Abstract
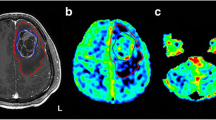
Background and purpose: Three-dimensional anisotropy contrast magnetic resonance axonography (3DAC) is a technique for diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI) that offers reliable visualization of the pyramidal tracts. This study evaluated condition of the pyramidal tract using 3DAC in glioblastoma patients with hemiparesis. Methods: In 18 glioblastoma patients before surgery, 3DAC findings of the pyramidal tract responsible for hemiparesis were compared with finding from proton density-weighted imaging (PDWI). To estimate extent of pyramidal tract destruction, fractional anisotropy (FA) values using diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging were examined for both the responsible and non-pathological pyramidal tracts. Results: In all five patients for whom PDWI indicated no hyperintense foci in the responsible pyramidal tract, 3DAC demonstrated no change in color. When PDWI revealed hyperintense foci, 3DAC showed two types of findings: no color change (five patients); or obscured dark area (six patients). When 3DAC showed a dark area, mean FA value in the responsible tract was significantly lower than that for the non-pathological tract.Conclusion: When PDWI indicates hyperintense foci on the pyramidal tract, 3DAC allows prediction of pyramidal tract condition, such as large tumor invasion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CC Gallen DF Sobel T Waltz M Aung B Copeland BJ Schwartz EC Hirschkoff FE. Bloom (1993) ArticleTitleNoninvasive presurgical neuromagnetic mapping of somatosensory cortex Neurosurgery 33 260–268 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyA2snit1w%3D Occurrence Handle8367048
SW Atlas RS Howard Suffix2nd J Maldjian D Alsop JA Detre J Listerud M D’Esposito KD Judy E Zager M. Stecker (1996) ArticleTitleFunctional magnetic resonance imaging of regional brain activity in patients with intracerebral gliomas: findings and implications for clinical management Neurosurgery 38 329–338 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-199602000-00019 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiD383ntVU%3D Occurrence Handle8869061
GR Cosgrove BR Buchbinder H. Jiang (1996) ArticleTitleFunctional magnetic resonance imaging for intracranial navigation Neurosurg Clin N Am 7 313–322 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymB1MfltlU%3D Occurrence Handle8726444
MS Berger RC. Rostomily (1997) ArticleTitleLow grade gliomas functional mapping resection strategies, extent of resection, and outcome J Neuro-Oncol 34 85–101 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1005715405413 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiA2MzotFA%3D
N Nakasato T Kumabe A Kanno S Ohtomo K Mizoi T. Yoshimoto (1997) ArticleTitleNeuromagnetic evaluation of cortical auditory function in patients with temporal lobe tumors J Neurosurg 86 610–618 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiB3svhtlA%3D Occurrence Handle9120623
H Karibe H Shimizu T Tominaga K Koshu T. Yoshimoto (2000) ArticleTitleDiffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the early evaluation of corticospinal tract injury to predict functional motor outcome in patients with deep intracerebral hemorrhage J Neurosurg 92 58–63 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c%2FotFyhuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10616083
T Krings MH Reinges R Thiex JM Gilsbach A. Thron (2001) ArticleTitleFunctional and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images of space-occupying lesions affecting the motor system: imaging the motor cortex and pyramidal tracts J Neurosurg 95 816–824 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MnltVOktg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11702872
RL Cooper DB Chang AC Young CJ Martin D. Ancker-Johnson (1974) ArticleTitleRestricted diffusion in biophysical systems Experiment Biophys J 14 161–177 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSuC2cnkslQ%3D
D. Le Bihan (1995) ArticleTitleDiffusion, perfusion and functional magnetic resonance imaging J Mal Vasc 20 203–214 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymD2snktV0%3D Occurrence Handle8543902
PW Schaefer PE Grant RG. Gonzalez (2000) ArticleTitleDiffusion-weighted MR imaging of the brain Radiology 217 331–345 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3crhtFertw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11058626
