Abstract
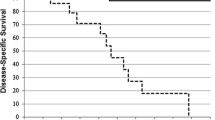
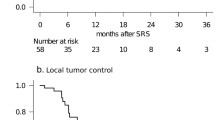
The purpose of this study is to determine the efficacy of Gamma Knife stereotactic radiosurgery (GK SRS) for intracranial hemangiopericytomas, and to investigate the optimal dose for successful tumor control without adverse effects. We evaluated 17 hemangiopericytomas of nine patients treated with GK SRS between 1999 and 2008. The mean tumor volume was 2.2 cm3 (range 0.2–9.9 cm3), and the mean and median marginal doses were 18.1 and 20 Gy (range 11–22 Gy), respectively, at the 50% isodose line. Mean clinical and radiological follow-up periods were 49 and 34 months, respectively. Successful tumor control was achieved in 14 of 17 lesions (82.4%) at time of last follow-up after GK SRS. Actuarial local tumor control rates at 1, 2, and 5 years after GK SRS were 100%, 84.6%, and 67.7%, respectively. No adverse effects, such as radiation necrosis or marked peritumoral edema, were observed in any patient. Marginal dose (≥17 Gy) was the only statistically significant factor for local tumor control on univariate analysis. Extended analysis using lesion data available from previous studies revealed that higher marginal dose (≥17 Gy) was also significant (P = 0.028). GK SRS provides an effective and safe adjuvant management option for patients with recurrent or residual hemangiopericytomas. Our results suggest that doses higher than previously used (around 15 Gy) are desirable to achieve better local tumor control of hemangiopericytomas. Close radiological follow-up is also necessary for early detection of small recurrent lesions.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HPC:
-
Hemangiopericytoma
- GK SRS:
-
Gamma Knife stereotactic radiosurgery
- RT:
-
Radiation therapy
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
References
Kano H, Niranjan A, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2008) Adjuvant stereotactic radiosurgery after resection of intracranial hemangiopericytomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 72:1333–1339
Kim JH, Jung HW, Kim YS, Kim CJ, Hwang SK, Paek SH, Kim DG, Kwun BD (2003) Meningeal hemangiopericytomas: long-term outcome and biological behavior. Surg Neurol 59:47–53 (discussion 53–44)
Olson C, Yen CP, Schlesinger D, Sheehan J (2009) Radiosurgery for intracranial hemangiopericytomas: outcomes after initial and repeat Gamma Knife surgery. J Neurosurg. doi:10.3171/2009.3.JNS0923
Payne BR, Prasad D, Steiner M, Steiner L (2000) Gamma surgery for hemangiopericytomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 142:527–536 (discussion 536–527)
Bastin KT, Mehta MP (1992) Meningeal hemangiopericytoma: defining the role for radiation therapy. J Neurooncol 14:277–287
Galanis E, Buckner JC, Scheithauer BW, Kimmel DW, Schomberg PJ, Piepgras DG (1998) Management of recurrent meningeal hemangiopericytoma. Cancer 82:1915–1920
Soyuer S, Chang EL, Selek U, McCutcheon IE, Maor MH (2004) Intracranial meningeal hemangiopericytoma: the role of radiotherapy: report of 29 cases and review of the literature. Cancer 100:1491–1497
Dufour H, Metellus P, Fuentes S, Murracciole X, Regis J, Figarella-Branger D, Grisoli F (2001) Meningeal hemangiopericytoma: a retrospective study of 21 patients with special review of postoperative external radiotherapy. Neurosurgery 48:756–762 (discussion 762–753)
Kirn DH, Kramer A (1996) Long-term freedom from disease progression with interferon alfa therapy in two patients with malignant hemangiopericytoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 88:764–765
Chamberlain MC, Glantz MJ (2008) Sequential salvage chemotherapy for recurrent intracranial hemangiopericytoma. Neurosurgery 63:720–726 (author reply 726–727)
Ecker RD, Marsh WR, Pollock BE, Kurtkaya-Yapicier O, McClelland R, Scheithauer BW, Buckner JC (2003) Hemangiopericytoma in the central nervous system: treatment, pathological features, and long-term follow up in 38 patients. J Neurosurg 98:1182–1187
Sun S, Liu A, Wang C (2009) Gamma Knife radiosurgery for recurrent and residual meningeal hemangiopericytomas. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 87:114–119
Chang SD, Sakamoto GT (2003) The role of radiosurgery for hemangiopericytomas. Neurosurg Focus 14:e14
Sheehan J, Kondziolka D, Flickinger J, Lunsford LD (2002) Radiosurgery for treatment of recurrent intracranial hemangiopericytomas. Neurosurgery 51:905–910 (discussion 910–911)
Alen JF, Lobato RD, Gomez PA, Boto GR, Lagares A, Ramos A, Ricoy JR (2001) Intracranial hemangiopericytoma: study of 12 cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 143:575–586
Coffey RJ, Cascino TL, Shaw EG (1993) Radiosurgical treatment of recurrent hemangiopericytomas of the meninges: preliminary results. J Neurosurg 78:903–908
Jaaskelainen J, Servo A, Haltia M, Wahlstrom T, Valtonen S (1985) Intracranial hemangiopericytoma: radiology, surgery, radiotherapy, and outcome in 21 patients. Surg Neurol 23:227–236
Guthrie BL, Ebersold MJ, Scheithauer BW, Shaw EG (1989) Meningeal hemangiopericytoma: histopathological features, treatment, and long-term follow-up of 44 cases. Neurosurgery 25:514–522
Shaw E, Scott C, Souhami L, Dinapoli R, Kline R, Loeffler J, Farnan N (2000) Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90-05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:291–298
Ojemann SG, Sneed PK, Larson DA, Gutin PH, Berger MS, Verhey L, Smith V, Petti P, Wara W, Park E, McDermott MW (2000) Radiosurgery for malignant meningioma: results in 22 patients. J Neurosurg 93(Suppl 3):62–67
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Nuclear Research and Development Program of the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation (KOSEF) grant funded by the Korean Government (MEST) (Grant: M800-20090068).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.W., Kim, D.G., Chung, HT. et al. Gamma Knife stereotactic radiosurgery for intracranial hemangiopericytomas. J Neurooncol 99, 115–122 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0114-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0114-z