Abstract
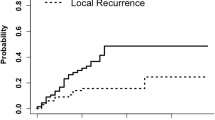
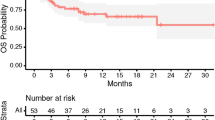
Following surgical resection for brain metastases, fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (FSRT) has been used as an alternative to single dose treatment for large cavities and to reduce risks of late toxicity. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the outcomes of patients treated with FSRT to the post-operative bed for both radioresistant and radiosensitive brain metastases. Between December 2009 and May 2013 a total of 65 patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases were treated with resection followed by FSRT. Patients were treated to a total dose of 20–30 Gy in five fractions. Median planning target volume (PTV) was 16.88 cm3 (range 4.87–128.43 cm3). The median follow-up for all patients was 8.5 months (range 1.1–28.6 months) with a median of 12.9 months for living patients. One and two year Kaplan–Meier estimates of local control were 87.0 and 70.0 %, respectively. Local control at 1 year was 85.6 and 88.0 % for radioresistant and radiosensitive tumors, respectively (p = 0.44). A PTV ≥17 cm3, was associated with local failure, HR 8.63 ((1.44–164.78); p = 0.02). One and two year distant control rates were 50.9 and 46.2 %, respectively with six patients (9.2 %) experiencing leptomeningeal disease. OS rates at 1 and 2 years were 65.2 and 47.5 %, respectively. Survival was significantly associated with recursive partitioning analysis class (p = 0.001) and graded prognostic assessment score (p = 0.005). One case of radionecrosis was noted on follow-up imaging. FSRT in five fractions offers excellent local control in both radiosensitive and radioresistant tumors with minimal toxicity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Regine WF, Dempsey RJ, Mohiuddin M, Kryscio RJ, Markesbery WR, Foon KA, Young B (1998) Postoperative radiotherapy in the treatment of single metastases to the brain: a randomized trial. JAMA, J Am Med Assoc 280:1485–1489
Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Walsh JW, Dempsey RJ, Maruyama Y, Kryscio RJ, Markesbery WR, Macdonald JS, Young B (1990) A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastases to the brain. N Engl J Med 322:494–500. doi:10.1056/NEJM199002223220802
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U, Villa S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG, Fariselli L, Tzuk-Shina T, Kortmann RD, Carrie C, Ben Hassel M, Kouri M, Valeinis E, van den Berge D, Collette S, Collette L, Mueller RP (2011) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952-26001 study. J Clin Oncol 29:134–141. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.30.1655
Crossen JR, Garwood D, Glatstein E, Neuwelt EA (1994) Neurobehavioral sequelae of cranial irradiation in adults: a review of radiation-induced encephalopathy. J Clin Oncol 12:627–642
Sun A, Bae K, Gore EM, Movsas B, Wong SJ, Meyers CA, Bonner JA, Schild SE, Gaspar LE, Bogart JA, Werner-Wasik M, Choy H (2011) Phase III trial of prophylactic cranial irradiation compared with observation in patients with locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: neurocognitive and quality-of-life analysis. J Clin Oncol 29:279–286. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.29.6053
Shaw E, Scott C, Souhami L, Dinapoli R, Kline R, Loeffler J, Farnan N (2000) Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90-05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:291–298
Bhatnagar AK, Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery for four or more intracranial metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64:898–903. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.08.035
Eaton BR, Gebhardt B, Prabhu R, Shu HK, Curran WJ Jr, Crocker I (2013) Hypofractionated radiosurgery for intact or resected brain metastases: defining the optimal dose and fractionation. Radiat Oncol 8:135. doi:10.1186/1748-717X-8-135
Kelly PJ, Lin YB, Yu AY, Alexander BM, Hacker F, Marcus KJ, Weiss SE (2012) Stereotactic irradiation of the postoperative resection cavity for brain metastasis: a frameless linear accelerator-based case series and review of the technique. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82:95–101. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.10.043
Prabhu R, Shu HK, Hadjipanayis C, Dhabaan A, Hall W, Raore B, Olson J, Curran W, Oyesiku N, Crocker I (2012) Current dosing paradigm for stereotactic radiosurgery alone after surgical resection of brain metastases needs to be optimized for improved local control. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83:e61–e66. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.12.017
Soltys SG, Adler JR, Lipani JD, Jackson PS, Choi CY, Puataweepong P, White S, Gibbs IC, Chang SD (2008) Stereotactic radiosurgery of the postoperative resection cavity for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 70:187–193. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.06.068
