Abstract
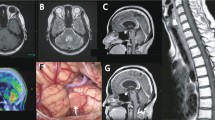
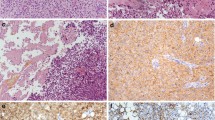
Cerebellar liponeurocytoma (cLPN) is a very rare central nervous system (CNS) tumour recently recognized as a clinical and pathological entity distinct from medulloblastoma (MB), and included in the WHO classification of CNS tumours under the heading “glioneuronal tumours”. cLPN typically develop in adult age and have a favourable prognosis compared with MB. In this work, we reviewed the clinical and neuroradiological data of two novel cases of adult cLPN diagnosed at our institution; one patient developed distant metastases. We tried to identify novel molecular markers for this malignancy. We found that the transcription factor NEUROG1 (but not ATOH1) is expressed in cLPN, unlike normal adult cerebellum, and that fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4), typically found in adipocytes, is significantly overexpressed compared with both normal adult cerebellum and human MB. These findings suggest cLPN occur as a result of transformation of cerebellar progenitors, which are distinct from cerebellar granule progenitors, and aberrantly differentiate into adipocyte-like tumour cells. They also suggest that analysis of FABP4 expression is of help to differentiate cLPN from MB.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kleihues P, Chimelli L, Giangaspero F (2000) Cerebellar liponeurocytoma. In: Kleihues P, Cavenee WK (eds) Pathology and genetics of tumours of the nervous system. IARC Press, Lyon, pp 110–111
Kleihues P, Chimelli L, Giangaspero F, Ohgaki H (2007) Cerebellar liponeurocytoma. In: Kleihues P, Cavenee WK (eds) WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. IARC Press, Lyon, pp 110–112
Horstmann S, Perry A, Reifenberger G, Giangaspero F, Huang H, Hara A, Masuoka J, Rainov NG, Bergmann M, Heppner FL, Brandner S, Chimelli L, Montagna N, Jackson T, Davis DG, Markesbery WR, Ellison DW, Weller RO, Taddei GL, Conti R, Del Bigio MR, González-Cámpora R, Radhakrishnan VV, Söylemezoglu F, Uro-Coste E, Qian J, Kleihues P, Ohgaki H (2004) Genetic and expression profiles of cerebellar liponeurocytomas. Brain Pathol 14(3):281–289
Chakraborti S, Mahadevan A, Govindan A, Yasha TC, Santosh V, Kovoor JM, Ramamurthi R, Alapatt JP, Hedge T, Shankar SK (2011) Supratentorial and cerebellar liponeurocytomas: report of four cases with review of literature. J Neurooncol 103(1):121–127
Owler BK, Makeham JM, Shingde M, Besser M (2005) Cerebellar liponeurocytoma. J Clin Neurosci 12:326–329
Buccoliero AM, Caldarella A, Bacci S, Gallina P, Taddei A, Di Lorenzo N, Romagnoli P, Taddei GL (2005) Cerebellar liponeurocytoma: morphological, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study of a relapsed case. Neuropathology 25(1):77–83
Châtillon CE, Guiot MC, Roberge D, Leblanc R (2009) Cerebellar liponeurocytoma with high proliferation index: treatment options. Can J Neurol Sci 36:658–661
Limaiem F, Bellil S, Chelly I, Bellil K, Mekni A, Jemel H, Haouet S, Zitouna M, Kchir N (2009) Recurrent cerebellar liponeurocytoma with supratentorial extension. Can J Neurol Sci 36(5):662–665
Sharma MC, Agarwal M, Suri A, Gaikwad S, Mukhopadhyay P, Sarkar C (2002) Lipomedulloblastoma in child: a controversial entity. Human Pathol 33(5):564–569
Aker FV, Ozkara S, Eren P, Peker O, Armagan S, Hakan T (2005) Cerebellar liponeurocytoma/lipidized medulloblastoma. J Neurooncol 71:53–59
Patel N, Fallah A, Provias J, Jha NK (2009) Cerebellar liponeurocytoma. Can J Surg 52(4):E117–E119
Hortobágyi T, Bódi L, Lantos PL (2007) Adult cerebellar liponeurocytoma with predominant pilocytic pattern and myoid differentiation. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 33:121–125
Jenkinson MD, Bosma JJ, Du Plessis D, Ohgaki H, Kleihues P, Warnke P, Rainov NG (2003) Cerebellar liponeurocytoma with an unusually aggressive clinical course: case report. Neurosurgery 53(6):1425–1427
Gross E, Kiechle M, Arnold N (2001) Mutation analysis of p53 in ovarian tumors by DHPLC. J Biochem Biophys Methods 47:73–81
Yan H, Parsons DW, Jin G, McLendon R, Rasheed BA, Yuan W, Kos I, Batinic-Haberle I, Jones S, Riggins GJ, Friedman H, Friedman A, Reardon D, Herndon J, Kinzler KW, Velculescu VE, Vogelstein B, Bigner DD (2009) IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in gliomas. N Engl J Med 360:765–773
Ellison DW, Onilude OE, Lindsey JC, Lusher ME, Weston CL, Taylor RE, Pearson AD, Clifford SC; United Kingdom Children’s Cancer Study Group Brain Tumour Committee (2005) beta-Catenin status predicts a favourable outcome in childhood medulloblastoma: the United Kingdom Children’s Cancer Study Group Brain Tumour Committee. J Clin Oncol 23(31): 7951–7957
Soylemezoglu F, Soffer D, Onol B, Schwechheimer K, Kleihues P (1996) Lipomatous medulloblastoma in adults. a distinct clinicopathological entity. Am J Surg Pathol 20(4):413–418
Goldowitz D, Hamre K (1998) The cells and molecules that make a cerebellum. Trends Neurosci 21:375–382
Salsano E, Croci L, Maderna E, Lupo L, Pollo B, Giordana MT, Consalez GG, Finocchiaro G (2007) Expression of the neurogenic basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor NEUROG1 identifies a subgroup of medulloblastomas not expressing ATOH1. Neuro Oncol 9(3):298–307
Cataltepe O, Arikan MC, Ghelfi E, Karaaslan C, Ozsurekci Y, Dresser K, Li Y, Smith TW, Cataltepe S (2011) Fatty acid binding protein 4 is expressed in distinct endothelial and non-endothelial cell populations in glioblastoma. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2011.01237.x
Elmasri H, Karaaslan C, Teper Y, Ghelfi E, Weng M, Ince TA, Kozakewich H, Bischoff J, Cataltepe S (2009) Fatty acid binding protein 4 is a target of VEGF and a regulator of cell proliferation in endothelial cells. FASEB J (official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology) 23:3865–3873
Kawai M, Rosen CJ (2010) PPARγ: a circadian transcription factor in adipogenesis and osteogenesis. Nat Rev Endocrinol 6(11):629–636
Ryan KK, Li B, Grayson BE, Matter EK, Woods SC, Seeley RJ (2011) A role for central nervous system PPAR-γ in the regulation of energy balance. Nat Med 17(5):623–626
Urbanska K, Pannizzo P, Grabacka M, Croul S, del Valle L, Khalili K, Reiss K (2008) Activation of PPARα inhibits IGF-I-mediated growth and survival responses in medulloblastoma cell lines. Int J Cancer 123:1015–1024
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anghileri, E., Eoli, M., Paterra, R. et al. FABP4 is a candidate marker of cerebellar liponeurocytomas. J Neurooncol 108, 513–519 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-0853-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-0853-0