Abstract
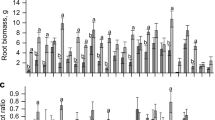
Potassium has important physiological functions in eucalypt plantations, increasing their productivity when applied to soil via mineral fertilizers. There is interest in identifying alternative sources to KCl owing to its high cost and limited reserves. The aim of the study was to test the effect of replacing KCl with NaCl and phonolite rock powder. Two comparisons were made: (1) application of 283 kg ha−1 of KCl compared with that of 2125 kg ha−1 of phonolite rock powder (equivalent to 170 kg ha−1 of K2O in both treatments); (2) application of 139 kg ha−1 of NaCl compared with that of 183 kg ha−1 of KCl (equivalent to 2.33 kmol Na and K, respectively). Radial growth, soil water content, leaf water potential (Ψ), accumulated transpiration, stem volume and biomass increment, as well as water use efficiency (WUE) were evaluated. In the first comparison, both fertilizations presented equal values for all characteristics evaluated. In the second, the accumulated transpiration in trees fertilized with KCl was 17% higher than that in plants fertilized with NaCl. In contrast, the WUE was 20% higher in the trees fertilized with NaCl than in those fertilized with KCl, reflecting the lower water consumption for the same increment in stem volume and biomass. We conclude that phonolite rock powder and NaCl are possible substitutes for conventional K fertilization performed with KCl.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida JCR, Laclau JP, Gonçalves JLM, Ranger J, Saint-André L (2010) A positive growth response to NaCl applications in Eucalyptus plantations established on K-deficit soils. For Ecol Manag 259:1786–1795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2009.08.032
Alvares CA, Stape JL, Sentelhas PC, Gonçalves JLM, Sparovek G (2013) Köppen’s climate classification map for Brazil. Meteorol Z 22:711–728. https://doi.org/10.1127/0941-2948/2013/0507
Bassaco MVM, Motta ACV, Pauletti V, Prior SA, Nisgoski S, Ferreira CF (2018) Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium requirements for Eucalyptus urograndis plantations in southern Brazil. New For 49:681–697. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-018-9658-0
Battie-Laclau P, Laclau JP, Piccolo MC, Arenque BC, Beri C, Mietton L, Muniz MRA, Jordan-Meille L, Buckeridge MS, Nouvellon Y, Ranger J, Bouillet JP (2013) Influence of potassium and sodium nutrition on leaf area components in Eucalyptus grandis trees. Plant Soil 371:19–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1663-7
Battie-Laclau P, Laclau JP, Beri C, Mietton L, Muniz MRA, Arenque BC, Piccolo MC, Jordan-Meille L, Bouillet JP, Nouvellon Y (2014a) Photosynthetic and anatomical responses of Eucalyptus grandis leaves to potassium and sodium supply in a field experiment. Plant Cell Environ 37:70–81. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12131
Battie-Laclau P, Laclau JP, Domec JC, Christina M, Bouillet JP, Piccolo MC, Gonçalves JLM, Moreira RM, Krusche AV, Bouvet JM, Nouvellon Y (2014b) Effects of potassium and sodium supply on drought-adaptive mechanisms in Eucalyptus grandis plantations. New Phytol 203:401–413. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12810
Battie-laclau P, Rojas JSD, Christina M, Nouvellon Y, Bouillet JP, Piccolo MC, Moreira MZ, Gonçalves JLM, Roupsard O, Laclau JP (2016) Potassium fertilization increases water-use efficiency for stem biomass production without affecting intrinsic water-use efficiency in Eucalyptus grandis plantations. For Ecol Manag 364:77–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2016.01.004
Briskin DP, Bloom A (2013) Nutrição mineral. In: Taiz L, Zeiger E (eds) Fisiologia vegetal. Artmed, Porto Alegre
Broadley M, Brown P, Cakmak I, Ma JF, Rengel Z, Zhao F (2012) Beneficial elements. In: Marschner H (ed) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Elsevier, London
Camargo OA, Moniz AC, Jorge JA, Valadares JMAS (2009) Métodos de Análise Química. Mineralógica e Física de Solos do Instituto Agronômico de Campinas, IAC, Campinas
Christina M, Laclau JP, Gonçalves JLM, Jourdan C, Nouvellon Y, Bouillet JP (2011) Almost symmetrical vertical growth rates above and below ground in one of the world’s most productive forests. Ecosphere 2:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1890/ES10-00158.1
