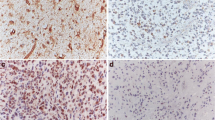
Abstract
Although there are many reports on the clinical use of the MIB-1 labeling index (LI), which is a measure of proliferative activity in astrocytomas; its significance varies between studies. There are no known molecules that are directly linked to the MIB-1 LI in astrocytomas. We evaluated the clinical value of the MIB-1 LI in our human glioblastoma cases and determined the molecules that possibly influenced the MIB-1 LI. An immunohistochemical study of the MIB-1 protein was performed and MIB-1 LIs of 38 glioblastomas were determined. In the same cases, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), platelet-derived growth factor receptor-α (PDGFRA), and sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor type 1 (S1P1), which are known regulators of glioma cell proliferation, were detected and quantified by quantitative real-time-PCR or western blotting. Kaplan–Meier survival curves for 38 patients with glioblastomas showed that a high MIB-1 LI correlated with poor survival (P < 0.05). Among the molecules tested, only the low expression of S1P1 was significantly correlated with the high MIB-1 LI in glioblastomas (P < 0.05). Multivariate analysis revealed that the S1P1 expression level was a significant prognostic factor. Our results indicate that the MIB-1 LI is an important prognostic factor in human glioblastomas. Furthermore, downregulation of S1P1 expression increases proliferative activity, and thus enhances the malignancy of glioblastomas, resulting in a poor survival.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD et al (2007) The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 114:97–109
Gerdes J, Schwab U, Lemke H et al (1983) Production of a mouse monoclonal antibody reactive with a human nuclear antigen associated with cell proliferation. Int J Cancer 31:13–20
Key G, Becker MH, Baron B et al (1993) New Ki-67-equivalent murine monoclonal antibodies (MIB 1–3) generated against bacterially expressed parts of the Ki-67 cDNA containing three 62 base pair repetitive elements encoding for the Ki-67 epitope. Lab Invest 68:629–636
Johannessen AL, Torp SH (2006) The clinical value of Ki-67/MIB-1 labeling index in human astrocytomas. Pathol Oncol Res 12:143–147
Ralte AM, Sharma MC, Karak AK et al (2001) Clinicopathological features, MIB-1 labeling index and apoptotic index in recurrent astrocytic tumors. Pathol Oncol Res 7:267–278
Reavey-Cantwell JF, Haroun RI, Zahurak M et al (2001) The prognostic value of tumor markers in patients with glioblastoma multiforme: analysis of 32 patients and review of the literature. J Neurooncol 55:195–204
Karamitopoulou E, Perentes E, Diamantis I et al (1994) Ki-67 immunoreactivity in human central nervous system tumors: a study with MIB 1 monoclonal antibody on archival material. Acta Neuropathol 87:47–54
Khalid H, Shibata S, Kishikawa M et al (1997) Immunohistochemical analysis of progesterone receptor and Ki-67 labeling index in astrocytic tumors. Cancer 80:2133–2140
Sallinen PK, Haapasalo HK, Visakorpi T et al (1994) Prognostication of astrocytoma patient survival by Ki-67 (MIB-1), PCNA, and S-phase fraction using archival paraffin-embedded samples. J Pathol 174:275–282
Di X, Nishizaki T, Harada K et al (1997) Proliferative potentials of glioma cells and vascular components determined with monoclonal antibody MIB-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 16:389–394
Hsu DW, Louis DN, Efird JT et al (1997) Use of MIB-1 (Ki-67) immunoreactivity in differentiating grade II and grade III gliomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 56:857–865
Enestrom S, Vavruch L, Franlund B et al (1998) Ki-67 antigen expression as a prognostic factor in primary and recurrent astrocytomas. Neurochir 44:25–30
Torp SH (2002) Diagnostic and prognostic role of Ki67 immunostaining in human astrocytomas using four different antibodies. Clin Neouropathol 21:252–257
Neder L, Colli BO, Machado HR et al (2004) MIB-1 labeling index in astrocytic tumors–a clinicopathologic study. Clin Neuropathol 6:262–270
Wakimoto H, Aoyagi M, Nakayama T et al (1996) Prognostic significance of Ki-67 labeling indices obtained using MIB-1 monoclonal antibody in patients with supratentorial astrocytomas. Cancer 77:373–380
McKeever PE, Ross DA, Strawderman MS et al (1997) A comparison of the predictive power for survival in gliomas provided by MIB-1, bromodeoxyuridine and proliferating cell nuclear antigen with histopathologic and clinical parameters. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 56:798–805
Schiffer D, Cavalla P, Chio A et al (1997) Proliferative activity and prognosis of low-grade astrocytomas. J Neurooncol 34:31–35
McKeever PE, Strawderman MS, Yamini B et al (1998) MIB-1 proliferation index predicts survival among patients with grade II astrocytoma. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 57:931–936
Torp SH, Alsaker M (2002) Ki-67 immunoreactivity, basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) expression, and microvessel density as supplementary prognostic tools in low-grade astrocytomas. Pathol Res Pract 198:261–265
Scott RJ, Hall PA, Haldane JS et al (1991) A comparison of immunohistochemical markers of cell proliferation with experimentally determined growth fraction. J Pathol 165:173–178
