Abstract
Introduction
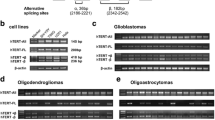
Alternative splicing of hTERT pre-mRNA is an important step in the regulation of telomerase activity, but the regulation mechanisms and functions remain unclear.
Methods
RT-PCR analysis was used to detect hTERT splicing in glioma cell lines and brain tissues. TRAP assay was used to detect the telomerase activity. Then, we designed and synthesized 2′-O-methyl-RNA phosphorothioate AONs and transfected them into glioma cells to detect the changes in telomerase activity. MTT assay, plate colony formation assay, western blotting and Annexin V/PI assay were used to detect cell proliferation and apoptosis. At last, bioinformatics analyses were used to predict the expression and function of splicing protein SRSF2 in gliomas.
Results
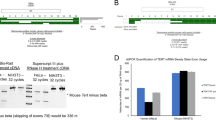
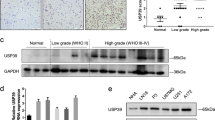
hTERT splicing occurs both in glioma cell lines and glioma patients’ tissues. The telomerase activity was related to the expression level of the full-length hTERT, rather than the total hTERT transcript level. AON-Ex726 was complementary to the sequence of the intronic splicing enhancer (ISE) in intron six, and significantly altered the splicing pattern of hTERT pre-mRNA, reducing the expression level of the full-length hTERT mRNA and increasing the expression level of the -β hTERT mRNA. After transfection with AON-Ex726, the level of apoptosis was increased, while telomerase activity and cell proliferation were significantly decreased. By bioinformatic predictions, we found the AON-Ex726 anchoring sequence in ISE overlaps the binding site of SRSF2 protein, which is up-regulated during the development of gliomas.
Conclusions
Our findings provided new targets and important clues for the gene therapy of gliomas by regulating the alternative splicing pattern of hTERT pre-mRNA.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiang J, Wang Y, Sušac L et al (2018) Structure of telomerase with telomeric DNA. Cell 173(5):1179–1190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.04.038
Zhao Y, Sfeir AJ, Zou Y et al (2009) Telomere extension occurs at most chromosome ends and is uncoupled from fill-in in human cancer cells. Cell 138(3):463–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.026
Chen L, Roake CM, Freund A et al (2018) An activity switch in human telomerase based on rna conformation and shaped by TCAB1. Cell 174(1):218–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.04.039
Blackburn EH, Epel ES, Lin J (2015) Human telomere biology: a contributory and interactive factor in aging, disease risks, and protection. Science 350(6265):1193–1198. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aab3389
Nguyen THD, Tam J, Wu RA, Greber BJ, Toso D, Nogales E, Collins K (2018) Cryo-EM structure of substrate-bound human telomerase holoenzyme. Nature 557(7704):190–195. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0062-x
Arndt GM, MacKenzie KL (2016) New prospects for targeting telomerase beyond the telomere. Nat Rev Cancer 16(8):508–524. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2016.55
Wang Z, Xu J, Geng X, Zhang W (2010) Analysis of DNA methylation status of the promoter of human telomerase reverse transcriptase in gastric carcinogenesis. Arch Med Res 41(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2009.11.001
Tang H, Wang H, Cheng X et al (2018) HuR regulates telomerase activity through TERC methylation. Nat Commun 9(1):2213. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04617-7
Borah S, Xi L, Zaug AJ et al (2015) Cancer. TERT promoter mutations and telomerase reactivation in urothelial cancer. Science 347(6225):1006–1010. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1260200
Bell RJ, Rube HT, Kreig A et al (2015) Cancer. The transcription factor GABP selectively binds and activates the mutant TERT promoter in cancer. Science 348(6238):1036–1039. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aab0015
Harley CB (2008) Telomerase and cancer therapeutics. Nat Rev Cancer 8(3):167–179. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2275
Min J, Wright WE, Shay JW (2017) Alternative lengthening of telomeres can be maintained by preferential elongation of lagging strands. Nucleic Acids Res 45(5):2615–2628. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1295
Baralle FE, Giudice J (2017) Alternative splicing as a regulator of development and tissue identity. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18(7):437–451. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2017.27