Christina M, Maire G, Battie-Laclau P, Nouvellon Y, Bouillet JP, Jourdan C, Gonçalves JLM, Laclau JP (2015) Measured and modeled interactive effects of potassium deficiency and water deficit on gross primary productivity and light-use efficiency in Eucalyptus grandis plantations. Glob Change Biol 21:2022–2039. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12817
Cortes GP, Ferreira RC, Cortes GP, Rampazzo L, Ferreira LC (2010) Fonolito como substituto do cloreto de potássio e/ou outras fontes de potássio na agricultura e pecuária no brasil. In: 1º Congresso Brasileiro de Rochagem, Brasília
DNPM (2016) Sumário mineral. Departamento Nacional de Produção Mineral, DNPM, Rio de Janeiro
Erel R, Ben-Gal A, Dag A, Schwartz A, Yermiyahu U (2014) Sodium replacement of potassium in physiological processes of olive trees (var. Barnea) as affected by drought. Tree Physiol 34:1102–1117. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpu081
FAO (2017) World fertilizer trends andoutlook 2020. Food and Agriculture Organization, Rome
Faria GE, Barros NF, Novais RF, Lima JC, Teixeira JL (2002) Yield and nutritional status of coppiced Eucalyptus stands as affected by potassium applied at planting time. Rev Árvore 26:577–584. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-67622002000500008
Fernandes FRC, Luz AB, Castilhos ZC (2010) Agrominerais para o Brasil. CETEM/MCT, Rio de Janeiro
Fisher RF, Binkley D (2000) Ecology and management of forest soils. Wiley, New York, p 489
Forrester DI (2013) Growth responses to thinning, pruning and fertilizer application in Eucalyptus plantations: a review of their production ecology and interactions. For Ecol Manag 310:336–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2013.08.047
Fromm J (2010) Wood formation of trees in relation to potassium and calcium nutrition. Tree Physiol 30:1140–1147. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpq024
Fuchs S, Leuschner C, Link R, Coners H, Schuldt B (2017) Calibration and comparison of thermal dissipation, heat ratio and heat field deformation sap flow probes for diffuse-porous trees. Agric For Meteorol 244–245:151–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2017.04.003
Gattward JN, Almeida AAF, Souza Junior JO, Gomes FP, Kronzucker HJ (2012) Sodium–potassium synergism in Theobroma cacao: stimulation of photosynthesis, water-use efficiency and mineral nutrition. Physiol Plant 146:350–362. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2012.01621.x
Gomes FP, Garcia CH (1993) A determinação de equações volumétricas na engenharia florestal. IPEF, Piracicaba
Gonçalves JLM (2011) Fertilização de Plantação de Eucalipto. In: Gonçalves JLM, Pulito AP, Arthur JC Jr, Silva LD (eds) Encontro brasileiro de Silvicultura. PTSM/IPEF/FUPEF, Piracicaba
Gonçalves JLM, Stape JL, Laclau JP, Bouillet JP, Ranger J (2008) Assessing the effects of early silvicultural management on long-term site productivity of fast-growing eucalypt plantations: the Brazilian experience. South For J For Sci 70:105–118. https://doi.org/10.2989/SOUTH.FOR.2008.70.2.6.534
Gonçalves JLM, Alvares CA, Higa AR, Silva LD, Alfenas AC, Stahl J, Ferraz SFB, Lima WP, Brancalion PHS, Hubner A, Bouillet JPD, Laclau JP, Nouvellon Y, Epron D (2013) Integrating genetic and silvicultural strategies to minimize abiotic and biotic constraints in Brazilian eucalypt plantations. For Ecol Manag 301:6–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2012.12.030
Granier A (1985) Une nouvelle méthode pour la mesure du flux de sève brute dans le tronc des arbres. Ann Sci For 42:193–200
Hakamada R, Hubbard RM, Ferraz S, Stape JL, Lemos C (2017) Biomass production and potential water stress increase with planting density in four highly productive clonal Eucalyptus genotypes. South For J For Sci 79:251–257. https://doi.org/10.2989/20702620.2016.1256041
Hubbard RM, Stape J, Ryan MG, Almeida AC, Rojas J (2010) Effects of irrigation on water use and water use efficiency in two fast growing Eucalyptus plantations. For Ecol Manag 259:1714–1721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2009.10.028
IBA (2017) Relatório anual 2017. Indústria Brasileira de Árvores, Brazilian Tree Industry (IBÁ)
