Abstract
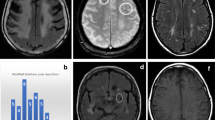
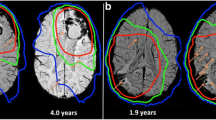
Post-radiation leukoencephalopathy is characterized by cognitive impairment and white matter alternations on imaging. Cerebral small vessel disease (SVD) is one of several suggested etiologies. Cerebral microinfarction (CMI) is a recently described marker of SVD. We sought to examine the rate of CMI as a biomarker of ongoing ischemia among patients who underwent brain radiotherapy (RT). 110 patients treated with RT for primary or metastatic brain tumors were enrolled. A total of 685 brain MRI tests performed 1–108 months post-radiation were examined. The annual incidence of CMI was calculated. Only 2 definite CMI were found (2/685, 0.3 %). The calculated annual incidence of CMI was 0.11. This incidence is similar to the normal population, and lower than the reported incidence in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage or cognitive impairment. CMI incidence in patients treated with brain RT is similar to the general population. This finding suggests that post-radiation leukoencephalopathy and cognitive impairment are not due to active SVD solely but rather secondary to other causes such as inflammation, metabolic or direct cell damage.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soussain C, Ricard D, Fike JR, Mazeron JJ, Psimaras D, Delattre JY (2009) CNS complications of radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Lancet 374:1639–1651
Conill C, Berenguer J, Vargas M, Lopez-Soriano A, Valduvieco I, Marruecos J, Vilella R (2007) Incidence of radiation-induced leukoencephalopathy after whole brain radiotherapy in patients with brain metastases. Clin Transl Oncol 9:590–595
Warrington JP, Ashpole N, Csiszar A, Woo-Lee Y, Ungvari Z, Sonntag W (2013) Whole brain radiation-induced vascular cognitive impairment: mechanisms and implications. J Vasc Res 50(6):445–457
Greene-Schloesser D, Robbins ME (2012) Radiation-induced cognitive impairment-from bench to bedside. Neuro Oncol 14:iv37–iv44
Armstrong CL, Gyato K, Awadalla AW, Lustig R, Tochner ZA (2004) A critical review of the clinical effects of therapeutic irradiation damage to the brain: the roots of controversy. Neuropsychol Rev 14(1):65–84
Wardlaw JM, Smith EE, Biessels GJ, Cordonnier C, Fazekas F, Frayne R et al (2013) Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol 12(8):822–838
Auriel E, Edlow BL, Reijmer YD, Fotiadis P, Ramirez-Martinez S, Ni J et al (2014) Microinfarct disruption of white matter structure A longitudinal diffusion tensor analysis. Neurology 83(2):182–188
Auriel E, Westover MB, Bianchi MT, Reijmer Y, Martinez-Ramirez S, Ni J et al (2015) Estimating total cerebral microinfarct burden from diffusion-weighted imaging. Stroke 46:2129–2135
Shoamanesh A, Catanese L, Sakai O, Pikula A, Kase CS (2013) Diffusion-weighted imaging hyperintensities in intracerebral hemorrhage: microinfarcts or microbleeds? Ann Neurol 73(6):795–796
Kimberly WT, Glison A, Rost NA, Rosand J, Viswanathan A, Smith EE et al (2009) Silent ischemic infarcts are associated with hemorrhage burden in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Neurology 72:1230–1235
Auriel E, Gurol ME, Ayres A, Dumas AP, Schwab KB, Vashkwvich A et al (2012) Characteristic distributions of intracerebral hemorrhage-associated diffusion-weighted lesions. Neurology 79:2335–2341
Wernicke AG, Smith AW, Taube S, Mehta MP (2016) Glioblastoma: radiation treatment margins, how small is large enough? Pract Radiat Oncol 6(5):298–305
Batool S, O’Donnell M, Sharma M, Islam S, Dagenais GR, Poirier P et al (2014) Incidental Magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted imaging–positive lesions are rare in neurologically asymptomatic community-dwelling adults. Stroke 45:2115–2117
Zuo PY, Chen XL, Liu YW, Xiao CL, Liu CY (2014) Increased risk of cerebrovascular events in patients with cancer treated with bevacizumab: a meta-analysis. PLoS One 9(7):e102484
Plummer C, Henderson RD, O’Sullivan JD, Read SJ (2011) Ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack after head and neck radiotherapy a review. Stroke 42:2410–2418
Gujral DM, Chahal N, Senior R et al (2014) Radiation-induced carotid artery atherosclerosis. Radiother Oncol 110:31–38
Murphy ES, Xie H, Merchant TE, Yu JS, Chao ST, Suh JH (2015) Review of cranial radiotherapy-induced vasculopathy. J Neurooncol 122:421–429
Lupo JM, Chuang CF, Chang SM, Barani IJ, Jimenez B, Hess CP, Nelson SJ (2012) 7 T susceptibility-weighted imaging to assess the effects of radiation therapy on normal appearing brain in patients with glioma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82(3):e493–e500
Pantoni L (2010) Cerebral small vessel disease: from pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol 9:689–701
Reijmer YD, van Veluw SJ, Greenberg SM (2016) Ischemic brain injury in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36(1):40–54
Rosso C, Drier A, Lacroix D, Mutlu G, Pires C, Lehéricy S et al (2010) Diffusion-weighted MRI in acute stroke within the first 6 h: 1.5 or 3.0 Tesla? Neurology 74(24):1946–1953
van Veluw SJ, Zwanenburg JJ, Rozemuller AJ, Luijten PR, Spliet WG, Biessels GJ (2015) The spectrum of MR detectable cortical microinfarcts: a classification study with 7-tesla postmortem MRI and histopathology. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 35(4):676–683
van Veluw SJ, Hilal S, Kuijf HJ, Ikram MK, Xin X, Yeow TB et al (2015) Cortical microinfarcts on 3 T MRI: clinical correlates in memory-clinic patients. Alzheimers Dement 11(12):1500–1509
Acknowledgments
We thank Nathan Shtraus, MSc, physicist and Chief of Radiation Services, and Ben W. Corn, MD Professor and Chair of the Institute of Radiotherapy at the Tel-Aviv Medical Center, for their assistance in dose calculations for this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J. A. Molad and D. T. Blumenthal have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molad, J.A., Blumenthal, D.T., Bokstein, F. et al. Mechanisms of post-radiation injury: cerebral microinfarction not a significant factor. J Neurooncol 131, 277–281 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2291-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2291-x