme. Oncotarget 8(26):42214–42225
Lee KS, Lee K, Yun S, Moon S, Park Y, Han JH, Kim CY, Lee HS, Choe G (2018) Prognostic relevance of programmed cell death ligand 1 expression in glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 136(3):453–461
Han J, Hong Y, Lee YS (2017) PD-L1 expression and combined status of PD-L1/PD-1-positive tumor infiltrating mononuclear cell density predict prognosis in glioblastoma patients. J Pathol Transl Med 51(1):40–48
Heynckes S, Gaebelein A, Haaker G, Grauvogel J, Franco P, Mader I, Carro MS, Prinz M, Delev D, Schnell O et al (2017) Expression differences of programmed death ligand 1 in de-novo and recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. Oncotarget 8(43):74170–74177
Liu Y, Carlsson R, Ambjorn M, Hasan M, Badn W, Darabi A, Siesjo P, Issazadeh-Navikas S (2013) PD-L1 expression by neurons nearby tumors indicates better prognosis in glioblastoma patients. J Neurosci 33(35):14231–14245
Miyazaki T, Ishikawa E, Matsuda M, Akutsu H, Osuka S, Sakamoto N, Takano S, Yamamoto T, Tsuboi K, Matsumura A (2017) Assessment of PD-1 positive cells on initial and secondary resected tumor specimens of newly diagnosed glioblastoma and its implications on patient outcome. J Neurooncol 133(2):277–285
Wang Z, Zhang C, Liu X, Wang Z, Sun L, Li G, Liang J, Hu H, Liu Y, Zhang W et al (2016) Molecular and clinical characterization of PD-L1 expression at transcriptional level via 976 samples of brain glioma. Oncoimmunology 5(11):e1196310
Wilmotte R, Burkhardt K, Kindler V, Belkouch MC, Dussex G, Tribolet N, Walker PR, Dietrich PY (2005) B7-homolog 1 expression by human glioma: a new mechanism of immune evasion. NeuroReport 16(10):1081–1085
Wintterle S, Schreiner B, Mitsdoerffer M, Schneider D, Chen L, Meyermann R, Weller M, Wiendl H (2003) Expression of the B7-related molecule B7–H1 by glioma cells: a potential mechanism of immune paralysis. Cancer Res 63(21):7462–7467
Xiu J, Piccioni D, Juarez T, Pingle SC, Hu J, Rudnick J, Fink K, Spetzler DB, Maney T, Ghazalpour A et al (2016) Multi-platform molecular profiling of a large cohort of glioblastomas reveals potential therapeutic strategies. Oncotarget 7(16):21556–21569
Zeng J, Zhang XK, Chen HD, Zhong ZH, Wu QL, Lin SX (2016) Expression of programmed cell death-ligand 1 and its correlation with clinical outcomes in gliomas. Oncotarget 7(8):8944–8955
Derer A, Spiljar M, Bäumler M, Hecht M, Fietkau R, Frey B, Gaipl US (2016) Chemoradiation increases PD-L1 expression in certain melanoma and glioblastoma cells. Front Immunol 7:610
Nduom EK, Wei J, Yaghi NK, Huang N, Kong LY, Gabrusiewicz K, Ling X, Zhou S, Ivan C, Chen JQ et al (2016) PD-L1 expression and prognostic impact in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol 18(2):195–205
Pratt D, Dominah G, Lobel G, Obungu A, Lynes J, Sanchez V, Adamstein N, Wang X, Edwards NA, Wu T et al (2019) Programmed death ligand 1 Is a negative prognostic marker in recurrent isocitrate dehydrogenase-wildtype glioblastoma. Neurosurgery 85(2):280–289
Doucette T, Rao G, Rao A, Shen L, Aldape K, Wei J, Dziurzynski K, Gilbert M, Heimberger AB (2013) Immune heterogeneity of glioblastoma subtypes: extrapolation from the cancer genome atlas. Cancer Immunol Res 1(2):112–122
Klemm F, Maas RR, Bowman RL, Kornete M, Soukup K, Nassiri S, Brouland JP, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Brennan C, Tabar V et al (2020) Interrogation of the microenvironmental landscape in brain tumors reveals disease-specific alterations of immune cells. Cell 181(7):1643-1660 e1617
Martinez-Lage M, Lynch TM, Bi Y, Cocito C, Way GP, Pal S, Haller J, Yan RE, Ziober A, Nguyen A et al (2019) Immune landscapes associated with different glioblastoma molecular subtypes. Acta Neuropathol Commun 7(1):203
Kaffes I, Szulzewsky F, Chen Z, Herting CJ, Gabanic B, Velázquez Vega JE, Shelton J, Switchenko JM, Ross JL, McSwain LF et al (2019) Human Mesenchymal glioblastomas are characterized by an increased immune cell presence compared to Proneural and Classical tumors. Oncoimmunology 8(11):e1655360
Liu C, Zhang Z, Ping Y, Qin G, Zhang K, Maimela NR, Huang L, Yang S, Zhang Y (2020) Comprehensive analysis of PD-1 gene expression, immune characteristics and prognostic significance in 1396 glioma patients. Cancer Manag Res 12:4399–4410
Ricklefs FL, Alayo Q, Krenzlin H, Mahmoud AB, Speranza MC, Nakashima H, Hayes JL, Lee K, Balaj L, Passaro C et al (2018) Immune evasion mediated by PD-L1 on glioblastoma-derived extracellular vesicles. Sci Adv 4(3):eaar2766.