Galarza-Muñoz G, Briggs FBS, Evsyukova I et al (2017) Human epistatic interaction controls IL7R splicing and increases multiple sclerosis risk. Cell 169(1):72–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.03.007
Kim W, Ludlow AT, Min J et al (2016) Regulation of the human telomerase gene TERT by telomere position effect-over long distances (TPE-OLD): implications for aging and cancer. PLoS Biol 14(12):e2000016. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2000016
Yi X, Shay JW, Wright WE (2001) Quantitation of telomerase components and hTERT mRNA splicing patterns in immortal human cells. Nucleic Acids Res 29(23):4818–4825
Wong MS, Shay JW, Wright WE (2014) Regulation of human telomerase splicing by RNA: RNA pairing. Nat Commun 5:3306. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4306
Hisatomi H, Ohyashiki K, Ohyashiki JH, Nagao K, Kanamaru T, Hirata H, Hibi N, Tsukada Y (2003) Expression profile of a gamma-deletion variant of the human telomerase reverse transcriptase gene. Neoplasia 5(3):193–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1476-5586(03)80051-9
Kole R, Krainer AR, Altman S (2012) RNA therapeutics: beyond RNA interference and antisense oligonucleotides. Nat Rev Drug Discov 11(2):125–140. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3625
Han G, Gu B, Cao L et al (2016) Hexose enhances oligonucleotide delivery and exon skipping in dystrophin-deficient mdx mice. Nat Commun 7:10981. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10981
Inoue A, Yamamoto N, Kimura M, Nishio K, Yamane H, Nakajima K (2014) RBM10 regulates alternative splicing. FEBS Lett 588(6):942–947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2014.01.052
Schnerwitzki D, Perner B, Hoppe B et al (2014) Alternative splicing of Wilms tumor suppressor 1 (Wt1) exon 4 results in protein isoforms with different functions. Dev Biol 393(1):24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.06.026
Palhais B, Præstegaard VS, Sabaratnam R, Doktor TK, Lutz S, Burda P, Suormala T, Baumgartner M, Fowler B, Bruun GH, Andersen HS, Kožich V, Andresen BS (2015) Splice-shifting oligonucleotide (SSO) mediated blocking of an exonic splicing enhancer (ESE) created by the prevalent c.903 + 469T> C MTRR mutation corrects splicing and restores enzyme activity in patient cells. Nucleic Acids Res 43(9):4627–4639. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv275
Smith LD, Leme de Calais F, Raponi M et al (2017) Novel splice-switching oligonucleotide promotes BRCA1 aberrant splicing and susceptibility to PARP inhibitor action. Int J Cancer 140(7):1564–1570. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.30574
Bauman JA, Li SD, Yang A, Huang L, Kole R (2010) Anti-tumor activity of splice-switching oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res 38(22):8348–8356. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq731
Liu J, Bhadra M, Sinnakannu JR et al (2017) Overcoming imatinib resistance conferred by the BIM deletion polymorphism in chronic myeloidleukemia with splice-switching antisense oligonucleotides. Oncotarget 8(44):77567–77585. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20658
Muntoni F, Wood MJ (2011) Targeting RNA to treat neuromuscular disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10(8):621–637. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3459
Venkatesh HS, Tam LT, Woo PJ et al (2017) Targeting neuronal activity-regulated neuroligin-3 dependency in high-grade glioma. Nature 549(7673):533–537. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature24014
Xue J, Zhao Z, Zhang L et al (2017) Neutrophil-mediated anticancer drug delivery for suppression of postoperative malignant gliomarecurrence. Nat Nanotechnol 12(7):692–700. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2017.54
Li G, Shen J, Cao J et al (2018) Alternative splicing of human telomerase reverse transcriptase in gliomas and its modulation mediated by CX-5461. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37(1):78. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0749-8
Herbert BS, Hochreiter AE, Wright WE, Shay JW (2006) Nonradioactive detection of telomerase activity using the telomeric repeat amplification protocol. Nat Protoc 1(3):1583–1590
Liu X, Wang Y, Chang G, Wang F, Wang F, Geng X. Alternative Splicing of hTERT Pre-mRNA: a potential strategy for the regulation of telomerase activity. Int J Mol Sci. 2017 18(3):pii E567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030567
Aldape K, Zadeh G, Mansouri S, Reifenberger G, von Deimling A (2015) Glioblastoma: pathology, molecular mechanisms and markers. Acta Neuropathol 129(6):829–848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1432-1
