Abstract
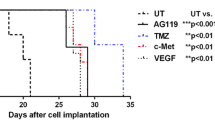
Aim of the study The extensive neovascularisation of malignant glioma is mainly influenced by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). The effect of ZD6474, a potent inhibitor of VEGF-receptor-2, was evaluated in combination with either radiotherapy or temozolomide. Methods The effects on glioma growth were investigated in the intracerebral BT4C rat glioma model. ZD6474 30 mg/kg was given alone or in combination with radiotherapy 12 Gy × 1 or with temozolomide 100 mg/kg for 3 days. Two different experiments were performed comparing ZD6474 to radiotherapy or temozolomide. For each experiment 28 animals were randomized into four groups. Results ZD6474 in combination with radiotherapy significantly decreased tumour area by 66% compared with controls whereas the combination with temozolomide decreased tumour area by 74%. Conclusions ZD6474 in combination with two standard modalities in the treatment of malignant glioma, radiotherapy and chemotherapy, markedly decreased the growth of an intracerebral experimental glioma. These results justify further investigations of these therapies in combination.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ et al (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996
Yamada Y, Nezu J, Shimane M et al (1997) Molecular cloning of a novel vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF-D. Genomics 42:483–488
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J (2003) The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 9:669–676
Ciardiello F, Tortora G (2001) A novel approach in the treatment of cancer: targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor. Clin Cancer Res 7:2958–2970
Dunn IF, Heese O, Black PM (2000) Growth factors in glioma angiogenesis: FGFs, PDGF, EGF, and TGFs. J Neurooncol 50:121–137
Feldkamp MM, Lau N, Rak J et al (1999) Normoxic and hypoxic regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) by astrocytoma cells is mediated by Ras. Int J Cancer 81:118–124
Hennequin LF, Stokes ES, Thomas AP et al (2002) Novel 4-anilinoquinazolines with C-7 basic side chains: design and structure activity relationship of a series of potent, orally active, VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J Med Chem 45:1300–1312
Wedge SR, Ogilvie DJ, Dukes M et al (2002) ZD6474 inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor signaling, angiogenesis, and tumor growth following oral administration. Cancer Res 62:4645–4655
Ciardiello F, Caputo R, Damiano V et al (2003) Antitumor effects of ZD6474, a small molecule vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, with additional activity against epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. Clin Cancer Res 9:1546–1556
Sandstrom M, Johansson M, Andersson U et al (2004) The tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD6474 inhibits tumour growth in an intracerebral rat glioma model. Br J Cancer 91:1174–1180
McCarty MF, Wey J, Stoeltzing O et al (2004) ZD6474, a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor with additional activity against epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, inhibits orthotopic growth and angiogenesis of gastric cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 3:1041–1048
Rich JN, Sathornsumetee S, Keir ST et al (2005) ZD6474, a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor, inhibits tumor growth of multiple nervous system tumors. Clin Cancer Res 11:8145–8157
Hanna NN, Seetharam S, Mauceri HJ et al (2000) Antitumor interaction of short-course endostatin and ionizing radiation. Cancer J 6:287–293
Fenton BM, Paoni SF, Ding I (2004) Pathophysiological effects of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2-blocking antibody plus fractionated radiotherapy on murine mammary tumors. Cancer Res 64:5712–5719
Geng L, Donnelly E, McMahon G et al (2001) Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling leads to reversal of tumor resistance to radiotherapy. Cancer Res 61:2413–2419
Steiner HH, Karcher S, Mueller MM et al (2004) Autocrine pathways of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in glioblastoma multiforme: clinical relevance of radiation-induced increase of VEGF levels. J Neurooncol 66:129–138
Liang K, Ang KK, Milas L et al (2003) The epidermal growth factor receptor mediates radioresistance. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 57:246–254
Bianco C, Tortora G, Bianco R et al (2002) Enhancement of antitumor activity of ionizing radiation by combined treatment with the selective epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839 (Iressa). Clin Cancer Res 8:3250–3258
