Abstract
Purpose
Immunotherapy has demonstrated efficacy in treatment of intracranial metastasis from melanoma, calling into question the role of intracranial radiotherapy (RT). Herein, we assessed the utilization patterns of intracranial RT in patients with melanoma brain metastasis and compared outcomes in patients treated with immunotherapy alone versus immunotherapy in addition to intracranial RT.
Methods
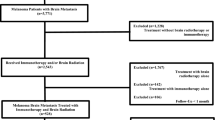
We queried the National Cancer Database (NCDB) for patients with melanoma brain metastases treated with immunotherapy and intracranial RT or immunotherapy alone. Multivariable logistic regression identified variables associated with increased likelihood of receiving immunotherapy alone. Multivariable Cox regression was used to identify co-variates predictive of overall survival (OS). Propensity matching was used to account for indication bias.
Results
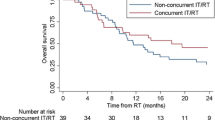
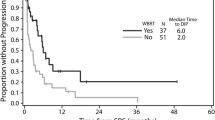
We identified 528 and 142 patients that were treated with combination therapy and immunotherapy alone, respectively. Patients with lower comorbidity score were more likely to receive immunotherapy alone. Extracranial disease and treatment at a non-academic center were associated with worse OS. Median OS for all patients was 11.0 months. Treatment with stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) in addition to immunotherapy was superior to immunotherapy alone, median OS of 19.0 versus 11.5 months (p = 0.006). Whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) in combination with immunotherapy performed worse than immunotherapy alone, median OS of 7.7 versus 11.5 months (p = 0.0255).
Conclusions
For melanoma patients requiring WBRT, immunotherapy alone may be reasonable in asymptomatic patients. For those eligible for SRS, combination therapy may provide better outcomes. Results of ongoing prospective studies will help provide guidance regarding the use of radioimmunotherapy in this population.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW et al (2004) Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 363:1665–1672
Tawbi HA, Forsyth PA, Algazi A et al (2018) Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab in melanoma metastatic to the brain. N Engl J Med 379:722–730
Long GV, Atkinson V, Lo S et al (2018) Combination nivolumab and ipilimumab or nivolumab alone in melanoma brain metastases: a multicentre randomised phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol 19:672–681
Hodi FS, O'Day SJ, McDermott DF et al (2010) Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med 363:711–723
Postow MA, Chesney J, Pavlick AC et al (2015) Nivolumab and ipilimumab versus ipilimumab in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med 372:2006–2017
Deyo RA, Cherkin DC, Ciol MA (1992) Adapting a clinical comorbidity index for use with ICD-9-CM administrative databases. J Clin Epidemiol 45:613–619
Stokes WA, Bronsert MR, Meguid RA et al (2018) Post-treatment mortality after surgery and stereotactic body radiotherapy for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 36:642–651
Cox DR (1972) Regression models and life- tables. J R Stat Soc 34:187–220
D'Agostino RB Jr (1998) Propensity score methods for bias reduction in the comparison of a treatment to a non-randomized control group. Stat Med 17:2265–2281
Meier ELKP (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457–481
Doss LL, Memula N (1982) The radioresponsiveness of melanoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 8:1131–1134
Espenel S, Vallard A, Rancoule C et al (2017) Melanoma: last call for radiotherapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 110:13–19
Fertil B, Malaise EP (1985) Intrinsic radiosensitivity of human cell lines is correlated with radioresponsiveness of human tumors: analysis of 101 published survival curves. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 11:1699–1707
Mohamad O, de Leon AD, Schroeder S et al (2018) Safety and efficacy of concurrent immune checkpoint inhibitors and hypofractionated body radiotherapy. Oncoimmunology. 7:e1440168
Dyer MA, Arvold ND, Chen YH et al (2014) The role of whole brain radiation therapy in the management of melanoma brain metastases. Radiat Oncol 9:143
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U et al (2011) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952–26001 study. J Clin Oncol 29:134–141
Zindler JD, Bruynzeel AME, Eekers DBP, Hurkmans CW, Swinnen A, Lambin P (2017) Whole brain radiotherapy versus stereotactic radiosurgery for 4–10 brain metastases: a phase III randomised multicentre trial. BMC Cancer 17:500
Stereotactic Radiosurgery Compared with hippocampal-avoidant whole brain radiotherapy (HA-WBRT) plus memantine for 5–15 brain metastases. https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT03550391. Accessed 11 Oct 2019
Soon YY, Tham IW, Lim KH, Koh WY, Lu JJ (2014) Surgery or radiosurgery plus whole brain radiotherapy versus surgery or radiosurgery alone for brain metastases. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014:CD009454
Hong AM, Fogarty GB, Dolven-Jacobsen K et al (2019) Adjuvant whole-brain radiation therapy compared with observation after local treatment of melanoma brain metastases: a multicenter, randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 37:3132–3141
Goldberg SB, Gettinger SN, Mahajan A et al (2016) Pembrolizumab for patients with melanoma or non-small-cell lung cancer and untreated brain metastases: early analysis of a non-randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 17:976–983
Margolin K, Ernstoff MS, Hamid O et al (2012) Ipilimumab in patients with melanoma and brain metastases: an open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 13:459–465
Lanier CM, Hughes R, Ahmed T et al (2019) Immunotherapy is associated with improved survival and decreased neurologic death after SRS for brain metastases from lung and melanoma primaries. Neurooncol Pract 6:402–409
Minniti G, Anzellini D, Reverberi C et al (2019) Stereotactic radiosurgery combined with nivolumab or Ipilimumab for patients with melanoma brain metastases: evaluation of brain control and toxicity. J Immunother Cancer 7:102
Gabani P, Fischer-Valuck BW, Johanns TM et al (2018) Stereotactic radiosurgery and immunotherapy in melanoma brain metastases: patterns of care and treatment outcomes. Radiother Oncol 128:266–273
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors involved have nothing to disclose and no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
White, R.J., Abel, S., Horne, Z.D. et al. Melanoma brain metastases: is it time to eliminate radiotherapy?. J Neurooncol 149, 27–33 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03485-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03485-w