Jung H, Lee D, Lee J et al (2015) Intron retention is a widespread mechanism of tumor-suppressor inactivation. Nat Genet 47(11):1242–1248. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3414
Bertaux-Skeirik N, Wunderlich M, Teal E et al (2017) CD44 variant isoform 9 emerges in response to injury and contributes to the regeneration of the gastric epithelium. J Pathol 242(4):463–475. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.4918
Bickmore WA, Oghene K, Little MH, Seawright A, van Heyningen V, Hastie ND (1992) Modulation of DNA binding specificity by alternative splicing of the Wilms tumor wt1 gene transcript. Science 257(5067):235–237
Lee MT, Ho SM, Tarapore P, Chung I, Leung YK (2013) Estrogen receptor β isoform 5 confers sensitivity of breast cancer cell lines to chemotherapeutic agent-induced apoptosis through interaction with Bcl2L12. Neoplasia 15(11):1262–1271
Romero A, García-García F, López-Perolio I et al (2015) BRCA1 Alternative splicing landscape in breast tissue samples. BMC Cancer 15:219. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-015-1145-9
Sharma S, Lichtenstein A (2009) Aberrant splicing of the E-cadherin transcript is a novel mechanism of gene silencing in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood 114(19):4179–4185. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-03-206482
Shultz JC, Goehe RW, Wijesinghe DS et al (2010) Alternative splicing of caspase 9 is modulated by the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway via phosphorylation of SRp30a. Cancer Res 70(22):9185–9196. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1545
Yi X, White DM, Aisner DL, Baur JA, Wright WE, Shay JW (2000) An alternate splicing variant of the human telomerase catalytic subunit inhibits telomeraseactivity. Neoplasia 2(5):433–440
Colgin LM, Wilkinson C, Englezou A, Kilian A, Robinson MO, Reddel RR (2000) The hTERTalpha splice variant is a dominant negative inhibitor of telomerase activity. Neoplasia 2(5):426–432
Xu JH, Wang YC, Geng X, Li YY, Zhang WM (2009) Changes of the alternative splicing variants of human telomerase reverse transcriptase during gastric carcinogenesis. Pathobiology 76(1):23–29. https://doi.org/10.1159/000178152
Robin V, Griffith G, Carter JL, Leumann CJ, Garcia L, Goyenvalle A (2017) Efficient SMN rescue following subcutaneous tricyclo-DNA antisense oligonucleotide treatment. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 7:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2017.02.009
Brambilla C, Folini M, Gandellini P, Daprai L, Daidone MG, Zaffaroni N (2004) Oligomer-mediated modulation of hTERT alternative splicing induces telomerase inhibition and cell growth decline in human prostate cancer cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 61(14):1764–1774
Sharma S, Liao W, Zhou X, Wong DT, Lichtenstein A (2011) Exon 11 skipping of E-cadherin RNA downregulates its expression in head and neck cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 10(9):1751–1759. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0248
Cheng Y, Luo C, Wu W, Xie Z, Fu X, Feng Y (2016) Liver-specific deletion of srsf2 caused acute liver failure and early death in mice. Mol Cell Biol 36(11):1628–1638. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.01071-15
Luo C, Cheng Y, Liu Y et al (2017) SRSF2 regulates alternative splicing to drive hepatocellular carcinoma development. Cancer Res 77(5):1168–1178. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-1919
Listerman I, Sun J, Gazzaniga FS, Lukas JL, Blackburn EH (2013) The major reverse transcriptase-incompetent splice variant of the human telomerase protein inhibits telomerase activity but protects from apoptosis. Cancer Res 73(9):2817–2828. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3082
Ludlow AT, Wong MS, Robin JD et al (2018) NOVA1 regulates hTERT splicing and cell growth in non-small cell lung cancer. Nat Commun 9(1):3112. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05582-x
Funding
This work was supported by the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 81671054, 81771135, 91649102, 31771520).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XG, FW: Conception and design, FW, XG, YC, CZ, GC: Development of methodology, FW,YC, CZ GC: Analysis and interpretation of data, FW, YC, CZ, XG: Writing, review and revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Cheng, Y., Zhang, C. et al. A novel antisense oligonucleotide anchored on the intronic splicing enhancer of hTERT pre-mRNA inhibits telomerase activity and induces apoptosis in glioma cells. J Neurooncol 143, 57–68 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03150-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03150-x