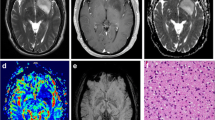
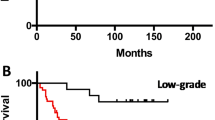
Abstract
The aim of this study was to assess whether combining multimodal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with the determination of the 1p/19q codeletion status could improve the ability to predict anaplastic transformation in low-grade oligodendrogliomas. Twenty patients with grade II oligodendrogliomas were followed-up using multimodal MR [proton MR spectroscopy (MRS), perfusion, and conventional MR imaging]. All patients diagnoses were histologically proven, and 1p/19q codeletion status was analyzed for all patients. Median follow-up was 30.5 ± 11.4 months. Anaplastic transformation was observed in six patients. The only MRI feature that was associated with anaplastic transformation was an elevation of the choline/creatine ratio >2.4 which was observed in 4 out of 6 patients with anaplastic transformation versus 1 out of 14 patients without anaplastic transformation. In patients without 1p/19q codeletion, an elevation of the choline/creatine ratio >2.4 was associated with the occurrence of anaplastic transformation in all cases (4 out of 4 patients), with a mean time of 12 months. In contrast, in patients with a 1p/19q codeletion, no anaplastic transformation was observed in the patient who had an elevation of >2.4 of the choline/creatine ratio and two patients demonstrated an anaplastic transformation without any elevation of this ratio.Prospective validation in a larger series is needed, yet the present study suggests that combining data from in vivo proton MRS and genetic analysis could be a promising strategy to predict time to anaplastic transformation at the individual level in patients with low-grade oligodendrogliomas and may help deciding when chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy should be initiated in these tumors.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Walker DG, Kaye AH (2003) Low-grade glial neoplasms. J ClinNeurosci 10:1–13
Forst DA, Nahed BV, Loeffler JS, Batchelor TT (2014) Low-GradeGliomas. Oncologist 19(4):403–413
Duffau H, Lopes M, Arthuis F, Bitar A, Sichez JP, Van Effenterre R et al (2005) Contribution of intraoperative electrical stimulations in surgery oflow-grade gliomas: a comparative study between two series without(1985-1996) and with (1996-2003) functional mapping in the sameinstitution. J NeurolNeurosurg Psychiatry 76:845–851
Abeloos L, Brotchi J, De Witte O (2007) Management of low-gradeglioma: a retrospective study concerning 201 patients. Neurochirurgie 53:277–283
Claus EB, Horlacher A, Hsu L, Schwartz RB, Dello-Iacono D, Talos F et al (2005) Survival rates in patients with low-grade gliomaafterintraoperative magnetic resonance image guidance. Cancer 103:1227–1233
Smith JS, Chang EF, Lamborn KR, Chang SM, Prados MD, Cha S et al (2008) Role of extent of resection in the long-term outcome oflow-grade hemispheric gliomas. J ClinOncol 26:1338–1345
McGirt MJ, Chaichana KL, Attenello FJ, Weingart JD, Than K, Burger PC et al (2008) Extent of surgical resection is independently associatedwith survival in patients with hemispheric infiltrating lowgradegliomas. Neurosurgery 63:700–707 author reply 707-8
Chang EF, Potts MB, Keles GE, Lamborn KR, Chang SM, Barbaro NM et al (2008) Seizure characteristics and control followingresection in 332 patients with low-grade gliomas. J Neurosurg 108:227–235
