Summary
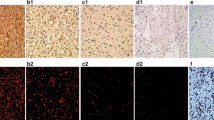
14-3-3 proteins have attracted much recent interest in the etiopathogenesis of human cancers owing to their involvement in the prevention of apoptosis. However, the expression of 14-3-3 in primary nervous system tumors has not been previously characterized. In this paper, Immunohistochemistry using a specific anti-14-3-3 antibody was performed on formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded archival tissue from 124 primary human nervous system tumors and 10 normal brain tissues. In the normal control brains, 14-3-3 immunoreactivity was localized mainly in the neuronal somata and processes, and some glial cells showed only weak immunoreactivity. However, 14-3-3 immunoreactivity was seen in the majority of astrocytomas [grade I (9/11), II (16/21), III (13/17), IV (17/21)]. There was no difference between the positive expression rates of 14-3-3 in different grades of astrocytomas (P = 0.968). But the intensity and degree of 14-3-3 immunoreactivity in diffuse astrocytomas, anaplastic astrocytoma, and glioblastoma multiformes showed trends with tumor grade, with glioblastomas having the highest positivity (P = 0.048). The 14-3-3 immunoreactivity was also seen in the majority of other gliomas [oligodendroglioma (2/3), anaplastic oligodendroglioma (4/4), ependymoma (1/2), anaplastic ependymoma (2/2), choroid plexus papilloma (3/3), pineocytoma (2/2), medulloblastoma (5/8)]. All meningiomas [syncytical (3), fibrous/fibroblastic (4), angiomatous (4), transitional/mixed (3)] were intensely and diffusely positive. All schwannomas (4), neurofibromas (2), pituitary adenomas (6) and craniopharyngiomas(4) also showed intense positive staining. These results showed that 14-3-3 is expressed in the majority of the primary human nervous system tumors. The up-regulated expression of 14-3-3 may be a common mechanism for evading apoptosis in most primary human nervous system tumors, and targeting 14-3-3 may be a novel promising strategy for the treatment of these tumors, especially for malignant tumors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitken A, Collinge DB, van Heusden BP, Isobe T, Roseboom PH, Rosenfeld G, Soll J, 14-3-3 proteins: a highly conserved, widespread family of eukaryotic proteins Trend Biochem Sci 17:498–501, 1992
Ferl RJ, Manak MS, Reyes MF, The 14-3-3s Genome Biol 3:3010.1–3010.7, 2002
Moore BW, Perez VJ, 1967 Specific acid proteins in the nervous system. In: Carlson FD, ed Physiological and Biochemical Aspects of Nervous Integration. Prentice Hall/Woods Hole, Woods Hole, pp 343–359
van Hemert MJ, Steensma HY, van Heusden GP, 14-3-3 proteins: key regulators of cell division, signalling and apoptosis Bioessays 23:936–946, 2001
Boston PF, Jackson P, Kynoch PAM, Thompson RJ, Purification, properties, and immunohistochemical localisation of human brain 14-3-3 protein J Neurochem 38:1466–1474, 1982
Baxter HC, Fraser JR, Liu WG, Forster JL, Clokie S, Steinacker P, Otto M, Bahn E, Wiltfang J, Aitken A, Specific 14-3-3 isoform detection and immunolocalization in prion diseases Biochem Soc Trans 30:387–391, 2002
Fu H, Subramanian RR, Masters SC, 14-3-3 proteins: structure, function, and regulation Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 40:617–647, 2000
Martin H, Patel Y, Jones D, Howell S, Robinson K, Aitken A, Antibodies against the major brain isoforms of 14-3-3 protein. An antibody specific for the N-acetylated amino-terminus of a protein FEBS Lett 331:296–303, 1993
Pozuelo Rubio M, Geraghty KM, Wong BH, Wood NT, Campbell DG, Morrice N, Mackintosh C, 14-3-3-Affinity purification of over 200 human phosphoproteins reveals new links to regulation of cellular metabolism, proliferation, and trafficking Biochem J 379:395–408, 2004
Hermeking H, The 14-3-3 cancer connection Nat Rev Cancer 3:931–43, 2003
Zha J, Harada H, Yang E, Jockel J, Korsmeyer SJ, Serine phosphorylation of death agonist BAD in response to survival factor results in binding to 14-3-3 not BCL-XL Cell 87:619–628, 1996
Xing H, Zhang S, Weinheimer C, Kovacs A, Muslin AJ, 14-3-3 proteins block apoptosis and differentially regulate MAPK cascades EMBO J 19:349–358, 2000
Subramanian RR, Masters SC, Zhang H, Fu H, Functional conservation of 14-3-3 isoforms in inhibiting Bad-induced apoptosis Experimental Cell Research 271:142–151, 2001
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME, Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor Cell 96:857–868, 1999
Basu S, Totty NF, Irwin MS, Sudol M, Downward J, Akt phophorylates the Yes-associated protein, YAP, to induce interaction with 14-3-3 and attenuation of p73-mediated apoptosis Mol Cell 11:11–23, 2003
