Abstract
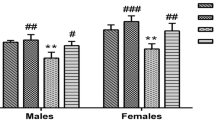
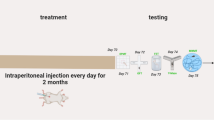
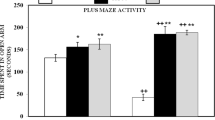
Aluminum (Al) is a potentially toxic element causing many neuropathological and behavioral alterations such as affective and cognitive disorders. Recently, several studies described melatonin (MEL) as an effective antidepressant and anxiolytic substance. This study aimed to assess the effects of MEL and Al combination on affective and cognitive behavior and oxidative stress in male Wistar rats. Animals were injected intraperitoneally with saline (0.9% NaCl), MEL (4 mg/kg), Al (1 mg/kg) or MEL (4 mg/kg) + Al (1 mg/kg) for 8 weeks. After the treatment period, open-field, elevated plus maze, forced swimming test, Y-maze and Morris water maze were used to evaluate anxiety-like, depression-like behaviors, spatial learning, and memory ability. The hippocampus was taken for biochemical examination. The results revealed that MEL and Al combination exerts anxiolytic and antidepressant effects and shows a positive effect on working memory and spatial learning compared to the Al treated groups. Also, biochemical analysis showed that MEL co-administration played a neuroprotective role, increasing superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and decreasing significantly nitric oxide (NO) and lipid peroxidation (LPO) levels in rat hippocampus in the MEL+Al treated groups. In conclusion, MEL in combination with Al has both anxiolytic and antidepressant effects, improves cognitive behavior and biochemical dysfunction.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
My manuscript has no associated data.
References
Gourier-Fréry C, Fréry N (2004) Aluminium. EMC - Toxicologie-Pathologie 1:79–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emctp.2004.04.002
Maya S, Prakash T, Madhu K Das, Goli D (2016) Multifaceted effects of aluminium in neurodegenerative diseases: A review. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 83:746–754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.07.035
Walton JR (2006) Aluminum in hippocampal neurons from humans with Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroToxicology 27:385–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2005.11.007
Tan D, Reiter RJ (2019) Mitochondria : the birth place, battle ground and the site of melatonin metabolism in cells. Melatonin Research 2:44–66. https://doi.org/10.32794/mr11250011
Ding K, Xu J, Wang H, et al (2015) Melatonin protects the brain from apoptosis by enhancement of autophagy after traumatic brain injury in mice. Neurochemistry International 91:46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2015.10.008
Favero G, Franceschetti L, Bonomini F, et al (2017) Review Article Melatonin as an Anti-Inflammatory Agent Modulating Inflammasome Activation. 2017:17–19. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1835195
Carola V, D’Olimpio F, Brunamonti E, et al (2002) Evaluation of the elevated plus-maze and open-field tests for the assessment of anxiety-related behaviour in inbred mice. Behavioural Brain Research 134:49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-4328(01)00452-1
Gentsch C, Lichtsteiner M, Feer H (1987) Open field and elevated plus-maze: A behavioural comparison between spontaneously hypertensive (SHR) and Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rats and the effects of chlordiazepoxide. Behavioural Brain Research 25:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-4328(87)90003-9
Naranjo-Rodriguez EB, Osornio AO, Hernandez-Avitia E, et al (2000) Anxiolytic-like actions of melatonin, 5-metoxytryptophol, 5-hydroxytryptophol and benzodiazepines on a conflict procedure. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 24:117–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0278-5846(99)00075-5
Porsolt RD, Anton G, Blavet N, Jalfre M (1978) Behavioural despair in rats: A new model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. European Journal of Pharmacology 47:379–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-2999(78)90118-8
Benabid N, Mesfioui A, Ouichou A (2008) Effects of photoperiod regimen on emotional behaviour in two tests for anxiolytic activity in Wistar rat. Brain Research Bulletin 75:53–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2007.07.016
Sierksma ASR, Van Den Hove DLA, Pfau F, et al (2014) Improvement of spatial memory function in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice after chronic inhibition of phosphodiesterase type 4D. Neuropharmacology 77:120–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.09.015
Morris R (2008) Developments of a water1maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. Search 11:7336–7336. https://doi.org/10.1016/016510270(84)9000714
Wong AA, Brown RE (1984) Age-related changes in visual acuity, learning and memory in C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice. Neurobiology of Aging 11:47–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0270(84)90007-4
