Abstract
Objective
To determine the incidence, the causes and the prognostic value for survival of acute confusion (delirium) in patients admitted to a general cancer hospital.
Patients
Hundred consecutive patients with confusion were examined; 78 had a metastatic disease, 11 had local tumor and 11 had no sign of tumor recurrence at admission. Patients with confusion represented 11.8% (95%CI: 9.7–14.2%) of admissions. Follow-up period lasted 18 months from the inclusion of the last patient.
Results
Structural brain lesions (SBL) were mostly metastatic and caused confusion in 36 patients. 57 patients had a toxic or metabolic encephalopathy (TME).The cause remained unexplained in 6 cases, and in one patient the final diagnosis was psychotic state. Most patients with TME had more than one abnormality which could cause confusion.
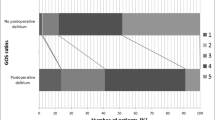
Confusion was reversible in 34 patients, and the odds for its regression was 3-fold higher in patients with TME (P = 0.02). Survival was significantly shorter (P = 0.02) in patients with SBL (median: 3 weeks) than in patients with TME (median: 8 weeks). However, the survival was significantly longer (P = 0.007) in patients with only one toxic or metabolic disorder (median: 20.5 weeks) than in patients with multiple changes (median: 5 weeks).
Conclusion
Confusion is common in general cancer population. TME is the leading etiology and it is due to multiple causes in most patients. SBL causes confusion in one third of the patients. Patients with TME have a greater chance to recover, and survive longer especially if they have only one toxic or metabolic change.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clouston PD, DeAngelis L, Posner JB (1992) The spectrum of neurological disease in patients with systemic cancer. Ann Neurol 31:268–273
Gilbert MR, Grossman SA (1986) Incidence and nature of neurologic problems in patients with solid tumor. Am J Med 81:951–954
Massie MJ, Holland J, Glass E. (1983) Delirium in terminally ill cancer patients. Am J Psychiatry 140:1048–1050
Steifel F, Fainsinger R, Bruera E (1992) Acute confusional state in patients with advanced cancer. J Pain Sympt Management 7:94–98
Lawlor PG, Gagnon B, Mancini IL et al (2000) Occurrence, cause and outcome of delirium in patients with advanced cancer. Arch Intern Med 160:786–794
Caraceni A, Nanni O, Maltoni M et al (2000) The impact of delirium on the short-term prognosis of advanced cancer patients. Cancer 89:1145–1149
Gagnon P, Allard P, Mâsse B, DeSerres M (2000) Delirium in terminal cancer: a prospective study using daily screening, early diagnosis and continuous monitoring. J Pain Sympt Manag 19:412–426
Morita T, Tei Y, Inoue S (2003) Impaired communication capacity and agitated delirium in terminally ill cancer patients: prevalence and identification or research focus. J Pain Sympt Manag 26:827–834
American Psychiatric Association (1994): Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th edn., American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Roth AJ, Modi R (2003) Psychiatric issues in older cancer patients. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 48:185–197
Minagawa H, Uchitomi Y, Yamawaki S, Ishitami K (1996) Psychiatric morbidity in terminally ill cancer patients. Cancer 78:1131–1137
Bolton CF, Young GB, Zochodne DW (1993) The neurological complications of sepsis. Ann Neurol 33:94–100
Jellema JG (1987) Hallucinations during sustained-release morphine and methadone administration. Lancet ii:392 (letter)
D’Souza M (1987) Unusual reaction to morphine. Lancet ii:98 (letter)
Ceraceni A, Martini C, De Conno F, Ventafrida V (1994) Organic brain syndrome and opioid administration. J Pain Sympt Manag 9:527–533
Chamberlain MC, Tsao-Wei D, Groshen S (2004) Neoplastic meningitis-related encephalopathy. Prognostic significance. Neurology 63:2159–2161
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doriath, V., Paesmans, M., Catteau, G. et al. Acute confusion in patients with systemic cancer. J Neurooncol 83, 285–289 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-006-9319-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-006-9319-6