Zhang L, Chen J, Fu H, Suppression of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1-induced cell death by 14-3-3 proteins Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:8511–8515, 1999
Nomura M, Shimizu S, Sugiyama T, Narita M, Ito T, Matsuda H, Tsujimoto Y, 14-3-3 Interacts directly with and negatively regulates pro-apoptotic Bax J Biol Chem 278:2058–2065, 2003
Craparo A, Freund R, Gustafson TA, 14-3-3 (epsilon) interacts with the insulin-like growth factor I receptor and insulin receptor substrate I in a phosphoserine-dependent manner J Biol Chem 272:11663–11669, 1997
Bonnefoy-Berard N, Liu YC, von Willebrand M, Sung A, Elly C, Mustelin T, Yoshida H, Ishizaka K, Altman A, Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity by association with 14-3-3 proteins in T cells Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:10142–10146, 1995
Zhang P., Chan SL, Fu W, Mendoza M, Mattson MP, TERT suppresses apoptotis at a premitochondrial step by a mechanism requiring reverse transcriptase activity and 14-3-3 protein binding ability FASEB J 17:767–769, 2003
Beyaert R, Heyninck K, Van Huffel S, A20 and A20-binding proteins as cellular inhibitors of nuclear factor-κB-dependent gene expression and apoptosis Biochem. Pharmacol. 60:1143–1151, 2000
Kleihues P, Cavenee WK, Pathology and genetics of tumours of the nervous system. LARC Press, Lyon, 2000, pp 6–7
Kawamoto Y, Akiguchi I, Nakamura S, Honjyo Y, Shibasaki H, Budka H, 14-3-3 proteins in Lewy bodies in Parkinson disease and diffuse Lewy body disease brains J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:245–253, 2002
Kawamoto Y, Akiguchi I, Nakamura S, Budka H, Accumulation of 14-3-3 proteins in glial cytoplasmic inclusions in multiple system atrophy Ann Neurol 52:722–731, 2002
Remmele W, Hildebrand U, Hienz HA, Klein PJ, Vierbuchen M, Behnken LJ, Heicke B, Scheidt E, Comparative histological, histochemical, immunhistochemical and biochemical studies on estrogen receptors, lectin receptors, and Barr bodies in human breast cancer Virchows Arch 409:127–147, 1986
Boston PF, Jackson P, Thompson RJ, Human 14-3-3 protein: radioimmunoassay, tissue distribution, and cerebrospinal fluid levels in patients with neurological disorders J Neurochem 38:1475–1482, 1982
Kawamoto Y, Akiguchi I, Kovacs GG, Flicker H, Budka H, Increased 14-3-3 immunoreactivity in glial elements in patients with multiple sclerosis Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 107:137–143, 2004
Rudin CM, Thompson CB, Apoptosis and disease: regulation and clinical relevance of programmed cell death Annu Rev Med 48:267–281, 1997
Newton HB, Molecular neuro-oncology and the development of targeted therapeutic strategies for brain tumors. Part 4:p53 signaling pathway Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 5:177–191, 2005
Johnson MD, Okedli E, Woodard A, Toms SA, Allen GS, Evidence for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt-p7S6 K pathway activation and transduction of mitogenic signals by platelet-derived growth factor in meningioma cells J Neurosurg 97:668–675, 2002
Mawrin C, Kirches E, Dietzmann K, Roessner A, Boltze C, Expression pattern of apoptotic markers in vestibular schwannomas Pathol Res Pract 198:813–819. 2002
Kulig E, Jin L, Qian X, Horvath E, Kovacs K, Stefaneanu L, Scheithauer BW, Lloyd RV, Apoptosis in nontumorous and neoplastic human pituitaries: expression of the Bcl-2 family of proteins Am J Pathol 154:767–774, 1999
Nakasu S, Matsumura K, Nioka H, Handa J, Lectin binding and bcl-2 protein expression in craniopharyngiomas Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 34:429–435, 1994
Masters SC, Fu H, Survival-promoting functions of 14-3-3 proteins Biochem Soc Trans 30:360–365, 2002
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Wei Yan and Dr. Fucheng Ma (Department of Pathology, Xijing Hospital, Fourth Military Medical University) for confirming the histopathological diagnosis of all the samples used in this research and helping to perform microscopic analysis for 14-3-3 immunoreactivity. We thank Dr. Fubo Xue’s help in statistical analysis. And we also thank Ms. Lei Song and Ms. Xiling Wang for material preparing for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, WD., Zhang, X., Zhang, JN. et al. Immunocytochemical detection of 14-3-3 in primary nervous system tumors. J Neurooncol 77, 125–130 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-005-9027-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-005-9027-7