Abstract
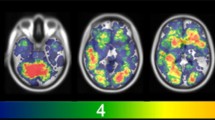
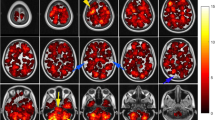
The frequency of the diagnosis of brain metastases has increased in recent years, probably due to an increased diagnostic sensitivity. Site predilection of brain lesions in oncological patients at the time of onset, may suggest mechanisms of brain-specific vulnerability to metastasis. The aim of the study is to determine the spatial distribution of intra-axial brain metastases by using voxel-wise statistics in breast and lung cancer patients. For this retrospective cross-sectional study, clinical data and MR imaging of 864 metastases at first diagnosis in 114 consecutive advanced cancer patients from 2006 to 2011 were included. Axial post-gadolinium T1 weighted images were registered to a standard template. Binary lesion masks were created after segmentation of volumes of interest. The voxel-based lesion-symptom mapping approach was used to calculate a t statistic describing the differences between groups. It was found that the lesions were more likely to be located in the parieto-occipital lobes and cerebellum for the total cohort and for the non small cell lung cancer group, and in the cerebellum for the breast cancer group. The voxel-wise inter-group comparisons showed the largest significant clusters in the cerebellum for the breast cancer group (p < 0.0008) and in the occipital lobe (p = 0.02) and cerebellum (p = 0.02) for the non small cell lung cancer group. We conclude a non-uniform distribution of metastatic brain lesions in breast and lung cancer patients that suggest differential vulnerability to metastasis in the different regions of the brain.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peretti-Viton P, Margain D, Murayama N et al (1991) Brain metastases. J Neuroradiol 18:161–172
Suh JH (2010) Stereotactic radiosurgery for the management of brain metastases. N Engl J Med 362(12):1119–1127
Jernal A, Murray T, Samuels A et al (2003) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 53:5–26
Nagao E, Yoshiura T, Hiwatashi A et al (2011) 3D turbo spin-echo sequence with motion-sensitized driven-equilibrium preparation for detection of brain metastases on 3T MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:664–670
Qian Y-F, Yu C-L, Zhang C et al (2008) MR T1-weighted inversion recovery imaging in detecting brain metastases: Could it replace T1-weighted spin-echo imaging? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:701–704
Schellinger PD, Meinck HM, Thron A (1999) Diagnostic accuracy of MRI compared to CCT in patients with brain metastases. J Neurooncol 44(3):275–281
Fidler IJ, Yano S, Zhang RD et al (2002) The seed and soil hypothesis: vascularization and brain metastases. Lancet Oncol 3(1):53–57
Hwang TL, Close TP, Grego JM et al (1996) Predilection of brain metastases in grey and white matter junction and vascular border zones. Cancer 77:1551–1555
Paget S (1989) The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast. 1889. Cancer Metastasis Rev 8:98–101
Delattre JY, Krol G, Thaler HT et al (1988) Distribution of brain metastases. Arch Neurol 45:741–744
Graf AH, Buchberger W, Langmayr H et al (1988) Site preference of metastatic tumors of the brain. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 412(5):493–498
Bender ET, Tomé WA (2011) Distribution of brain metastases: implications for non-uniform dose prescriptions. Br J Radiol 84(1003):649–658
Hengel K, Sidhu G, Choi J et al (2012) Attributes of brain metastases from breast and lung cancer. Int J Clin Oncol (Epub ahead of print)
Mazziotta JC, Toga AW, Evans A et al (1995) A probabilistic atlas of the human brain: theory and rationale for its development. The international consortium for brain mapping (ICBM). NeuroImage 2(2):89–101
Charil A, Zijdenbos AP, Taylor J et al (2003) Statistical mapping analysis of lesion location and neurological disability in multiple sclerosis: application to 452 patient data sets. NeuroImage 19(3):532–544
Wen W, Sachdev PS (2004) Extent and distribution of white matter hyperintensities in stroke patients: the Sydney Stroke Study. Stroke 35(12):2813–2819
Smith SM (2004) Overview of fMRI analysis. Br J Radiol 77(2):S167–75
Bates E, Wilson SM, Saygin AP et al (2003) Voxel-based lesion-symptom mapping. Nat Neurosci 6(5):448–450
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D et al (2002) Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. NeuroImage 15(1):273–289
Tsukada Y, Fouad A, Pickren JW et al (1983) Central nervous system metastasis from breast carcinoma. Autopsy study. Cancer 52:2349–2354
Ghia A, Tomé WA, Thomas S et al (2007) Distribution of brain metastases in relation to the hippocampus: implications for neurocognitive functional preservation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 68(4):971–977
van der Sande JJ, van Tinteren H, Brandsma D et al (2009) Brain metastases in patients with pelvic or abdominal malignancy do not prevail in the posterior fossa: a retrospective study. J Neurol 256(9):1485–1487
Hendrikse J, Petersen ET, van Laar PJ et al (2008) Cerebral border zones between distal end branches of intracranial arteries: MR imaging. Radiology 246:572–580
Armulik A, Genové G, Mäe M et al (2010) Pericytes regulate the blood-brain barrier. Nature 468:557–561
Carbonell WS, Ansorge O, Sibson N et al (2009) The vascular basement membrane as “soil” in brain metastasis. PLoS One 4(6):e5857
Lorger M, Felding-Habermann B (2010) Capturing changes in the brain microenvironment during initial steps of breast cancer brain metastasis. Am J Pathol 176(6):2958–2971
Lorger M, Krueger JS, O’Neal M, Staflin K et al (2009) Activation of tumor cell integrin alpha v beta 3 controls angiogenesis and metastatic growth in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(26):10666–10671
Bos PD, Zhang XH, Nadal C et al (2009) Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to the brain. Nature 459:1005–1009
Hendrikse J, Van der Grond J, Lu H et al (2004) Flow territory mapping of the cerebral arteries with regional perfusion MRI. Stroke 35:882–887
Van Laar PJ, Hendrikse J, Golay X et al (2006) In vivo flow territory mapping of major brain feeding arteries. NeuroImage 29:136–144
Kajita Y, Takayasu M, Suzuki Y et al (1995) Regional differences in cerebral vasomotor control by nitric oxide. Brain Res Bull 38:365–369
Iadecola C (1993) Regulation of the cerebral microcirculation during neural activity: Is nitric oxide the missing link? Trends Neurosci 16:206–15
Nozaki K, Moskowitz MA, Maynard KI et al (1993) Possible origins and distribution of immunoreactive nitric oxide synthetase-containing nerve fibers in cerebral arteries. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 13:70–79
Cavaglia M, Dombrowski SM, Drazba J et al (2001) Regional variation in brain capillary density and vascular response to ischemia. Brain Res 910:81–93
Edvinsson L (1982) Vascular autonomic nerves and corresponding receptors in brain vessels. Pathol Biol (Paris) 30(5):261–268
Edvinsson L, Nielsen KC, Owman C et al (1972) Sympathetic neural influence on norepinephrine vasoconstriction in brain vessels. Arch Neurol 27:492–495
Ito H, Yokoyama I, Iida H et al (2000) Regional differences in cerebral vascular response to PaCo2 changes in humans measured by positron emission tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:1264–1279
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quattrocchi, C.C., Errante, Y., Gaudino, C. et al. Spatial brain distribution of intra-axial metastatic lesions in breast and lung cancer patients. J Neurooncol 110, 79–87 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-0937-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-0937-x