Abstract
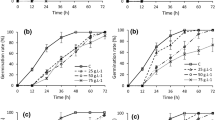
Agroforestry is a leading alternative for food security and forest conservation. A full understanding of positive and negative, i.e. allelopathic, interactions between crops and forest trees is necessary for producing crops and conserving forests especially within the threatened Mediterranean forest ecosystems. The present study explored the allelopathic effects of green and senescent leaf and soil extracts of two agroforestry trees—Pinus halepensis and Quercus coccifera—on the germination of wheat, barley, lentil, chickpea, and fababean as the major grain crops of Jordan. Results revealed that allelopathic effects reduced seed germination of these crops. Germination reduction reached a maximum of 75% in fababean treated with green extracts of Q. coccifera and differed among crops and extract sources, but not between tree species. Comparing between green and senescent leaf and soil extract, regarding their effect on germination percentage, it was noticed that these effects were similar in some crops and were different in others. Germination responses were generally different between cereals and legumes where cereals tend to be less affected by allelopathic influences than legumes, especially fababean. We suggest using cereals such as wheat and barley in agroforestry practices in the Mediterranean region of Jordan.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Eisawi D, El-Oqlah A, Oran S, Lahham J (1996) Plant biodiversity in Jordan. In: Jaradat AA (ed) Plant genetic resources of Jordan. IPGRI, Aleppo, pp 13–51
Alrababah MA, Alhamad MN, Bataineh MM, Suwaileh AF, Al-Horani AS (2007a) Arboreal diversity and aboveground biomass in a semi-arid Mediterranean forest ecosystem: case of Kufur-khal natural reserve. Jordan J Agric Sci 3(4):363–375
Alrababah MA, Alhamad MN, Suwaileh A, Algharaibeh M (2007b) Biodiversity of semi-arid Mediterranean grasslands: impact of grazing and afforestation. Appl Veg Sci 10:257–264. doi:10.1658/1402-2001(2007)10[257:BOSMGI]2.0.CO;2
AOSA (1986) Rules for testing seeds. J Seed Technol 6:1–125
De Bell DS (1971) Phytotoxic effects of cherry bark-oak. For Sci 17:180–185
El-Khawas SA, Shehata MM (2005) The allelopathic potentialities of Acacia nilotica and Eucalyptus rostrata on monocot (Zea mays L.) and dicot (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) plants. Biotechnology 4(1):23–34. doi:10.3923/biotech.2005.23.34
Fitter A (2003) Making allelopathy respectable. Science 301(5638):1337–1338. doi:10.1126/science.1089291
Garcia-Barrios L, Gonzalez-Espinosa M (2004) Change in oak to pine dominant in secondary forests may reduce shifting agriculture yields: experimental evidence from Chiapas, Mexico. Agric Ecosyst Environ 102:389–401. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2003.08.013
GCEP (2001) Conservation and sustainable use of biological diversity in Jordan. Jordan Biodiversity, First National Report, UNEP, Amman
Gliessman SR (1978) Allelopathy as a potential mechanism of dominance in the humid tropics. Trop Ecol 19:200–208
ISTA (1985) Rules for seed testing. Seed Sci Technol 13:300–520
Janeson DA (1961) Growth inhibitors in native plants of north Arizona. Rocky Mountains forest range experiment station, Research note (61), USDA
Kil BS (1992) Effect of pine allelochemicals on selected species in Korea. In: Rizvi SJH, Rizvi V (eds) Allelopathy basic applied aspects. Chapman and hall, London, pp 205–241
Kil BS (1999) Research on allelopathy in Korea. In: Narwal SS (ed) Allelopathy update: volume 1, International status. Science Publishers Inc, Enfield, pp 247–270
Kohli RK, Singh D, Verma RC (1990) Influence of eucalypt shelterbelt on winter season agroecosystems. Agric Ecosyst Environ 33(1):23–31. doi:10.1016/0167-8809(90)90141-Y
Kohli RK, Batish D, Singh HP (1998) Allelopathy and its implications in agroecosystems. J Crop Prod 1(1):169–202. doi:10.1300/J144v01n01_08
Lee IK, Monsi M (1963) Ecological studies on Pinus desiflora forest. I. Effect of plant substances on the floristic composition of undergrowth. Bot Mag 76:400–413
Levizou E, Karageorgou P, Psaras GK, Manetas Y (2002) Inhibitory effects of water soluble leaf leachates from Dittrichia viscose on lettuce root growth, statocyte development and graviperception. Flora 197:152–157
