Abstract
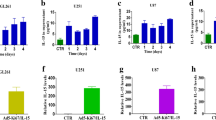
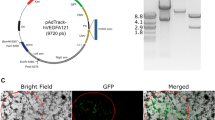
Malignant brain tumors grow by coopting the existing vasculature, a process involving the release of angiopoietin-2 (Angpt2) from endothelial cells and its binding to the Tie2 receptor. The first goal of this study was to examine the therapeutic potential of two proteins that could interfere with Angpt2, namely Angpt3 and the soluble extracellular domain of Tie2 (sTie2). The second goal was to develop a lentiviral vector capable of delivering such proteins while offering the possibility to identify and destroy the genetically modified cells. To this end, we designed a bicistronic construct expressing the marker enhanced green fluorescent protein fused to the suicide gene herpes simplex virus 1 thymidine kinase. GL261 glioma cells transduced with this vector could be tracked and killed on command by the administration of the prodrug ganciclovir, either in vitro or after implantation into mouse brains. High levels of Angpt3 or sTie2 could be achieved with this vector; however, Angpt3 increased capillary destabilization and glioma growth, whereas sTie2 exerted no effect. Overall, this study helps to understand the importance of the Tie2 signaling pathway in glioma development and the role of Angpt3, but suggests that neither this molecule nor sTie2 are effective agents against malignant gliomas. This study also provides a lentiviral vector design for safer gene therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Louis DN (2006) Molecular pathology of malignant gliomas. Annu Rev Pathol 1:97–117
Holash J, Maisonpierre PC, Compton D, Boland P, Alexander CR, Zagzag D, Yancopoulos GD, Wiegand SJ (1999) Vessel cooption, regression, and growth in tumors mediated by angiopoietins and VEGF. Science 284:1994–1998
Fischer I, Gagner JP, Law M, Newcomb EW, Zagzag D (2005) Angiogenesis in gliomas: biology and molecular pathophysiology. Brain Pathol 15:297–310
Dome B, Hendrix MJ, Paku S, Tovari J, Timar J (2007) Alternative vascularization mechanisms in cancer: pathology and therapeutic implications. Am J Pathol 170:1–15
Reiss Y, Machein MR, Plate KH (2005) The role of angiopoietins during angiogenesis in gliomas. Brain Pathol 15:311–317
Yancopoulos GD, Davis S, Gale NW, Rudge JS, Wiegand SJ, Holash J (2000) Vascular-specific growth factors and blood vessel formation. Nature 407:242–248
Nourhaghighi N, Teichert-Kuliszewska K, Davis J, Stewart DJ, Nag S (2003) Altered expression of angiopoietins during blood-brain barrier breakdown and angiogenesis. Lab Invest 83:1211–1222
Stratmann A, Risau W, Plate KH (1998) Cell type-specific expression of angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2 suggests a role in glioblastoma angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 153:1459–1466
Tait CR, Jones PF (2004) Angiopoietins in tumours: the angiogenic switch. J Pathol 204:1–10
Villeneuve J, Galarneau H, Beaudet MJ, Tremblay P, Chernomoretz A, Vallieres L (2008) Reduced glioma growth following dexamethasone or anti-angiopoietin 2 treatment. Brain Pathol 18:401–414
Valenzuela DM, Griffiths JA, Rojas J, Aldrich TH, Jones PF, Zhou H, McClain J, Copeland NG, Gilbert DJ, Jenkins NA, Huang T, Papadopoulos N, Maisonpierre PC, Davis S, Yancopoulos GD (1999) Angiopoietins 3 and 4: diverging gene counterparts in mice and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:1904–1909
Lin P, Buxton JA, Acheson A, Radziejewski C, Maisonpierre PC, Yancopoulos GD, Channon KM, Hale LP, Dewhirst MW, George SE, Peters KG (1998) Antiangiogenic gene therapy targeting the endothelium-specific receptor tyrosine kinase Tie2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:8829–8834
Lin P, Polverini P, Dewhirst M, Shan S, Rao PS, Peters K (1997) Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis using a soluble receptor establishes a role for Tie2 in pathologic vascular growth. J Clin Invest 100:2072–2078
Raikwar SP, Temm CJ, Raikwar NS, Kao C, Molitoris BA, Gardner TA (2005) Adenoviral vectors expressing human endostatin-angiostatin and soluble Tie2: enhanced suppression of tumor growth and antiangiogenic effects in a prostate tumor model. Mol Ther 12:1091–1100