Minniti G, Esposito V, Clarke E, Scaringi C, Lanzetta G, Salvati M, Raco A, Bozzao A, Maurizi Enrici R (2013) Multidose stereotactic radiosurgery (9 Gy ×3) of the postoperative resection cavity for treatment of large brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 86:623–629. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.03.037
Wen PY, Loeffler JS (1999) Management of brain metastases. Oncology 13:941–954–957–961 discussion 961–942, 949
Choi CY, Chang SD, Gibbs IC, Adler JR, Harsh GRt, Atalar B, Lieberson RE, Soltys SG (2012) What is the optimal treatment of large brain metastases? An argument for a multidisciplinary approach. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 84:688–693. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.01.028
Jagannathan J, Yen CP, Ray DK, Schlesinger D, Oskouian RJ, Pouratian N, Shaffrey ME, Larner J, Sheehan JP (2009) Gamma Knife radiosurgery to the surgical cavity following resection of brain metastases. J Neurosurg 111:431–438. doi:10.3171/2008.11.JNS08818
Blonigen BJ, Steinmetz RD, Levin L, Lamba MA, Warnick RE, Breneman JC (2010) Irradiated volume as a predictor of brain radionecrosis after linear accelerator stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77:996–1001. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.06.006
McPherson CM, Suki D, Feiz-Erfan I, Mahajan A, Chang E, Sawaya R, Lang FF (2010) Adjuvant whole-brain radiation therapy after surgical resection of single brain metastases. Neuro-oncology 12:711–719. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noq005
Selek U, Chang EL, Hassenbusch SJ 3rd, Shiu AS, Lang FF, Allen P, Weinberg J, Sawaya R, Maor MH (2004) Stereotactic radiosurgical treatment in 103 patients for 153 cerebral melanoma metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59:1097–1106. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.12.037
Manon R, O’Neill A, Knisely J, Werner-Wasik M, Lazarus HM, Wagner H, Gilbert M, Mehta M, Eastern Cooperative Oncology G (2005) Phase II trial of radiosurgery for one to three newly diagnosed brain metastases from renal cell carcinoma, melanoma, and sarcoma: an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group study (E 6397). J Clin Oncol 23:8870–8876. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.01.8747
Han JH, Kim DG, Chung HT, Paek SH, Park CK, Jung HW (2012) Radiosurgery for large brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83:113–120. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.06.1965
Atalar B, Modlin LA, Choi CY, Adler JR, Gibbs IC, Chang SD, Harsh GRt, Li G, Nagpal S, Hanlon A, Soltys SG (2013) Risk of leptomeningeal disease in patients treated with stereotactic radiosurgery targeting the postoperative resection cavity for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.07.034
Hashimoto K, Narita Y, Miyakita Y, Ohno M, Sumi M, Mayahara H, Kayama T, Shibui S (2011) Comparison of clinical outcomes of surgery followed by local brain radiotherapy and surgery followed by whole brain radiotherapy in patients with single brain metastasis: single-center retrospective analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81:e475–e480. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.02.016
Jensen CA, Chan MD, McCoy TP, Bourland JD, de Guzman AF, Ellis TL, Ekstrand KE, McMullen KP, Munley MT, Shaw EG, Urbanic JJ, Tatter SB (2011) Cavity-directed radiosurgery as adjuvant therapy after resection of a brain metastasis. J Neurosurg 114:1585–1591. doi:10.3171/2010.11.JNS10939
Robbins JR, Ryu S, Kalkanis S, Cogan C, Rock J, Movsas B, Kim JH, Rosenblum M (2012) Radiosurgery to the surgical cavity as adjuvant therapy for resected brain metastasis. Neurosurgery 71:937–943. doi:10.1227/NEU.0b013e31826909f2
Jo KI, Lim DH, Kim ST, Im YS, Kong DS, Seol HJ, Nam DH, Lee JI (2012) Leptomeningeal seeding in patients with brain metastases treated by gamma knife radiosurgery. J Neurooncol 109:293–299. doi:10.1007/s11060-012-0892-6
Siomin VE, Vogelbaum MA, Kanner AA, Lee SY, Suh JH, Barnett GH (2004) Posterior fossa metastases: risk of leptomeningeal disease when treated with stereotactic radiosurgery compared to surgery. J Neurooncol 67:115–121
Narayana A, Chang J, Yenice K, Chan K, Lymberis S, Brennan C, Gutin PH (2007) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy using intensity-modulated radiotherapy in patients with one or two brain metastases. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 85:82–87. doi:10.1159/000097923
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, K.A., Freilich, J.M., Abuodeh, Y. et al. Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy to the post-operative cavity for radioresistant and radiosensitive brain metastases. J Neurooncol 118, 179–186 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1417-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1417-2