Abstract
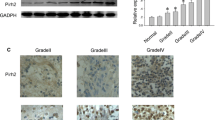
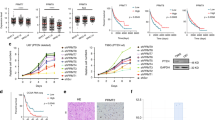
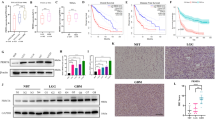
Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) catalyzes the formation of ω-NG,N′G-symmetric dimethylarginine residues on histones as well as other proteins. These modifications play an important role in cell differentiation and tumor cell growth. However, the role of PRMT5 in human glioma cells has not been characterized. In this study, we assessed protein expression profiles of PRMT5 in control brain, WHO grade II astrocytomas, anaplastic astrocytomas, and glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) by immunohistochemistry. PRMT5 was low in glial cells in control brain tissues and low grade astrocytomas. Its expression increased in parallel with malignant progression, and was highly expressed in GBM. Knockdown of PRMT5 by small hairpin RNA caused alterations of p-ERK1/2 and significantly repressed the clonogenic potential and viability of glioma cells. These findings indicate that PRMT5 is a marker of malignant progression in glioma tumors and plays a pivotal role in tumor growth.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang Y, Bedford MT (2013) Protein arginine methyltransferases and cancer. Nat Rev 13(1):37–50
Friesen WJ, Paushkin S, Wyce A et al (2001) The methylosome, a 20S complex containing JBP1 and pICln, produces dimethylarginine-modified Sm proteins. Mol Cell Biol 21(24):8289–8300
Hsu JM, Chen CT, Chou CK et al (2011) Crosstalk between Arg 1175 methylation and Tyr 1173 phosphorylation negatively modulates EGFR-mediated ERK activation. Nat Cell Biol 13(2):174–181
Jansson M, Durant ST, Cho EC et al (2008) Arginine methylation regulates the p53 response. Nat Cell Biol 10(12):1431–1439
Teng Y, Girvan AC, Casson LK et al (2007) AS1411 alters the localization of a complex containing protein arginine methyltransferase 5 and nucleolin. Cancer Res 67(21):10491–10500
Scoumanne A, Zhang J, Chen X (2009) PRMT5 is required for cell-cycle progression and p53 tumor suppressor function. Nucleic Acids Res 37(15):4965–4976
Andreu-Perez P, Esteve-Puig R, Esteve-Puig R, de Torre-Minguela C et al (2011) Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 regulates ERK1/2 signal transduction amplitude and cell fate through CRAF. Sci Signal 4(190):ra58
Pal S, Baiocchi RA, Byrd JC et al (2007) Low levels of miR-92b/96 induce PRMT5 translation and H3R8/H4R3 methylation in mantle cell lymphoma. EMBO J 26(15):3558–3569
Wang L, Pal S, Sif S (2008) Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 suppresses the transcription of the RB family of tumor suppressors in leukemia and lymphoma cells. Mol Cell Biol 28(20):6262–6277
Kim JM, Sohn HY, Yoon SY et al (2005) Identification of gastric cancer-related genes using a cDNA microarray containing novel expressed sequence tags expressed in gastric cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 11(2 Pt 1):473–482
Eckert D, Biermann K, Nettersheim D et al (2008) Expression of BLIMP1/PRMT5 and concurrent histone H2A/H4 arginine 3 dimethylation in fetal germ cells, CIS/IGCNU and germ cell tumors. BMC Dev Biol 8:106
Powers MA, Fay MM, Factor RE et al (2011) Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 accelerates tumor growth by arginine methylation of the tumor suppressor programmed cell death 4. Cancer Res 71(16):5579–5587
Bao X, Zhao S, Liu T et al (2013) Overexpression of PRMT5 promotes tumor cell growth and is associated with poor disease prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer. J Histochem Cytochem 61(3):206–217
Tanaka H, Hoshikawa Y, Oh-hara T et al (2009) PRMT5, a novel TRAIL receptor-binding protein, inhibits TRAIL-induced apoptosis via nuclear factor-kappaB activation. Mol Cancer Res 7(4):557–569
Yang M, Sun J, Sun X et al (2009) Caenorhabditis elegans protein arginine methyltransferase PRMT-5 negatively regulates DNA damage-induced apoptosis. PLoS Genet 5(6):e1000514
Aggarwal P, Vaites LP, Kim JK et al (2010) Nuclear cyclin D1/CDK4 kinase regulates CUL4 expression and triggers neoplastic growth via activation of the PRMT5 methyltransferase. Cancer Cell 18(4):329–340
Pal S, Vishwanath SN, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Sif S (2004) Human SWI/SNF-associated PRMT5 methylates histone H3 arginine 8 and negatively regulates expression of ST7 and NM23 tumor suppressor genes. Mol Cell Biol 24(21):9630–9645
Tee WW, Pardo M, Theunissen TW et al (2010) PRMT5 is essential for early mouse development and acts in the cytoplasm to maintain ES cell pluripotency. Genes Dev 24(24):2772–2777
Chittka A (2010) Dynamic distribution of histone H4 arginine 3 methylation marks in the developing murine cortex. PLoS One 5(11):e13807