Kahloula K, Eddine D, Adli H, et al (2014) Effet de l ’ exposition chronique au nickel sur les fonctions neurocomportementales chez les rats Wistar pendant la période de développement. Toxicologie Analytique & Clinique 26:186–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxac.2014.09.056
Draper HH, Hadley M (1990) Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. Methods in enzymology 186:421–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(90)86135-i
Freitas RM, Sousa FCF, Vasconcelos SMM, et al (2004) Pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus in rats: lipid peroxidation level, nitrite formation, GABAergic and glutamatergic receptor alterations in the hippocampus, striatum and frontal cortex. Pharmacology, biochemistry, and behavior 78:327–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2004.04.004
Chao CC, Hu S, Molitor TW, et al (1992) Activated microglia mediate neuronal cell injury via a nitric oxide mechanism. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 149:2736–2741. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.149.8.2736
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: Improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Analytical Biochemistry 44:276–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(71)90370-8
Zghari O, Rezqaoui A, Ouakki S, et al (2018) Effect of Chronic Aluminum Administration on Affective and Cognitive Behavior in Male and Female Rats. 179–196. https://doi.org/10.4236/jbbs.2018.84012
Taïr K, Kharoubi O, Taïr OA, et al (2016) Aluminium-induced acute neurotoxicity in rats: Treatment with aqueous extract of Arthrophytum (Hammada scoparia). Journal of Acute Disease 5:470–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joad.2016.08.028
Buraimoh AA, Ojo SA, Hambolu JO, et al (2011) Effects of Aluminium Chloride on Anxiety-Related Behaviour. Department of Human Anatomy, Department of Veterinary Anatomy, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria. 2:65–69
Rebai O, Djebli NE (2008) Chronic Exposure to Aluminum Chloride in Mice : Exploratory Behaviors and Spatial Learning. 2:26–33
Ali AA, Ahmed HI, El-samea HAA, El-demerdash E (2016) Alzheimer ’ s Disease & Parkinsonism The Potential Effect of Caffeine and Nicotine Co-administration against Aluminum-induced Alzheimer ’ s disease in Rats. 6:. https://doi.org/10.4172/2161-0460.1000236
Sethi P, Jyoti A, Singh R, et al (2008) NeuroToxicology Aluminium-induced electrophysiological , biochemical and cognitive modifications in the hippocampus of aging rats. 29:1069–1079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2008.08.005
Sharma DR, Wani WY, Sunkaria A, et al (2013) Quercetin protects against chronic aluminum-induced oxidative stress and ensuing biochemical, cholinergic, and neurobehavioral impairments in rats. Neurotoxicity Research 23:336–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-012-9351-6
Ribes D, Colomina MT, Vicens P, Domingo JL (2008) Effects of oral aluminum exposure on behavior and neurogenesis in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. 214:293–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.08.017
Zghari O, Lamtai M, Azirar S, et al (2023) Neuroprotective Effects of Melatonin Against Neurotoxicity Induced by Intrahippocampal Injection of Aluminum in Male Wistar Rats: Possible Involvement of Oxidative Stress Pathway. Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences 11:711–719. https://doi.org/10.17582/journal.aavs/2023/11.5.711.719
Zghari O, Azirar S, Lamtai M, et al (2023) Intrahippocampal dose-dependent effects of aluminum injection on affective and cognitive response in male Wistar rat: potential role of oxidative stress. Egyptian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences 10:460–475. https://doi.org/10.1080/2314808X.2023.2229623
El Brouzi MY, Lamtai M, Zghari O, et al (2020) Intrahippocampal Effects of Nickel Injection on the Affective and Cognitive Response in Wistar Rat: Potential Role of Oxidative Stress. Biological Trace Element Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02457-5
Naila N, Makthar W, Lamtai M, et al (2021) Effect of intra-hippocampal lead injection on affective and cognitive disorders in male WISTAR rats: Possible involvement of oxidative stress. E3S Web Conf 319:2017. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202131902017
Salim S (2017) Oxidative stress and the central nervous system. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 360:201–205. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.116.237503
Auti ST, Kulkarni YA (2019) Neuroprotective effect of cardamom oil against aluminum induced neurotoxicity in rats. Frontiers in Neurology 10:. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.00399
Shaik A, Shenoy S, Anupama V, et al (2019) Antidepressants modulate behavioral, biochemical, and histological alterations induced by chronic aluminum chloride administration in wistar rats. Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics 10:16–21. https://doi.org/10.4103/jpp.JPP_135_18