INMET (2019). http://www.inmet.gov.br/portal/index.php?r=estacoes/estacoesConvencionais. Accessed 23 Jan 2019
Kang JJ, Zhao WZ, Zhao M, Zheng Y, Yang F (2015) NaCl and Na2SiO3 coexistence strengthens growth of the succulent xerophyte Nitraria tangutorum under drought. Plant Growth Regul 77:223–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-015-0055-9
Kronzucker HJ, Coskun D, Schulze LM, Wong JR, Britto DT (2013) Sodium as nutrient and toxicant. Plant Soil 369:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1801-2
Laclau JP, Almeida JCR, Gonçalves JLM, Saint-André L, Ventura M, Ranger J, Moreira RM, Nouvellon Y (2009) Influence of nitrogen and potassium fertilization on leaflifespan and allocation of above-ground growth in Eucalyptus plantations. Tree Physiol 29:111–124. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpn010
Laclau JP, Silva EA, Lambais GR, Bernoux M, Maire G, Stape JL, Bouillet JP, Gonçalves JLM, Jourdan C, Nouvellon Y (2013) Dynamics of soil exploration by fine roots down to a depth of 10 m throughout the entire rotation in Eucalyptus grandis plantations. Front Plant Sci 4:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00243
Ma Q, Yue LJ, Zhang JL, Wu GQ, Bao AK, Wang SM (2012) Sodium chloride improves photosynthesis and water status in the succulent xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum. Tree Physiol 32:4–13. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpr098
Marcar NE, Guo J, Crawford DF (1999) Response of Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehnh., E. globulus Labill. ssp. globulus and E. grandis W.Hill to excess boron and sodium chloride. Plant Soil 208:251–257. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004594028069
Marengo JA, Alves LM (2015) Crise hídrica em São Paulo em 2014: seca e desmatamento. Geousp Espaço e Tempo 19:485–494. https://doi.org/10.11606/issn.2179-0892.geousp.2015.100879
Martins V, Silva DRG, Marchi G, Leite MCA, Martins ES, Gonçalves ASF, Guilherme LRG (2015) Effect of alternative multinutrient sources on soil chemical properties. Rev Bras Cienc Solo 39:194–204. https://doi.org/10.1590/01000683rbcs20150587
Melo EASC, Gonçalves JLM, Rocha JHT, Hakamada RE, Bazani JH, Wenzel AVA, Arthur Junior JC, Borges JS, Malheiros R, Lemos CCZ, Ferreira EVO, Ferraz AV (2016) Responses of clonal eucalypt plantations to N, P and K fertilizer application in different edaphoclimatic conditions. Forests 7:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/f7010002
Ninyerola M, Pons X, Roure JM (2000) A methodological approach of climatological modelling of air temperature and precipitation through GIS techniques. Int J Climatol 20:1823–1841. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0088(20001130)20:14%3c1823:AID-JOC566%3e3.0.CO;2-B
Qureshi TM, Ashraf MY, Bano A, Hussain F (2007) Ion partitioning, K/Ca and K/Na ratios of Eucalyptus camaldulensis grown under NaCl salinity. Pak J Bot 39:2565–2574
Raij BV, Andrade JC, Cantarella H, Quaggio JA (2001) Análise Química Para Avaliação da Fertilidade de Solos Tropicais. IAC, Campinas
Robinson N, Harper RJ, Smettem KRJ (2006) Soil water depletion by Eucalyptus spp. integrated into dryland agricultural systems. Plant Soil 286:141–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-006-9032-4
Santos HG, Jacomine PKT, Anjos LHC, Oliveira VA, Lumbreras JF, Coelho MR, Almeida JA, Cunha TJF, Oliveira JB (2013) Sistema Brasileiro de Classificação de Solos. Embrapa, Brasilia
Scolforo JRS, Thiersch CR (2004) Biometria florestal: medição, volumetria e gravimetria. UFLA/FAEPE, Lavras
Sette CR Jr, Tomazello Filho M, Dias CTS, Laclau JP (2010) Growth in diameter of Eucalyptus grandis W. Hill. ex Maiden trees and relationship with climatic variables and mineral fertilization. Rev Árvore 34:979–990. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-67622010000600003
Shoemaker HE, McLean EO, Pratt PF (1961) Buffer methods for determination of lime requirements of soils with appreciable amount of exchangeable aluminum. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 25:274–277. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1961.03615995002500040014x