Chittka A, Nitarska J, Grazini U, Richardson WD (2012) Transcription factor positive regulatory domain 4 (PRDM4) recruits protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) to mediate histone arginine methylation and control neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation. J Biol Chem 287(51):42995–43006
Jemal A, Murray T, Samuels A et al (2003) Cancer statistics, 2003. CA Cancer J Clin 53(1):5–26
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P (2005) Population-based studies on incidence, survival rates, and genetic alterations in astrocytic and oligodendroglial gliomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64(6):479–489
Tran B, Rosenthal MA (2010) Survival comparison between glioblastoma multiforme and other incurable cancers. J Clin Neurosci 17(4):417–421
Ishibashi H, Suzuki T, Suzuki S et al (2003) Sex steroid hormone receptors in human thymoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88(5):2309–2317
Robertson D, Savage K, Reis-Filho JS, Isacke CM (2008) Multiple immunofluorescence labelling of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue. BMC Cell Biol 9:13
Inai T, Mancuso M, Hashizume H et al (2004) Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling in cancer causes loss of endothelial fenestrations, regression of tumor vessels, and appearance of basement membrane ghosts. Am J Pathol 165(1):35–52
Wiederschain D, Wee S, Chen L et al (2009) Single-vector inducible lentiviral RNAi system for oncology target validation. Cell Cycle 8(3):498–504
Han X, Stewart JE Jr, Bellis SL et al (2001) TGF-beta1 up-regulates paxillin protein expression in malignant astrocytoma cells: requirement for a fibronectin substrate. Oncogene 20(55):7976–7986
Karkhanis V, Hu YJ, Baiocchi RA et al (2011) Versatility of PRMT5-induced methylation in growth control and development. Trends Biochem Sci 36(12):633–641
Lee JH, Cook JR, Yang ZH et al (2005) PRMT7, a new protein arginine methyltransferase that synthesizes symmetric dimethylarginine. J Biol Chem 280(5):3656–3664
Zhao Q, Rank G, Tan YT et al (2009) PRMT5-mediated methylation of histone H4R3 recruits DNMT3A, coupling histone and DNA methylation in gene silencing. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16(3):304–311
Ancelin K, Lange UC, Hajkova P et al (2006) Blimp1 associates with Prmt5 and directs histone arginine methylation in mouse germ cells. Nat Cell Biol 8(6):623–630
Bedford MT, Clarke SG (2009) Protein arginine methylation in mammals: who, what, and why. Mol Cell 33(1):1–13
Huang J, Vogel G, Yu Z, Almazan G, Richard S (2011) Type II arginine methyltransferase PRMT5 regulates gene expression of inhibitors of differentiation/DNA binding Id2 and Id4 during glial cell differentiation. J Biol Chem 286(52):44424–44432
Friedmann-Morvinski D, Bushong EA, Ke E et al (2012) Dedifferentiation of neurons and astrocytes by oncogenes can induce gliomas in mice. Science 338(6110):1080–1084
Dunn GP, Rinne ML, Wykosky J et al (2012) Emerging insights into the molecular and cellular basis of glioblastoma. Genes Dev 26(8):756–784
Verhaak RG, Hoadley KA, Purdom E et al (2010) Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell 17(1):98–110
Krakstad C, Chekenya M (2010) Survival signalling and apoptosis resistance in glioblastomas: opportunities for targeted therapeutics. Mol Cancer 9:135
Marshall CJ (1995) Specificity of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling: transient versus sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Cell 80(2):179–185
Olsen BB, Svenstrup TH, Guerra B (2012) Downregulation of protein kinase CK2 induces autophagic cell death through modulation of the mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways in human glioblastoma cells. Int J Oncol 41(6):1967–1976
Pang L, Sawada T, Decker SJ, Saltiel AR (1995) Inhibition of MAP kinase kinase blocks the differentiation of PC-12 cells induced by nerve growth factor. J Biol Chem 270(23):13585–13588
Ravi RK, Weber E, McMahon M et al (1998) Activated Raf-1 causes growth arrest in human small cell lung cancer cells. J Clin Investig 101(1):153–159
Cho EC, Zheng S, Munro S et al (2012) Arginine methylation controls growth regulation by E2F-1. EMBO J 31(7):1785–1797
Acknowledgments
NIH NCI Grants P30CA013148 (UAB Comprehensive Cancer Center Core Support Grant); P50CA097247, P20CA151129 (G. Y. Gillespie); St. Baldrick’s Foundation (G. K. Friedman); VA Merit Review (P. H. King).
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has a conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, X., Li, R., Zhang, W. et al. Expression of PRMT5 correlates with malignant grade in gliomas and plays a pivotal role in tumor growth in vitro. J Neurooncol 118, 61–72 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1419-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1419-0