Karim AB, Afra D, Cornu P, Bleehan N, Schraub S, De Witte O et al (2002) Randomised trial on the efficacy of radiotherapy for cerebrallow-grade glioma in the adult: European Organization for Researchand Treatment of Cancer Study 22845 with the Medical ResearchCouncil study BRO4: an interim analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 52:316–324
van den Bent MJ, Afra D, de Witte O, Ben Hassel M, Schraub S, Hoang-Xuan K et al (2005) Long-term efficacy of early versus delayedradiotherapy for low-grade astrocytoma and oligodendrogliomainadults: the EORTC 22845 randomised trial. Lancet 366:985–990
Shaw E, Arusell R, Scheithauer B, O’Fallon J, O’Neill B, Dinapoli R et al (2002) Prospective randomized trial of low- versus highdoseradiation therapy in adults with supratentorial low-gradeglioma: initial report of a North Central Cancer Treatment Group/Radiation Therapy Oncology Group/Eastern Cooperative OncologyGroup study. J ClinOncol 20:2267–2276
Hoang-Xuan K, Capelle L, Kujas M, Taillibert S, Duffau H, Lejeune J et al (2004) Temozolomide as initial treatment for adultswithlow-grade oligodendrogliomas or oligoastrocytomas and correlationwith chromosome 1p deletions. J ClinOncol 22:3133–3138
Buckner JC, GesmeJr D, O’Fallon JR, Hammack JE, Stafford S, Brown PD et al (2003) Phase II trial of procarbazine, lomustineandvincristine as initial therapy for patients with low-grade oligodendrogliomaoroligoastrocytoma: efficacy and associations with chromosomal abnormalities. J ClinOncol 21:251–255
Mason WP, Krol GS, DeAngelis LM (1996) Low-grade oligodendrogliomaresponds to chemotherapy. Neurology 46:203–207
Armstrong CL, Hunter JV, Ledakis GE, Cohen B, Tallent EM, Goldstein BH et al (2002) Late cognitive and radiographic changes relatedto radiotherapy: initial prospective findings. Neurology 59:40–48
Klein M, Heimans JJ, Aaronson NK, van der Ploeg HM, Grit J, Muller M et al (2002) Effect of radiotherapy and other treatment-relatedfactors on mid-term to long-term cognitive sequelae in low-gradegliomas: a comparative study. Lancet 360:1361–1368
Brown PD, Buckner JC, O’Fallon JR, Iturria NL, Brown CA, O’Neill BP et al (2003) Effects of radiotherapy on cognitive function inpatients with low-grade glioma measured by the folsteinminimentalstate examination. J ClinOncol 21:2519–2524
Taphoorn MJ, Klein M (2004) Cognitive deficits in adult patientswithbrain tumors. Lancet Neurol 3:159–168
Laack NN, Brown PD, Ivnik RJ, Furth AF, Ballman KV, Hammack JE et al (2005) Cognitive function after radiotherapy forsupratentorial low-grade glioma: a North Central Cancer TreatmentGroup prospective study. Int J RadiatOncolBiolPhys 63:1175–1183
Douw L, Klein M, Fagel SS, van den Heuvel J, Taphoorn MJ, Aaronson NK et al (2009) Cognitive and radiological effects of radiotherapyin patients with low-grade glioma: long-term follow-up. Lancet Neurol 8:810–818
Bleeker FE, Lamba S, Leenstra S, Troost D, Vandertop WP, Hulsebos T et al (2009) IDH1 mutations at residue p. R132 (IDH1(R132)) occur frequently in high-grade gliomas but not in othersolid tumors. Hum Mutat 30:7–11
Yan H, Parsons DW, Jin G, McLendon R, Rasheed BA, Yuan W et al (2009) IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in gliomas. NEngl J Med 360:765–773
Balss J, Meyer J, Mueller W, Korshunov A, Hartmann C, vonDeimling A (2008) Analysis of the IDH1 codon132 mutation in braintumors. Acta Neuropathol 116:597–602
Reifenberger J, Reifenberger G, Liu L, James CD, Wechsler W, Collins VP (1994) Olecular genetic analysis of oligodendroglialtumorsshows preferential allelic deletions on 19q and 1p. Am J Pathol 145:1175–1190