Al-Amin MM, Chowdury MIA, Saifullah ARM, et al (2019) Levocarnitine Improves AlCl3-Induced Spatial Working Memory Impairment in Swiss albino Mice. Frontiers in Neuroscience 13:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00278
Jangra A, Lukhi MM, Sulakhiya K, et al (2014) Protective effect of mangiferin against lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive and anxiety-like behaviour in mice. European Journal of Pharmacology 740:337–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.07.031
Sulakhiya K, Kumar P, Jangra A, et al (2014) Honokiol abrogates lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive like behavior by impeding neuroinflammation and oxido-nitrosative stress in mice. European Journal of Pharmacology 744:124–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.09.049
Benyettou I, Kharoubi O, Hallal N, et al (2017) Aluminium-induced behavioral changes and oxidative stress in developing rat brain and the possible ameliorating role of omega-6/omega-3 ratio. Journal of Biological Sciences 17:106–117. https://doi.org/10.3923/jbs.2017.106.117
Albendea CD, Gómez-Trullén EM, Fuentes-Broto L, et al (2007) Melatonin reduces lipid and protein oxidative damage in synaptosomes due to aluminium. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology 21:261–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2007.04.002
El-Missiry MA, Shalaby F (2000) Role of β-carotene in ameliorating the cadmium-induced oxidative stress in rat brain and testis. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology 14:238–243. https://doi.org/10.1002/1099-0461(2000)14:5<238::AID-JBT2>3.0.CO;2-X
Gonzalez MA, Alvarez MDL, Pisani GB, et al (2007) Involvement of oxidative stress in the impairment in biliary secretory function induced by intraperitoneal administration of aluminum to rats. Biological Trace Element Research 116:329–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02698017
Al-Amin MM, Reza HM, Saadi HM, et al (2016) Astaxanthin ameliorates aluminum chloride-induced spatial memory impairment and neuronal oxidative stress in mice. European Journal of Pharmacology 777:60–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.02.062
Kumar V, Dip K (2014) NeuroToxicology Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in aluminium neurotoxicity and its amelioration : A review. 41:154–166
Lin MT, Beal MF (2006) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature 443:787–795
Wallace DC (1999) Mitochondrial diseases in man and mouse. Science 283:1482–1488
Xu SC, He M Di, Zhong M, et al (2010) Melatonin protects against Nickel-induced neurotoxicity in vitro by reducing oxidative stress and maintaining mitochondrial function. Journal of Pineal Research 49:86–94. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2010.00770.x
Zaky A, Mohammad B, Moftah M, et al (2013) Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 is a key modulator of aluminum-induced neuroinflammation. BMC Neuroscience 14:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-14-26
Al-olayan EM, El-khadragy MF, Moneim AEA (2015) The protective properties of melatonin against aluminium-induced neuronal injury. 196–202. https://doi.org/10.1111/iep.12122
Moncada S, Bolaños JP (2006) Nitric oxide, cell bioenergetics and neurodegeneration. Journal of Neurochemistry 97:1676–1689. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03988.x
El Mrabet F., Ouakki S, Mesfioui A, et al (2012) Pinealectomy and Exogenous Melatonin Regulate Anxiety-Like and Depressive-Like Behaviors in Male and Female Wistar Rats. Neuroscience and Medicine 03:394–403. https://doi.org/10.4236/nm.2012.34049
Ouakki S, El Mrabet FZ, Lagbouri I, et al (2013) Melatonin and Diazepam Affect Anxiety-Like and Depression-Like Behavior in Wistar Rats : Possible Interaction with Central GABA Neurotransmission. Journal of Behavioral and Brain Science 3:522–533
Corrales A, Martínez P, García S, et al (2013) Long-term oral administration of melatonin improves spatial learning and memory and protects against cholinergic degeneration in middle-aged Ts65Dn mice, a model of Down syndrome. Journal of Pineal Research 54:346–358. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12037
García T, Ribes D, Colomina MT, et al (2009) Evaluation of the protective role of melatonin on the behavioral effects of aluminum in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Toxicology 265:49–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2009.09.009
Olcese JM, Cao C, Mori T, et al (2009) Protection against cognitive deficits and markers of neurodegeneration by long-term oral administration of melatonin in a transgenic model of Alzheimer disease. Journal of Pineal Research 47:82–96. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2009.00692.x
McKenna JT, Christie MA, Jeffrey BA, et al (2012) Chronic ramelteon treatment in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Archives italiennes de biologie 150:5–14. https://doi.org/10.4449/aib.v149i5.1375
