Abstract
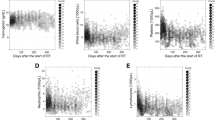
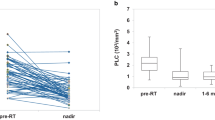
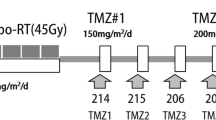
Prolonged severe lymphopenia has been shown to persist beyond a year in glioma patients after radiation therapy (RT) with concurrent and adjuvant chemotherapy. This study examines the differential impact of concurrent versus adjuvant chemotherapy on lymphopenia after RT. WHO grade II–III glioma patients who received RT with concurrent and/or adjuvant chemotherapy from 2007 to 2016 were retrospectively analyzed. Concurrent chemotherapy was temozolomide (TMZ), and adjuvant chemotherapy was either TMZ or procarbazine/lomustine/vincristine (PCV). Absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) was analyzed at baseline, 1.5, 3, 6, and 12 months after the start of RT. Univariable and multivariable logistic regression were used to identify the clinical variables in predicting acute or late lymphopenia. There were 151 patients with evaluable ALC: 91 received concurrent and adjuvant TMZ (CRT + ADJ), 32 received only concurrent TMZ (CRT), and 28 received only adjuvant TMZ or PCV (ADJ). There were 9 (10%) versus 6 (19%) versus 0 (0%) cases of grade 3 lymphopenia (ALC < 500/mm3) at 6 weeks and 4 (6%) versus 0 (0%) versus 3 (17%) cases at 12 months in CRT + ADJ, CRT and ADJ groups, respectively. On multivariable analyses, concurrent chemotherapy (odds ratio [OR] 72.3, p < 0.001), female sex (OR 10.8, p < 0.001), and older age (OR 1.06, p = 0.002) were the most significant predictors for any grade ≥ 1 lymphopenia (ALC < 1000/mm3) at 1.5 months. Older age (OR 1.08, p = 0.02) and duration of adjuvant chemotherapy (OR 1.19, p = 0.003) were significantly associated with grade ≥ 1 lymphopenia at 12 months. Thus, concurrent chemotherapy appears as the dominant contributor to the severity of acute lymphopenia after RT in WHO grade II–III glioma patients, and duration of adjuvant chemotherapy appears as the key factor to prolonged lymphopenia.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stupp R, WP Mason MJ van den (2005) B et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. New Engl J Med 352(10):987–996
Cairncross G, Wang M, Shaw E, Jenkins R, Brachman D, Buckner J et al (2013) Phase III trial of chemoradiotherapy for anaplastic oligodendroglioma: long-term results of RTOG 9402. J Clin Oncol 31(3):337–343
Wick W, Roth P, Hartmann C, Hau P, Nakamura M, Stockhammer F et al (2016) Long-term analysis of the NOA-04 randomized phase III trial of sequential radiochemotherapy of anaplastic glioma with PCV or temozolomide. Neuro-Oncology 18(11):1529–1537
Buckner JC, Shaw EG, Pugh SL, Chakravarti A, Gilbert MR, Barger GR et al (2016) Radiation plus Procarbazine, CCNU, and vincristine in low-grade glioma. New Engl J Med 374(14):1344–1355. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1500925
Hughes MA, Parisi M, Grossman S, Kleinberg L (2005) Primary brain tumors treated with steroids and radiotherapy: low CD4 counts and risk of infection. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 62(5):1423–1426
Grossman SA, Ye X, Lesser G, Sloan A, Carraway H, Desideri S et al (2011) Immunosuppression in patients with high-grade gliomas treated with radiation and temozolomide. Clin Cancer Res 17(16):5473–5480
Mendez JS, Govindan A, Leong J, Gao F, Huang J, Campian JL (2016) Association between treatment-related lymphopenia and overall survival in elderly patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 127(2):329–335
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC et al (2009) Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol 10(5):459–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70025-7
Speirs CK, Simpson JR, Robinson CG, Dewees TA, Tran DD, Linette G et al (2015) Impact of 1p/19q codeletion and histology on outcomes of Anaplastic gliomas treated with radiation therapy and temozolomide. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 91(2):268–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.10.027
Ryken TC, Parney I, Buatti J, Kalkanis SN, Olson JJ (2015) The role of radiotherapy in the management of patients with diffuse low grade glioma: a systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J Neurooncol 125(3):551–583
Delgado-López PD, Corrales-García EM, Martino J, Lastra-Aras E, Dueñas-Polo MT (2017) Diffuse low-grade glioma: a review on the new molecular classification, natural history and current management strategies. Clin Transl Oncol https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-017-1631-4
van den Bent MJ, Baumert B, Erridge SC, Vogelbaum MA, Nowak AK, Sanson M et al. (2017) Interim results from the CATNON trial (EORTC Study 26053–22054) of treatment with concurrent and adjuvant temozolomide for 1p/19q non-co-deleted anaplastic glioma: a phase 3, randomised, open-label intergroup study. Lancet. 6736(17):1–9. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0140673617314423
Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK et al (2016) The 2016 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Acta Neuropathol 131(6):803–820
Contreras J, Zhao T, Perkins S, Sun B, Goddu S, Mutic S et al (2016) The world’s first single-room proton therapy facility: two-year experience. Pract Radiat Oncol 7(1):e71–e76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prro.2016.07.003
Wong ET, Lok E, Gautam S, Swanson KD (2015) Dexamethasone exerts profound immunologic interference on treatment efficacy for recurrent glioblastoma. Br J Cancer 113(2):232–241. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2015.238
Huang J, Dewees TA, Badiyan SN, Speirs CK, Mullen DF, Fergus S et al (2015) Clinical and dosimetric predictors of acute severe lymphopenia during radiation therapy and concurrent temozolomide for high-grade glioma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 92(5):1000–1007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.04.005
Gupta T, Mohanty S, Moiyadi A, Jalali R (2013) Factors predicting temozolomide induced clinically significant acute hematologic toxicity in patients with high-grade gliomas: a clinical audit. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115:1814–1819
Armstrong TS, Cao Y, Scheurer ME, Vera-Bolanos E, Manning R, Okcu MF et al (2009) Risk analysis of severe myelotoxicity with temozolomide: the effects of clinical and genetic factors. Neuro Oncol 11(6):825–832. https://doi.org/10.1215/15228517-2008-120
Anderson GD (2008) Gender differences in pharmacological response. Int Rev Neurobiol 83:1–10
Sansoni P, Cossarizza A, Brianti V, Fagnoni F, Snelli G, Monti D et al (1993) Lymphocyte subsets and natural killer cell activity in healthy old people and centenarians. Blood 82(9):2767–2773. http://www.bloodjournal.org/content/82/9/2767.long?sso-checked=true
Perng P, Lim M (2015) Immunosuppressive mechanisms of malignant gliomas: parallels at non-CNS sites. Front Oncol 5:153. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2015.00153/full
Perry JR, Laperriere N, O’Callaghan CJ, Brandes AA, Menten J, Phillips C et al (2017) Short-course radiation plus temozolomide in elderly patients with glioblastoma. New Engl J Med 376(11):1027–1037. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1611977
Kleinberg L, Grossman S, Piantadosi S, Zeltzman M, Wharam M (1999) The effects of sequential versus concurrent chemotherapy and radiotherapy on survival and toxicity in patients with newly diagnosed high-grade astrocytoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 44(3):535–543
Yovino S, Kleinberg L, Grossman SA, Narayanan M, Ford E (2013) The etiology of treatment-related lymphopenia in patients with malignant gliomas: modeling radiation dose to circulating lymphocytes explains clinical observations and suggests methods of modifying the impact of radiation on immune cells. Cancer Invest 31(2):140–144. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.3109/07357907.2012.762780?journalCode=icnv20
MacLennan IC, Kay HE (1978) Working Party on Leukemia in Childhood. Analysis of treatment in childhood leukemia. IV. The critical association between dose fractionation and immunosuppression induced by cranial irradiation. Cancer 41:108–111
Su YB, Sohn S, Krown SE, Livingston PO, Wolchok JD, Quinn C et al (2004) Selective CD4+ lymphopenia in melanoma patients treated with temozolomide: a toxicity with therapeutic implications. J Clin Oncol 22(4):610–616
Baumert BG, Hegi ME, van den Bent MJ, von Deimling A, Gorlia T, Hoang-Xuan K et al (2016) Temozolomide chemotherapy versus radiotherapy in high-risk low-grade glioma (EORTC 22033–26033): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 intergroup study. Lancet Oncol 17(11):1521–1532
Fisher BJ, Hu C, Macdonald DR, Lesser G, Coons S, Brachman DG et al (2015) Phase 2 study of temozolomide-based chemoradiation therapy for high-risk low-grade Gliomas: Preliminary Results of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group 0424. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 91(3):497–504
Blumenthal DT, Gorlia T, Gilbert MR, Kim MM, Burt Nabors L, Mason WP et al (2017) Is more better? the impact of extended adjuvant temozolomide in newly diagnosed glioblastoma: a secondary analysis of EORTC and NRG Oncology/RTOG. Neuro Oncol 19(8):1119–1126
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We have no conflict of interests to disclose for this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, A.J., Campian, J.L., Hui, C. et al. Impact of concurrent versus adjuvant chemotherapy on the severity and duration of lymphopenia in glioma patients treated with radiation therapy. J Neurooncol 136, 403–411 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-017-2668-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-017-2668-5