Winkler F, Kozin SV, Tong RT et al (2004) Kinetics of vascular normalization by VEGFR2 blockade governs brain tumor response to radiation: role of oxygenation, angiopoietin-1, and matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Cell 6:553–563
Bergenheim AT, Elfverson J, Gunnarsson P-O et al (1994) Cytotoxic effect and uptake of estramustine in a rat glioma model. Int J Oncol 5:293–299
Johansson M, Henriksson R, Bergenheim AT et al (2000) Interleukin-2 and histamine in combination inhibit tumour growth and angiogenesis in malignant glioma. Br J Cancer 83:826–832
Scholzen T, Gerdes J (2000) The Ki-67 protein: from the known and the unknown. J Cell Physiol 182:311–322
Weidner N (1993) Tumor angiogenesis: review of current applications in tumor prognostication. Semin Diagn Pathol 10:302–313
Johansson M, Bergenheim AT, Widmark A et al (1999) Effects of radiotherapy and estramustine on the microvasculature in malignant glioma. Br J Cancer 80:142–148
Nilsson J, Vallbo C, Guo D et al (2001) Cloning, characterization, and expression of human LIG1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 284:1155–1161
Bleehen NM, Wiltshire CR, Plowman PN et al (1981) A randomized study of misonidazole and radiotherapy for grade 3 and 4 cerebral astrocytoma. Br J Cancer 43:436–442
Huncharek M (1998) Meta-analytic re-evaluation of misonidazole in the treatment of high grade astrocytoma. Anticancer Res 18:1935–1939
Lund EL, Bastholm L, Kristjansen PE (2000) Therapeutic synergy of TNP-470 and ionizing radiation: effects on tumor growth, vessel morphology, and angiogenesis in human glioblastoma multiforme xenografts. Clin Cancer Res 6:971–978
Williams KJ, Telfer BA, Brave S et al (2004) ZD6474, a potent inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling, combined with radiotherapy: schedule-dependent enhancement of antitumor activity. Clin Cancer Res 10:8587–8593
Brazelle WD, Shi W, Siemann DW (2006) VEGF-associated tyrosine kinase inhibition increases the tumor response to single and fractionated dose radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 65:836–841
Damiano V, Melisi D, Bianco C et al (2005) Cooperative antitumor effect of multitargeted kinase inhibitor ZD6474 and ionizing radiation in glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 11:5639–5644
Sandstrom M, Bergstrom P, Johansson M et al (2005) Synergistic effects of the VEGF-R tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD6474 and radiotherapy on tumour growth in the intracerebral BT4C rat glioma model. In: Conference proceedings. EANO, Edinburgh, Scotland, 5–8 May 2005
Jain RK (2001) Normalizing tumor vasculature with anti-angiogenic therapy: a new paradigm for combination therapy. Nat Med 7:987–989
Tong RT, Boucher Y, Kozin SV et al (2004) Vascular normalization by vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 blockade induces a pressure gradient across the vasculature and improves drug penetration in tumors. Cancer Res 64:3731–3736
Benjamin LE, Golijanin D, Itin A et al (1999) Selective ablation of immature blood vessels in established human tumors follows vascular endothelial growth factor withdrawal. J Clin Invest 103:159–165
Williams KJ, Telfer BA, Stratford IJ et al (2003) ZD6474, a potent inhibitor of VEGF signaling, combined with radiotherapy: schedule-dependent enhancement of anti-tumor activity in a lung tumor xenograft model. In: Conference proceedings. AACR, Washington, USA, 11–14 July 2003
Hlatky L, Hahnfeldt P, Folkman J (2002) Clinical application of antiangiogenic therapy: microvessel density, what it does and doesn’t tell us. J Natl Cancer Inst 94:883–893
Acknowledgements
Kerstin Bergh is acknowledged for skilful technical assistance and Britt-Inger Gladzki for taking great care of the animals. This work was supported by grants from the Swedish Society Against Cancer, Lion’s Cancer Research Foundation, and J. C. Kempes Minnes Stipendiefond, Umeå University, Sweden. The work was also supported by an unrestricted research grant from Schering-Plough Sweden AB. ZD6474 was provided from AstraZeneca, Alderley Park, UK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Preliminary parts of this study were presented on EANO, Edinburgh, May 2005 and on ECCO, Paris, October 2005.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sandström, M., Johansson, M., Bergström, P. et al. Effects of the VEGFR inhibitor ZD6474 in combination with radiotherapy and temozolomide in an orthotopic glioma model. J Neurooncol 88, 1–9 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9527-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9527-3