Lill RE, Waid JS (1975) Volatile phytotoxic substances formed by litter of Pinus radiata. N Z J For Sci 5:165–170
Lill RE, Mewha JA (1976) Production of ethylene by incubated litter of Pinus radiate. Soil Biol Biochem 8:61–63. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(76)90023-7
Lill RE, Mewha JA, Cole ALJ (1979) The influence of volatile substances from incubated litter of Pinus radiata on seed germination. Ann Bot (Lond) 43:81–85
McPherson JK, Thompson GL (1972) Competitive and allelopathic suppression of understory by Oklahoma oak forests. Bull Torrey Bot Club 99(6):293–300. doi:10.2307/2997071
MOA (1995) Training in management of forest and rangelands: part I. Basis of proposals for the management of forests and rangelands: a management plan for Jordan for the period 1996–2005, Department of Forestry, Ministry of Agriculture, Field Document no. 8, Amman
Nandal DPS, Bisla SS, Narwal SS, Kaushik JC (1994) Allelopathic interactions in agroforestry systems. In: Narwal SS, Tauro P (eds) Allelopathy in agriculture and forestry. Scientific Publishers, Jodhpur, pp 93–130
Narwal SS (1994a) Allelopathic problems in Indian agriculture and prospects of research. In: Narwal SS, Tauro P (eds) Allelopathy in agriculture and forestry. Scientific Publishers, Jodhpur, pp 37–57
Narwal SS (1994b) Allelopathy in crop production. Scientific Publishers, Jodhpur
Nektarios PA, Economou G, Avgoulas C (2005) Allelopathic effects of Pinus halepensis needles on turfgrasses and biosensor plants. Hortscience 40(1):246–250
Pulido FJ, Diaz M, Hidalgo de Trucios SJ (2001) Size structure and regeneration of Spanish holm oak Quercus ilex forests and dehesas: effects of agroforestry use on their long-term sustainability. For Ecol Manag 146:1–3. doi:10.1016/S0378-1127(00)00443-6
Reigosa MJ, Sanchez-Moreiras A, Gonzalez L (1999) Ecophysiological approach in allelopathy. Crit Rev Plant Sci 18(5):577–608. doi:10.1016/S0735-2689(99)00392-5
Richardson DR, Williamson GB (1988) Allelopathic effects of shrubs of sand pine shrub on Pines and grasses of the sand hills. For Sci 34:592–602
Rizvi SJH, Tahir M, Rizvi V, Kohli RK, Ansari A (1999) Allelopathic interactions in agroforestry systems. Crit Rev Plant Sci 18(6):773–796. doi:10.1080/07352689991309487
Russo VM, Webber CL, Myers DL (1997) Kenaf extract affects germination and post germination development of weed, grass and vegetable seeds. Ind Crops Prod 6:59–69. doi:10.1016/S0926-6690(96)00206-3
SAS Institute Inc (2003) JMPIN User’s Guide. Cary
Singh D, Kohli RK (1992) Impact of Eucalyptus tereticornis Sm. Shelterbelts on crops. Agrofor Syst 20(3):253–266. doi:10.1007/BF00053143
Singh SK, Verma KR (1988) Allelopathic effects of leachates and extracts of Pinus roxburghii on legumes in Kumaon, Himalayes. Indian J Agric Sci 58:412–413
Singh HP, Batish DR, Kohli RK (1998) Effect of Poplar (Populus deltoids) shelterbelt on the growth and yield of wheat in Punjab, India. Agrofor Syst 40(2):207–213. doi:10.1023/A:1005949818756
Singh HP, Kohli RK, Batish DR (1999a) Impact of Populus deltoides and Dalbergia sissoo shelterbelts on wheat—a comparative study. Int Tree Crop J 10(1):51–60
Singh HP, Kohli RK, Batish DR, Kaushal PS (1999b) Allelopathy of Gymnospermous Trees. J For Res 4:245–254. doi:10.1007/BF02762256
Singh HP, Kohli RK, Batish DR (2001) Allelopathic interference of Populus deltoides with some winter season crops. Agron 21(2):139–146. doi:10.1051/agro:2001114
Vyvyan JR (2002) Allelochemicals as leads for new herbicides and agrochemicals. Tetrahedron 58:1631–1646. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(02)00052-2
Zohary M (1962) Plant life of Palestine. The Ronald Press Company, New York
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of the Deanship of Scientific Research at the Jordan University of Science & Technology (JUST). We also acknowledge the lab assistance of Mr. Ahmad Alqudah. Seeds were kindly provided by National Center for Agricultural Research and Extension (NCARE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alrababah, M.A., Tadros, M.J., Samarah, N.H. et al. Allelopathic effects of Pinus halepensis and Quercus coccifera on the germination of Mediterranean crop seeds. New Forests 38, 261–272 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-009-9145-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-009-9145-8