Silva EA, Cassiolato AMR, Maltoni KL, Scabora MH (2008) Effects of ground basalt and organic residues on the chemical and microbiological aspects on bare subsoil and on the growth of Astronium fraxinifolium Schott. Rev Árvore 32:323–333. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-67622008000200015
Silva DRG, Marchi G, Spehar CR, Guilherme LRG, Rein TA, Soares DA, Avila FW (2012) Characterization and nutrient release from silicate rocks and influence on chemical changes in soil. Rev Bras Cienc Solo 36:951–962. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-06832012000300025
Silva PHM, Poggiani F, Libardi PL, Gonçalves AN (2013) Fertilizer management of eucalypt plantations on sandy soil in Brazil: initial growth and nutrient cycling. For Ecol Manag 301:67–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2012.10.033
Snowdon P (2002) Modeling Type 1 and Type 2 growth responses in plantations after application of fertilizer or other silvicultural treatments. For Ecol Manag 163:229–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1127(01)00582-5
Stape JL, Binkley D, Ryan MG (2004a) Eucalyptus production and the supply, use and efficiency of use of water, light and nitrogen across a geographic gradient in Brazil. For Ecol Manag 193:17–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2004.01.020
Stape JL, Binkley D, Ryan MG, Gomes AN (2004b) Water use, water limitation, and water use efficiency in a Eucalyptus plantation. Bosque 25:35–41
Subbarao GV, Ito O, Berry WL, Wheeler RM (2003) Sodium: a functional plant nutrient. Crit Rev Plant Sci 22:391–416. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352680390243495
Tatagiba SD, Pezzopane JEM, Reis EF, Dardengo MCJD, Effgen TAM (2007) Physiologic behavior of two clones of Eucalyptus in dry and rainy season. Cerne 13:149–159
Tatagiba SD, Pezzopane JEM, Reis EF (2015) Photosynthesis in Eucalyptus under different environmental conditions. Eng Agric 23:336–345. https://doi.org/10.13083/reveng.v23i4.573
Tedersoo L, May TW, Smith ME (2010) Ectomycorrhizal lifestyle in fungi: global diversity, distribution, and evolution of phylogenetic lineages. Mycorrhiza 20:217–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-009-0274-x
Teixeira AMS, Sampaio JA, Garrido FMS, Medeiros ME (2012) Evaluation of phonolite rock as a potassium fertilizer alternative. Holos 5:21–33. https://doi.org/10.15628/holos.2012.1102
Teixeira AMS, Garrido FMS, Medeiros ME, Sampaio JA (2015) Effect of thermal treatments on the potassium and sodium availability in phonolite rock powder. Int J Miner Process 145:57–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2015.07.002
Thornthwaite CW, Mather JR (1955) The water balance. Publ Climatol Lab Climatol Dresel Inst Technol 8:1–104
Whitehead D, Beadle CL (2004) Physiological regulation of productivity and water use in Eucalyptus: a review. For Ecol Manag 193:113–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2004.01.026
Wilpert K, Lukes M (2003) Ecochemical effects of phonolite rock powder, dolomite and potassium sulfate in a spruce stand on an acidified glacial loam. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 65:115–127. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022103325310
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge CAPES and FAPESP for funding the project through scholarships and to CNPq for project financing (No. 406809/2016-0) and postdoctoral scholarship (No. 150505/2014-0). We are also grateful for the financing of part of the project by Mineração Curimbaba S.A., for permission to conduct research in the study area and logistical support of International Paper, and for the technical and administrative support of the Forest Science and Research Institute (IPEF). The first author thanks Cindy Prescott and Robert Guy for their hospitality and academic discussions during the author’s study-exchange stay at the University of British Columbia (UBC), Canada (CAPES-BEX6286/15-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Toledo, F.H.S.F., de Moraes Gonçalves, J.L., Mariño, Y.A. et al. Aboveground biomass, transpiration and water use efficiency in eucalypt plantation fertilized with KCl, NaCl and phonolite rock powder. New Forests 51, 469–488 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-019-09743-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-019-09743-8