Benetkiewicz M, Idbaih A, Cousin PY, Boisselier B, Marie Y, Criniere E et al (2009) NOTCH2 is neither rearranged nor mutated in t(1;19) positive oligodendrogliomas. PLoS ONE 4(e4107):28
Cairncross JG, Ueki K, Zlatescu MC, Lisle DK, Finkelstein DM, Hammond RR et al (1998) Specific genetic predictors of chemotherapeuticresponse and survival in patients with anaplastic oligodendrogliomas. J Natl Cancer Inst 90:1473–1479
Cairncross G, Berkey B, Shaw E, Jenkins R, Scheithauer v, Brachman D et al (2006) Phase III trial of chemotherapy plus radiotherapycompared with radiotherapy alone for pure and mixed anaplasticoligodendroglioma: intergroup Radiation Therapy Oncology GroupTrial 9402. J ClinOncol 24:2707–2714
van den Bent MJ, Carpentier AF, Brandes AA, Sanson M, Taphoorn MJ, Bernsen HJ et al (2006) Adjuvant procarbazine, lomustineand vincristine improves progression-free survival but not overallsurvival in newly diagnosed anaplastic oligodendrogliomas and oligoastrocytomas:arandomised European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer phase III trial. J ClinOncol 24:2715–2722
Hartmann C, Hentschel B, Tatagiba M, Schramm J, Schnell O, Seidel C, Stein R, Reifenberger G, Pietsch T, von Deimling A, Loeffler M, Weller M (2011) German Glioma Network. Molecular markers in low-grade gliomas: predictive or prognostic? Clin Cancer Res 17(13):4588–4599
Rollin N, Guyotat J, Streichenberger N, Honnorat J, Tran Minh VA, Cotton F (2006) Clinical relevance of diffusion and perfusion magnetic resonance imaging in assessing intra-axial brain tumors. Neuroradiology 48(3):150–159
Sugahara T, Korogi Y, Kochi M, Ikushima I, Hirai T, Okuda T, Shigematsu Y, Liang L, Ge Y, Ushio Y, Takahashi M (1998) Correlation of MR imaging-determined cerebral blood volumemaps with histologic and angiographic determination of vascularityofgliomas. AJR Am J Roentgenol 171:1479–1486
Danchaivijitr N, Waldman AD, Tozer DJ, Benton CE, BrasilCaseiras G, Tofts PS, Rees JH, Jager HR (2008) Low-gradegliomas: do changes in rCBV measurements at longitudinalperfusion-weighted MR imaging predict malignant transformation? Radiology 247:170–178
McKnight TR, Lamborn KR, Love TD, Berger MS, Chang S, Dillon WP, Bollen A, Nelson SJ (2007) Correlation of magneticresonance spectroscopic and growth characteristics within GradesII and III gliomas. J Neurosurg 106:660–666
Miller BL, Chang L, Booth R, Ernst T, Cornford M, Nikas D, McBride D, Jenden DJ (1996) In vivo 1H MRS choline: correlationwith in vitro chemistry/histology. Life Sci 58:1929–193536
Nafe R, Herminghaus S, Raab P, Wagner S, Pilatus U, Schneider B, Schlote W, Zanella F, Lanfermann H (2003) Preoperativeproton-MR spectroscopy of gliomas correlation with quantitativenuclear morphology in surgical specimen. J Neurooncol 63:233–245
Gupta RK, Cloughesy TF, Sinha U, Garakian J, Lazareff J, Rubino G, Rubino L, Becker DP, Vinters HV, Alger JR (2000) Relationships between choline magnetic resonance spectroscopy, apparent diffusion coefficient and quantitative histopathology inhuman glioma. J Neurooncol 50:215–226
Urenjak J, Williams SR, Gadian DG, Noble M (1993) Protonnuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy unambiguously identifiesdifferent neural cell types. J Neurosci 13:981–989
Guillevin R, Menuel C, Taillibert S, Capelle L, Costalat R, Abud L, Habas C, De Marco G, Hoang-Xuan K, Chiras J, Vallée JN (2011) Predicting the outcome of gradeIIgliomatreated with temozolomide using protonmagneticresonancespectroscopy. Br J Cancer 104(12):1854–1861
Guillevin R, Menuel C, Abud L, Costalat R, Capelle L, Hoang-Xuan K, Habas C, Chiras J, Vallée JN (2012) Proton MR spectroscopy in predicting the increase of perfusion MR imaging for WHOgradeIIgliomas. J Magn Reson Imaging 35(3):543–550