Grabowski MM, Sankey EW, Ryan KJ, Chongsathidkiet P, Lorrey SJ, Wilkinson DS, Fecci PE (2021) Immune suppression in gliomas. J Neurooncol 151(1):3–12
Brown CE, Alizadeh D, Starr R, Weng L, Wagner JR, Naranjo A, Ostberg JR, Blanchard MS, Kilpatrick J, Simpson J et al (2016) Regression of glioblastoma after chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy. N Engl J Med 375(26):2561–2569
Chamberlain MC, Kim BT (2017) Nivolumab for patients with recurrent glioblastoma progressing on bevacizumab: a retrospective case series. J Neurooncol 133(3):561–569
Mantica M, Pritchard A, Lieberman F, Drappatz J (2018) Retrospective study of nivolumab for patients with recurrent high grade gliomas. J Neurooncol 139(3):625–631
Cloughesy TF, Mochizuki AY, Orpilla JR, Hugo W, Lee AH, Davidson TB, Wang AC, Ellingson BM, Rytlewski JA, Sanders CM et al (2019) Neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 immunotherapy promotes a survival benefit with intratumoral and systemic immune responses in recurrent glioblastoma. Nat Med 25(3):477–486
Galon J, Costes A, Sanchez-Cabo F, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B, Lagorce-Pagès C, Tosolini M, Camus M, Berger A, Wind P et al (2006) Type, density, and location of immune cells within human colorectal tumors predict clinical outcome. Science 313(5795):1960–1964
Huh JW, Lee JH, Kim HR (2012) Prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes for patients with colorectal cancer. Archiv Surgery (Chicago, Ill: 1960) 147(4):366–372.
Galluzzi L, Chan TA, Kroemer G, Wolchok JD, López-Soto A (2018) The hallmarks of successful anticancer immunotherapy. Sci Transl Med 10(459).
Chen DS, Mellman I (2017) Elements of cancer immunity and the cancer-immune set point. Nature 541(7637):321–330
Dunn GP, Dunn IF, Curry WT (2007) Focus on TILs: prognostic significance of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in human glioma. Cancer Immun 7:12
Woroniecka KI, Rhodin KE, Chongsathidkiet P, Keith KA, Fecci PE (2018) T-cell dysfunction in glioblastoma: applying a new framework. Clin Cancer Res 24(16):3792–3802
Dix AR, Brooks WH, Roszman TL, Morford LA (1999) Immune defects observed in patients with primary malignant brain tumors. J Neuroimmunol 100(1–2):216–232
Kim WJ, Dho YS, Ock CY, Kim JW, Choi SH, Lee ST, Kim IH, Kim TM, Park CK (2019) Clinical observation of lymphopenia in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 143(2):321–328
Funding
This work was funded by FEDER—Fundo Europeu de Desenvolvimento Regional funds through the COMPETE 2020—Operacional Programme for Competitiveness and Internationalisation (POCI), Portugal 2020, and by FCT—Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia/ Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia e Ensino Superior under the project FCT/02/SAICT/2017/030625.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: CN and JP; Methodology: CN, DL, RT, FS; Formal analysis and investigation: CN, ASR, RT, FS, JP; Writing—original draft preparation: CN; Writing—review and editing: CN, ASR, RT, JR, FS, CF, JP; Supervision: JP.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study has been performed in accordance with the national regulative law for the handling of biological specimens from tumor banks, being the samples exclusively available for research purposes in retrospective studies, as well as under the international Helsinki declaration. Moreover, it has been also approved by the ethics committee at Centro Hospitalar Universitário do Porto (2017-104 (093-DEFI/091-CES).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noronha, C., Ribeiro, A.S., Taipa, R. et al. PD-L1 tumor expression is associated with poor prognosis and systemic immunosuppression in glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 156, 453–464 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-021-03907-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-021-03907-3