Summary
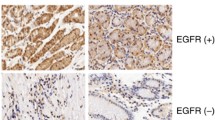
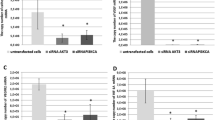
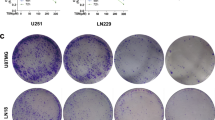
Objectives:To study the inhibitory effects of plasmid-based siRNA targeting human epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) on tumor proliferation and invasion of TJ905 glioblastoma cells. Methods: Two siRNA expression constructs targeting human EGFR extracellular domain (516–536) and catalytic domain (2400–2420) were transfected into TJ905 cell as mediated by Lipofectamine. Immunofluorescence assay and Western blotting were used to detect EGFR expression. Cell cycle was analyzed by flow cytometry, cell proliferative activity was measured by MTT assay. The expression and enzymatic activity of MMP9 were measured by Western blotting and gelatin zymography. Cell invasive capability was evaluated by Transwell method. Results: The expression of EGFR was knocked-down by 90 and 92, respectively in siRNA constructs transfected groups as indicated by immunofluorescence assay and Western blotting. The flow cytometric analysis showed that the S phase fraction (SPF) was lowered in both siRNAs transfected cells than that in parental cells and the cells transfected with empty vector. Compared to parental cells and the cells transfected with empty vector, the survival rates of glioma cells transfected with the siRNAs dramatically dropped down from the first day after implantation (P<0.05) as indicated by MTT assay. Meanwhile, the expression and enzymatic activity of MMP9 decreased significantly in siRNAs transfected in TJ905 cells, and cell invasive potential was also greatly inhibited in the Transwell study. Conclusion: The siRNA expression constructs targeting EGFR could specifically suppress EGFR expression, inhibit cell growth, induce cell cycle arrest and suppress invasion. The plasmid-based siRNA targeting human EGFR approach should be a new strategy for gene therapy of malignant gliomas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A Wells (1999) ArticleTitleEGF receptor. Review Int J Biochem Cell 31 637–643 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1357-2725(99)00015-1 Occurrence Handle10404636
J Mendelsohn J Baselga (2000) ArticleTitleThe EGF receptor family as targets for cancer therapy Oncogene 19 6550–6665 Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.onc.1204082 Occurrence Handle11426640
XW Liu PY Pu ZX Gao et al. (1998) ArticleTitleStudy on the expression of epidermal growth factor receptor gene in human gliomas Chin J Neurosurg 14 71–74
P Pu X Liu A Liu et al. (2000) ArticleTitleInhibitory effect of antisense epidermal growth factor receptor RNA on the proliferation of rat C6 glioma cells in vitro and in vivo J Neurosurg 92 132–139 Occurrence Handle10616092
A Fire S Xu CC Mello et al. (1998) ArticleTitlePotent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans Nature 391 806–811 Occurrence Handle10.1038/35888 Occurrence Handle9486653
PD Zamore (2001) ArticleTitleRNA interference: listening to the sound of silence Nat Struct Biol 8 746–751 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nsb0901-746 Occurrence Handle11524674
T Sijen F Simmer A Fire et al. (2001) ArticleTitleOn the role of RNA amplification in dsRNA-triggered gene silencing Cell 107 465–476 Occurrence Handle11719187
SL Wang F Li PY Pu et al. (1996) ArticleTitleThe establishment and characteristics of human glioblastoma cell lines TJ899 and TJ905 J Tianjin Med 12 416–418
WK Cavenee (2002) ArticleTitleGenetics and new approaches to cancer therapy Carcinogenesis 23 683–686 Occurrence Handle10.1093/carcin/23.5.683 Occurrence Handle12016138
SR Datta A Brunet ME. Greenberg (1999) ArticleTitleCellular survival: a play in three Akts Gene Dev 13 2905–2927 Occurrence Handle10.1101/gad.13.22.2905 Occurrence Handle10579998
A Lal CA Glazer HM Martison et al. (2002) ArticleTitleMutant epidermal growth factor receptor up-regulated molecular effectors of tumor invasion Cancer Res 62 3335–3339 Occurrence Handle12067969
Pu PY, Kang CS, Li J, et al.: The effects of antisense AKT2 RNA on the inhibition of malignant glioma cell growth in vitro and in vivo. J Neurooncol (in press)
Pu PY, Kang CS, Li J, et al.: Antisense and dominant-negative AKT2 cDNA inhibits glioma cell invasion. Tumor Biol (in press)
T Kubiatowski T Jang MB Lachyankar et al. (2001) ArticleTitleAssociation of increased phosphotidylinositol 3-kinase signaling with increased invasiveness and gelatinase activity in malignant gliomas J Neurosurg 95 379–380 Occurrence Handle11565856
HB Newton (2003) ArticleTitleMolecular neuro-oncology and development of targeted therapeutic strategies for brain tumors. Part 1: growth factor and Ras signaling pathways Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 3 595–614
HB Newton (2004) ArticleTitleMolecular neuro-oncology and development of targeted therapeutic strategies for brain tumors. Part 2: PI3K/AKT/PTEN, mTOR,SHH/PTCH and angiogenesis Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 4 105–128 Occurrence Handle10.1586/14737140.4.1.105 Occurrence Handle14748662
DM Dykxhoorn CD Novina PA Sharp (2003) ArticleTitleKilling the messenger: short RNAs that silence gene expression Nat Rev 4 457–467 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nrm1129 Occurrence Handle12778125
P Nagy DJ Arndt-Jovin TM Jovin (2003) ArticleTitleSmall interfering RNAs suppress the expression of endogenous and GFP-fused epidermal growth factor receptor (erbB1) and induce apoptosis in erbB1-overexpressing cells Exp Cell Res 285 39–49 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0014-4827(02)00050-2 Occurrence Handle12681285
L Zhang N Yang A Mohamed-Hadley et al. (2003) ArticleTitleVector-based RNAi, a novel tool for isoform-specific knock-down of VEGF and anti-angiogenesis gene therapy of cancer Biochem Biophys Res Commun 303 1169–1178 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0006-291X(03)00495-9 Occurrence Handle12684059
T Holen M Amrzguioui MT Wiiger et al. (2002) ArticleTitlePositional effects of short interfering RNAs targeting the human coagulation trigger tissue factor Nucleic Acids Res. 30 1757–1766 Occurrence Handle10.1093/nar/30.8.1757 Occurrence Handle11937629
J Harborth SM Elbashir K Vandenburgh et al. (2003) ArticleTitleSequence, chemical and structural variation of small interfering RNAs and short hairpin RNAs and the effect on mammalian gene silencing Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 13 83–105 Occurrence Handle10.1089/108729003321629638 Occurrence Handle12804036
UT Kumiko N Yuki Ti Fumitaka et al. (2004) ArticleTitleGuidelines for the selection of highly effective siRNA sequences for mammalian and chick RNA interference Nucleic Acids Res 32 936–948 Occurrence Handle10.1093/nar/gkh247 Occurrence Handle14769950
Y Zhang YF Zhang J Bryant et al. (2004) ArticleTitleIntravenous RNA interference gene therapy targeting the human epidermal growth factor receptor prolongs survival in intracranial brain cancer Clin Cancer Res 10 3667–3677
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, CS., Pu, PY., Li, YH. et al. An in vitro Study on the Suppressive Effect of Glioma Cell Growth Induced by Plasmid-Based Small Interference RNA (siRNA) Targeting Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. J Neurooncol 74, 267–273 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-004-8322-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-004-8322-z