H Aoyama K Kamada H Shirato F Takeuchi S Kuriki Y Iwasaki K. Miyasaka (2003) ArticleTitleVisualization of the corticospinal tract pathway using magnetic resonance axonography and magnetoencephalography for stereotactic irradiation planning of arteriovenous malformations Radiother Oncol 68 27–32 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0167-8140(03)00032-X Occurrence Handle12885449
AI Holodny TH Schwartz M Ollenschleger WC Liu M. Schulder (2001) ArticleTitleTumor involvement of the corticospinal tract: diffusion magnetic resonance tractography with intraoperative correlation J Neurosurg. 95 1082 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38%2FktVyjsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11765829
H Parmar YY Sitoh TT. Yeo (2004) ArticleTitleCombined magnetic resonance tractography and functional magnetic resonance imaging in evaluation of brain tumors involving the motor system J Comput Assist Tomogr 28 551–556 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00004728-200407000-00019 Occurrence Handle15232390
T Watanabe Y Honda Y Fujii M Koyama H Matsuzawa R. Tanaka (2001) ArticleTitleThree-dimensional anisotropy contrast magnetic resonance axonography to predict the prognosis for motor function in patients suffering from stroke J Neurosurg 94 955–960 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3Mzks12ktw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11409525
Watanabe T, Honda Y, Fujii Y, Koyama M, Tanaka R (2004). Serial evaluation of axonal function in patients with brain death by using anisotropic diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosurg 56–60
BP Witwer R Moftakhar KM Hasan P Deshmukh V Haughton A Field K Arfanakis J Noyes CH Moritz ME Meyerand HA Rowley AL Alexander B. Badie (2002) ArticleTitleDiffusion-tensor imaging of white matter tracts in patients with cerebral neoplasm J Neurosurg 97 568–575 Occurrence Handle12296640
T Nakada H Matsuzawa IL. Kwee (1994) ArticleTitleMagnetic resonance axonography of the rat spinal cord Neuroreport 27 2053–2056
T Nakada N Nakayama Y Fujii IL. Kwee (1999) ArticleTitleClinical application of three-dimensional anisotropy contrast magnetic resonance axonography Technical note. J Neurosurg 90 791–795 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3gsl2ksA%3D%3D
T Inoue H Shimizu T. Yoshimoto (1999) ArticleTitleImaging the pyramidal tract in patients with brain tumors Clin Neurol Neurosurg 101 4–10 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0303-8467(98)00069-9 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3nslKqug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10350195
T Inoue H Shimizu T Yoshimoto H. Kabasawa (2001) ArticleTitleSpatial functional distribution in the corticospinal tract at the corona radiata: a three-dimensional anisotropy contrast study Neurol Med Chir 41 293–299 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MvgslWiuw%3D%3D
VA Coenen T Krings L Mayfrank RS Polin MH Reinges A Thron JM. Gilsbach (2001) ArticleTitleThree-dimensional visualization of the pyramidal tract in a neuronavigation system during brain tumor surgery: first experiences and technical note Neurosurgery 49 86–93 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-200107000-00013 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MzosFymtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11440464
AI Holodny TH Schwartz M Ollenschleger WC Liu M. Schulder (2001) ArticleTitleTumor involvement of the corticospinal tract: diffusion magnetic resonance tractography with intraoperative correlation J Neurosurg 95 1082 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38%2FktVyjsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11765829
K Kamada K Houkin Y Iwasaki F Takeuchi S Kuriki K Mitsumori Y. Sawamura (2002) ArticleTitleRapid identification of the primary motor area by using magnetic resonance axonography J Neurosurg 97 558–567 Occurrence Handle12296639
H Kashimura T Inoue K Ogasawara Ogawa. (2003) ArticleTitlePreoperative evaluation of neural tracts by use of three-dimensional anisotropy contrast imaging in a patient with brainstem cavernous angioma: technical case report Neurosurgery 52 1226–1230
RH Darwin BP Drayer SJ Riederer HZ Wang JR. MacFall (1986) ArticleTitleT2 estimates in healthy and diseased brain tissue: a comparison using various MR pulse sequences Radiology 160 375–381 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BimB28%2FmtFI%3D Occurrence Handle3726116