Xu Y, Liu YJ, Yu Q (2004) Angiopoietin-3 inhibits pulmonary metastasis by inhibiting tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res 64:6119–6126
Lee HJ, Cho CH, Hwang SJ, Choi HH, Kim KT, Ahn SY, Kim JH, Oh JL, Lee GM, Koh GY (2004) Biological characterization of angiopoietin-3 and angiopoietin-4. Faseb J 18:1200–1208
Sinn PL, Sauter SL, McCray PBJ (2005) Gene therapy progress and prospects: development of improved lentiviral and retroviral vectors—design, biosafety, and production. Gene Ther 12:1089–1098
Fillat C, Carrio M, Cascante A, Sangro B (2003) Suicide gene therapy mediated by the Herpes Simplex virus thymidine kinase gene/Ganciclovir system: fifteen years of application. Curr Gene Ther 3:13–26
Kokoris MS, Sabo P, Adman ET, Black ME (1999) Enhancement of tumor ablation by a selected HSV-1 thymidine kinase mutant. Gene Ther 6:1415–1426
Watson DJ, Kobinger GP, Passini MA, Wilson JM, Wolfe JH (2002) Targeted transduction patterns in the mouse brain by lentivirus vectors pseudotyped with VSV, Ebola, Mokola, LCMV, or MuLV envelope proteins. Mol Ther 5:528–537
Ausman JI, Shapiro WR, Rall DP (1970) Studies on the chemotherapy of experimental brain tumors: development of an experimental model. Cancer Res 30:2394–2400
Szatmari T, Lumniczky K, Desaknai S, Trajcevski S, Hidvegi EJ, Hamada H, Safrany G (2006) Detailed characterization of the mouse glioma 261 tumor model for experimental glioblastoma therapy. Cancer Sci 97:546–553
Vallieres L, Sawchenko PE (2003) Bone marrow-derived cells that populate the adult mouse brain preserve their hematopoietic identity. J Neurosci 23:5197–5207
Villeneuve J, Tremblay P, Vallieres L (2005) Tumor necrosis factor reduces brain tumor growth by enhancing macrophage recruitment and microcyst formation. Cancer Res 65:3928–3936
Mizuguchi H, Xu Z, Ishii-Watabe A, Uchida E, Hayakawa T (2000) IRES-dependent second gene expression is significantly lower than cap-dependent first gene expression in a bicistronic vector. Mol Ther 1:376–382
Nag S, Papneja T, Venugopalan R, Stewart DJ (2005) Increased angiopoietin2 expression is associated with endothelial apoptosis and blood–brain barrier breakdown. Lab Invest 85:1189–1198
Xu Y, Liu YJ, Yu Q (2004) Angiopoietin-3 is tethered on the cell surface via heparan sulfate proteoglycans. J Biol Chem 279:41179–41188
Rothstein JD, Brem H (2001) Excitotoxic destruction facilitates brain tumor growth. Nat Med 7:994–995
Takano T, Lin JH, Arcuino G, Gao Q, Yang J, Nedergaard M (2001) Glutamate release promotes growth of malignant gliomas. Nat Med 7:1010–1015
Savaskan NE, Heckel A, Hahnen E, Engelhorn T, Doerfler A, Ganslandt O, Nimsky C, Buchfelder M, Eyupoglu IY (2008) Small interfering RNA-mediated xCT silencing in gliomas inhibits neurodegeneration and alleviates brain edema. Nat Med 14:629–632
Zadeh G, Qian B, Okhowat A, Sabha N, Kontos CD, Guha A (2004) Targeting the Tie2/Tek receptor in astrocytomas. Am J Pathol 164:467–476
Rondaij MG, Bierings R, Kragt A, van Mourik JA, Voorberg J (2006) Dynamics and plasticity of Weibel-Palade bodies in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:1002–1007
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Cancer Research Society and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada. L.V. received a Career Award from the Rx&D Health Research Foundation and the Canadian Institutes for Health Research (CIHR). M.J.B. was supported by grants to L.V. from the CIHR and the Laurye Lapointe Foundation. N.R. was the recipient of a scholarship from the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología de México. J.V. was supported by studentships from the CIHR and the Fonds de la Recherche en Santé du Québec. We thank Mr. Maurice Dufour for technical assistance with flow cytometry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beaudet, MJ., Rueda, N., Kobinger, G.P. et al. Construction of a ganciclovir-sensitive lentiviral vector to assess the influence of angiopoietin-3 and soluble Tie2 on glioma growth. J Neurooncol 99, 1–11 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-0095-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-0095-y