McCormick D, Chong H, Hobbs C et al (1993) Detection of the Ki-67 antigen in fixed and wax embedded sections with the monoclonal antibody Mib1. Histopathology 22:355–360
Smith JS, Tachibana I, Passe SM et al (2001) PTEN mutation, EGFR amplification, and outcome in patients with anaplastic astrocytoma and glioblastoma multiforme. J Natl Cancer Inst 93:1246–1256
Choe G, Horvath S, Cloughesy TF et al (2003) Analysis of the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase signaling pathway in glioblastoma patients in vivo. Cancer Res 63:2742–2746
Reifenberger G, Collins VP (2004) Pathology and molecular genetics of astrocytic gliomas. J Mol Med 82:656–670
Ranza E, Facoetti A, Morbini P et al (2007) Exogenous platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) induces human astrocytoma cell line proliferation. Anticancer Res 27:2161–2166
Spiegel S, Milstien S (2003) Sphingosine-1-phosphate: an enigmatic signalling lipid. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:397–407
Hla T (2004) Physiological and pathological actions of sphingosine 1-phosphate. Semin Cell Dev Biol 15:513–520
Takuwa Y, Takuwa N, Sugimoto N (2002) The Edg family G protein-coupled receptors for lysophospholipids: their signaling properties and biological activities. J Biochem 131:767–771
Young N, Van Brocklyn JR (2006) Signal transduction of sphingosine-1-phosphate G protein-coupled receptors. Sci World J 6:946–966
Yoshida Y, Nakada M, Sugimoto N, Harada T, Hayashi Y, Kita D, Uchiyama N, Hayashi Y, Yachie A, Takuwa Y, Hamada JI (2009) Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor type 1 regulates glioma cell proliferation and correlates with patient survival. Int J Cancer 9999(999A). doi:10.1002/ijc.24933
Stummer W, Pichlmeier U, Meinel T, ALA-Glioma Study Group et al (2006) Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of malignant glioma: a randomised controlled multicentre phase III trial. Lancet Oncol 7:392–401
Xue D, Albright RE Jr (1999) Preoperative anaplastic glioma tumor volume effects on patient survival. J Surg Oncol 72:199–205
Nakada M, Drake KL, Nakada S et al (2006) Ephrin-B3 ligand promotes glioma invasion through activation of Rac1. Cancer Res 66:8492–8500
Deckert M, Reifenberger G, Wechsler W (1989) Determination of the proliferative potential of human brain tumors using the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 115:179–188
Hitchcock CL (1991) Ki-67 staining as a means to simplify analysis of tumor cell proliferation. Am J Clin Pathol 96:444–446
Mellinghoff IK, Wang MY, Vivanco I et al (2005) Molecular determinants of the response of glioblastomas to EGFR kinase inhibitors. N Engl J Med 353:2012–2024
Hilton DA, Love S, Barber R et al (1998) Accumulation of p53 and Ki-67 expression do not predict survival in patients with fibrillary astrocytomas or the response of these tumors to radiotherapy. Neurosurgery 42:724–729
Dowsett M, Dunbier AK (2008) Emerging biomarkers and new understanding of traditional markers in personalized therapy for breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14:8019–8026
Donati V, Fontanini G, Dell’Omodarme M et al (2007) WWOX expression in different histologic types and subtypes of non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13:884–891
Tan PH, Bay BH, Yip G et al (2005) Immunohistochemical detection of Ki67 in breast cancer correlates with transcriptional regulation of genes related to apoptosis and cell death. Mod Pathol 18:374–381
Galanis E, Buckner J, Kimmel D et al (1998) Gene amplification as a prognostic factor in primary and secondary high-grade malignant gliomas. Int J Oncol 13:717–724
Sano T, Lin H, Chen X et al (1999) Differential expression of MMAC/PTEN in glioblastoma multiforme: relationship to localization and prognosis. Cancer Res 59:1820–1824
Frederick L, Wang XY, Eley G et al (2000) Diversity and frequency of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in human glioblastomas. Cancer Res 60:1383–1387
McGirt MJ, Chaichana KL, Gathinji M et al (2009) Independent association of extent of resection with survival in patients with malignant brain astrocytoma. J Neurosurg 110:156–162
Medical Research Council Brain Tumor Working Party (2001) Randomized trial of procarbazine, lomustine, and vincristine in the adjuvant treatment of high-grade astrocytoma. A Medical Research Council trial. J Clin Oncol 19:509–518
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by Grants-in-aid for young scientists’ research from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, Technology, and Culture (B-19790992 to M.N.), and grants from The Japan Brain Foundation (to M.N.), The Foundation for Promotion of Cancer Research (to M.N.), and The Hokkoku Cancer Research Foundation (to M.N., D.K., Y.H., and JI. H.). Akiko Imamura assisted with immunohistochemistry for MIB-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, Y., Nakada, M., Harada, T. et al. The expression level of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor type 1 is related to MIB-1 labeling index and predicts survival of glioblastoma patients. J Neurooncol 98, 41–47 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-0064-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-0064-5