Hlaihel C, Guilloton L, Guyotat J, Streichenberger N, Honnorat J, Cotton F (2010) Predictivevalue of multimodalityMRI using conventional, perfusion, and spectroscopyMR in anaplastictransformation of low-gradeoligodendrogliomas. J Neurooncol 97(1):73–80
Galldiks N, Stoffels G, Ruge MI, Rapp M, Sabel M, Reifenberger G, Erdem Z, Shah NJ, Fink GR, Coenen HH, Langen KJ (2013) Role of O-(2-18F-fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine PET as a diagnostic tool for detection of malignant progression in patients with low-grade glioma. J Nucl Med 54(12):2046–2054
Kaloshi G, Benouaich-Amiel A, Diakite F, Taillibert S, Lejeune J, Laigle-Donadey F, Renard MA, Iraqi W, Idbaih A, Paris S, Capelle L, Duffau H, Cornu P, Simon JM, Mokhtari K, Polivka M, Omuro A, Carpentier A, Sanson M, Delattre JY, Hoang-Xuan K (2007) Temozolomide for low-grade gliomas: predictive impact of 1p/19q loss on response and outcome. Neurology 68(21):1831–1836
Mandonnet E, Delattre JY, Tanguy ML, Swanson KR, Carpentier AF, Duffau H, Cornu P, Van Effenterre R, Alvord EC Jr, Capelle L (2003) Continuous growth of mean tumor diameter in a subset of grade II gliomas. Ann Neurol 53(4):524–528
Pallud J, Taillandier L, Capelle L, Fontaine D, Peyre M, Ducray F, Duffau H, Mandonnet E (2012) Quantitative morphological magnetic resonance imaging follow-up of low-grade glioma: a plea for systematic measurement of growth rates. Neurosurgery 71:729–739 discussion 739-40
Gupta RK, Cloughesy TF, Sinha U, Garakian J, Lazareff J, Rubino G, Rubino L, Becker DP, Vinters HV, Alger JR (2000) Relationships between choline magnetic resonance spectroscopy, apparent diffusion coefficient and quantitative histopathology in human glioma. J Neurooncol 50(3):215–226
Pallud J, Blonski M, Mandonnet E, Audureau E, Fontaine D, Sanai N, Bauchet L, Peruzzi P, Frénay M, Colin P, Guillevin R, Bernier V, Baron MH, Guyotat J, Duffau H, Taillandier L, Capelle L (2013) Velocity of tumor spontaneous expansion predicts long-term outcomes for diffuse low-grade gliomas. NeuroOncol 15(5):595–606
Lemasson B, Chenevert TL, Lawrence TS, Tsien C, Sundgren PC, Meyer CR, Junck L, Boes J, Galbán S, Rehemtulla A, Ross BD, Galbán CJ (2013) Impact of perfusion map analysis on early survival prediction accuracy in glioma patients. TranslOncol 6(6):766–774
Kunz M, Thon N, Eigenbrod S, Hartmann C, Egensperger R, Herms J, Geisler J, la Fougere C, Lutz J, Linn J, Kreth S, von Deimling A, Tonn JC, Kretzschmar HA, Pöpperl G, Kreth FW (2011) Hot spots in dynamic18FET-PET delineate malignant tumor parts within suspected WHO grade II gliomas. NeuroOncol 13(3):307–316
Wharton SB, Maltby E, Jellinek DA, Levy D, Atkey N, Hibberd S, Crimmins D, Stoeber K, Williams GH (2007) Subtypes of oligodendroglioma defined by 1p,19q deletions, differ in the proportion of apoptotic cells but not in replication-licensed non-proliferating cells. Acta Neuropathol 113(2):119–127
Acknowledgments
Dr. Stephane Sanchez (Biostatistics and Public Health Department of the Hospices Civils de Lyon) for his expertise and help on statistics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bourdillon, P., Hlaihel, C., Guyotat, J. et al. Prediction of anaplastic transformation in low-grade oligodendrogliomas based on magnetic resonance spectroscopy and 1p/19q codeletion status. J Neurooncol 122, 529–537 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1737-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1737-x