Silva AF, Socorro M, Aguiar S, et al (2013) Hippocampal neuronal loss , decreased GFAP immunoreactivity and cognitive impairment following experimental intoxication of rats with aluminum citrate. 1491:23–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2012.10.063
Garcia-Santos G, Martin V, Rodriguez-Blanco J, et al (2012) Fas/Fas ligand regulation mediates cell death in human Ewing’s sarcoma cells treated with melatonin. British journal of cancer 106:1288–1296. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2012.66
Maes M, Galecki P, Chang YS, Berk M (2011) A review on the oxidative and nitrosative stress (O&NS) pathways in major depression and their possible contribution to the (neuro)degenerative processes in that illness. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 35:676–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.05.004
Rahman MF, Wang J, Patterson TA, et al (2009) Expression of genes related to oxidative stress in the mouse brain after exposure to silver-25 nanoparticles. Toxicology Letters 187:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2009.01.020
Lima FD, Souza MA, Furian AF, et al (2008) Na+,K+-ATPase activity impairment after experimental traumatic brain injury: Relationship to spatial learning deficits and oxidative stress. Behavioural Brain Research 193:306–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2008.05.013
Kucukatay V, Aǧar A, Gumuslu S, Yargiçoǧlu P (2007) Effect of sulfur dioxide on active and passive avoidance in experimental diabetes mellitus: Relation to oxidant stress and antioxidant enzymes. International Journal of Neuroscience 117:1091–1107. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207450600934531
Allagui MS, Feriani A, Saoudi M, et al (2014) Effects of melatonin on aluminium-induced neurobehavioral and neurochemical changes in aging rats. Food and Chemical Toxicology 70:84–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2014.03.043
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Rosales-Corral S, et al (2018) Mitochondria: Central organelles for melatonins antioxidant and anti-Aging actions. Molecules 23
Tan DX, Manchester LC, Terron MP, et al (2007) One molecule, many derivatives: A never-ending interaction of melatonin with reactive oxygen and nitrogen species? Journal of Pineal Research 42:28–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2006.00407.x
Reiter RJ, Acuña-Castroviejo D, Tan DX, Burkhardt S (2001) Free radical-mediated molecular damage. Mechanisms for the protective actions of melatonin in the central nervous system. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 939:200–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03627.x
Koh PO (2008) Melatonin regulates nitric oxide synthase expression in ischemic brain injury. Journal of Veterinary Medical Science 70:747–750. https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.70.747
Ucar M, Korkmaz A, Reiter RJ, et al (2007) Melatonin alleviates lung damage induced by the chemical warfare agent nitrogen mustard. Toxicology Letters 173:124–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2007.07.005
Rodriguez C, Mayo JC, Sainz RM, et al (2004) Regulation of antioxidant enzymes: A significant role for melatonin. Journal of Pineal Research 36:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1600-079X.2003.00092.x
Reiter R, Tan D-X, Rosales-Corral S, C. Manchester L (2013) The Universal Nature, Unequal Distribution and Antioxidant Functions of Melatonin and Its Derivatives. Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry 13:373–384. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389557511313030006
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their heartfelt and deepest condolences to family and friends of Prof. Ali OUICHOU. The neuroscience family in Morocco will miss one of its significant members, and the University Ibn Tofail has lost a great academic professor, who has contributed to the growth of the neuroscience community in Morocco. May his soul rest in peace.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Oussama Zghari and Sofia Azirar performed the experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the paper. Mouloud Lamtai participated in behavioral analysis and statistical significance. Aboubaker El Hessni reviewed and provided comments on the content and interpretation of the manuscript. Ali Ouichou and Abdelhalem Mesfioui supervised the work, revised and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interests with authors or other organizations.
Ethics approval
The experimental procedures were carried out in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and approved by the Animal Ethics Committee (Local Institutional Research Committee).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zghari, O., Azirar, S., Lamtai, M. et al. Melatonin counteracts aluminum-induced affective and cognitive disorders and oxidative damage in male wistar rats. Neurosci Behav Physi 53, 917–928 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-023-01465-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-023-01465-x