NG Papadakis D Xing GC Houston JM Smith MI Smith MF James AA Parsons CL Huang LD Hall TA. Carpenter (1999) ArticleTitleA study of rotationally invariant and symmetric indices of diffusion anisotropy Magn Reson Imaging 17 IssueID6 881–892 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0730-725X(99)00029-6 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1MzjtFSjtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10402595
AG Sorensen O Wu WA Copen TL Davis RG Gonzalez WJ Koroshetz TG Reese BR Rosen VJ Wedeen RM. Weisskoff (1999) ArticleTitleHuman acute cerebral ischemia: detection of changes in water diffusion anisotropy by using MR imaging Radiology 212 IssueID3 785–792 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1MvgslKrtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10478247
S. Brunnstrom (1966) ArticleTitleMotor testing procedures in hemiplegia J APTA 46 357–375 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CCmC3c7kvVA%3D
MG. Yasargil (1993) Microneurosurgery IV A (In 4 volumes) Georg Thieme Stuttgart/New York Verlag. 127–134
P Barzo A Marmarou P Fatouros K Hayasaki F. Corwin (1997) ArticleTitleContribution of vasogenic and cellular edema to traumatic brain swelling measured by diffusion-weighted imaging J Neurosurg 87 900–907 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2FksVSmug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9384402
M Castillo SK. Mukherji (1999) ArticleTitleEarly abnormalities related to postinfarction Wallerian degeneration: evaluation with MR diffusion-weighted imaging J Comput Assist Tomogr 23 1004–1007 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00004728-199911000-00034 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c%2FlsFGjsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10589585
P Mukherjee MM Bahn RC McKinstry JS Shimony TS Cull E Akbudak AZ Snyder TE. Conturo (2000) ArticleTitleDifferences between gray matter and white matter water diffusion in stroke: diffusion-tensor MR imaging in 12 patients Radiology 215 211–220 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c3hslWqsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10751489
H Igarashi Y Katayama T Tsuganezawa M Yamamuro A Terashi C. Owan (1998) ArticleTitleThree-dimensional anisotropy contrast (3DAC) magnetic resonance imaging of the human brain: application to assess Wallerian degeneration Intern Med 37 662–668 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1cvhs12gsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9745851
NK Gonatas HM Zimmerman S. Levine (1963) ArticleTitleUltrastructure of inflammation with edema in the rat brain Am J Pathol 42 455–469 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CC2C2c%2FmslQ%3D Occurrence Handle13948960
RB Schwartz RV Mulkern H Gudbjartsson F. Jolesz (1998) ArticleTitleDiffusion-weighted MR imaging in hypertensive encephalopathy: clues to pathogenesis AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19 859–862 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c3ntlGmtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9613500
T Sugahara Y Korogi M Kochi I Ikushima Y Shigematu T Hirai T Okuda L Liang Y Ge Y Komohara Y Ushio M. Takahashi (1999) ArticleTitleUsefulness of diffusion-weighted MRI with echo-planar technique in the evaluation of cellularity in gliomas J Magn Reson Imaging 9 53–60 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1522-2586(199901)9:1<53::AID-JMRI7>3.0.CO;2-2 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M7ltlOhsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10030650
K Okamoto J Ito K Ishikawa K Sakai S. Tokiguchi (2000) ArticleTitleDiffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging in differential diagnosis of brain tumors and tumor-like conditions Eur Radiol 10 1342–1350 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s003309900310 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M%2Flt1Sgtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10939505
KM Gauvain RC McKinstry P Mukherjee A Perry JJ Neil BA Kaufman RJ. Hayashi (2002) ArticleTitleEvaluating pediatric brain tumor cellularity with diffusion-tensor imaging AJR Am J Roentgenol 177 449–454
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beppu, T., Inoue, T., Kuzu, Y. et al. Utility of three-dimensional anisotropy contrast magnetic resonance axonography for determining condition of the pyramidal tract in glioblastoma patients with hemiparesis. J Neurooncol 73, 137–144 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-004-3340-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-004-3340-4