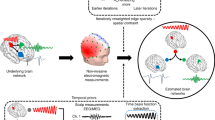
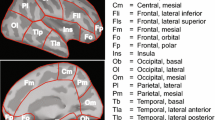
Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological diseases in the world, with about 30% of cases not amenable to pharmacological intervention and potentially requiring surgical intervention. The process of localizing the epileptogenic zone – the area associated with seizure initiation in patients with focal epilepsy – involves examining different areas of the brain for the presence of interictal discharges. In this paper, we propose a new methodology for noninvasive investigation of the fi ne spatiotemporal structure of interictal discharges observed on the magnetoencephalogram (MEG). We applied a traveling wave model to regularize the inverse MEG problem. The algorithm represents the neural activity generating an interictal discharge as a superimposition of local waves propagating along radial paths and generated by a single point source. The LASSO method with positive coeffi cients was applied to determine the combination of waves generated with different parameters giving the best match with the recorded MEG for each discharge. The properties of the algorithm were analyzed using realistic simulations of MEG data. The method was then applied to analysis of MEG data from three patients with drug-resistant multifocal epilepsy. Some of the discharges yielded wave-like patterns with clear propagation dynamics, while for others, the observed activity could not be explained by the wave superimposition model. Moreover, discharges with clear propagation dynamics showed marked spatial clustering correlating with the epileptogenic zones described in the case histories of two of the three patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian, E. D. and Matthews, B. H. C., “The interpretation of potential waves in the cortex,” J. Physiol., 81, No. 4, 440–471 (1934).
Adrian, E. D. and Yamagiwa, K., “The origin of the Berger rhythm,” Brain, 58, No. 3, 323–351 (1935).
Bahramisharif, A., van Gerven, M. A. J., Aarnoutse, E. J., et al., “Propagating neocortical gamma bursts are coordinated by traveling alpha waves,” J. Neurosci., 33, No. 48, 18,849–18,854 (2013).
Chamberlain, A., Viventi, J., Blanco, J., et al., “Millimeterscale epileptiform spike patterns and their relationship to seizures,” in: 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (2011), pp. 761–764.
Chizhov, A. V., Zefirov, A. V., Amakhin, D. V., et al., “Minimal model of interictal and ictal discharges Epileptor-2,” PLoS Comput. Biol., 14, No. 5, e1006186 (2018).
Donders, F. C., “On the speed of mental processes,” Acta Psychol., 30, 412–431 (1969).
Ermentrout, G. B. and Kleinfeld, D., “Traveling electrical waves in cortex,” Neuron, 29, No. 1, 33–44 (2001).
Ferezou, I., Haiss, F., Gentet, L. J., et al., “Spatiotemporal dynamics of cortical sensorimotor integration in behaving mice,” Neuron, 56, No. 5, 907–923 (2007).
Fischl, B., “FreeSurfer,” NeuroImage, 62, No. 2, 774–781 (2012).
Freeman, W. J. and Barrie, J. M., “Analysis of spatial patterns of phase in neocortical gamma EEGs in rabbit,” J. Neurophysiol., 84, No. 3, 1266–1278 (2000).
Fries, P., “A mechanism for cognitive dynamics: neuronal communication through neuronal coherence,” Trends Cogn. Sci., 9, No. 10, 474–480 (2005).
Fries, P., “Rhythms for cognition: Communication through coherence,” Neuron, 88, No. 1, 220–235 (2015).
Giannini, M., Alexander, D. M., Nikolaev, A. R., and van Leeuwen, C., “Large-scale traveling waves in EEG activity following eye movement,” Brain Topogr., 31, No. 4, 608–622 (2018).
Gramfort, A., Luessi, M., Larson, E., et al., “MEG and EEG data analysis with MNE-Python,” Front. Neurosci., 7, No. 267, 1–13 (2013).
Hamalainen, M., Hari, R., Ilmoniemi, R. J., et al., “Magnetoencephalography – theory, instrumentation, and applications to noninvasive studies of the working human brain,” Rev. Mod. Phys., 65, No. 2 (1993).
Hangya, B., Tihanyi, B. T., Entz, L., et al., “Complex propagation patterns characterize human cortical activity during slow-wave sleep,” J. Neurosci., 31, No. 24, 8770–8779 (2011).
Hindriks, R., van Putten, M., and Deco, G., “Intra-cortical propagation of EEG alpha oscillations,” NeuroImage, 103, 444–453 (2014).
Huang, X., Troy, W. C., Yang, Q., et al., “Spiral waves in disinhibited mammalian neocortex,” J. Neurosci., 24, No. 44, 9897–9902 (2004).
Komoltsev, I. G., Sinkin, M. V., Volkova, A. A., et al., “A translational study on acute traumatic brain injury: high incidence of epileptiform activity on human and rat electrocorticograms and histological correlates in rats,” Brain Sci., 10, No. 9), 570 (2020).
Koptelova, A., Bikmullina, R., Medvedovsky, M., et al., “Ictal and interictal MEG in pediatric patients with tuberous sclerosis and drug resistant epilepsy,” Epilepsy Res., 140, 162–165 (2018).
Krylov, V. V., Gekht, A. B., Trifonov, I. S., et al., “Outcomes of the surgical treatment of patients with drug-resistant forms of epilepsy,” Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr., 119, No. 9–2, 13–18 (2016).
Lubenov, E. V. and Siapas, A. G., “Hippocampal theta oscillations are travelling waves,” Nature, 459, No. 7246, 534–539 (2009).
Mak-McCully, R. A., Rosen, B. Q., Rolland, M., et al., “Distribution, amplitude, incidence, co-occurrence, and propagation of human k-complexes in focal transcortical recordings,” eNeuro, 2, No. 4, Eneuro. 0028-15.2015 (2015).
Martinet, L.-E., Fiddyment, G., Madsen, J. R., et al., “Human seizures couple across spatial scales through travelling wave dynamics,” Nat. Commun., 8, No. 1) (2017).
Massimini, M., “The sleep slow oscillation as a traveling wave,” J. Neurosci., 24, No. 31, 6862–6870 (2004).
Mosher, J. C. and Leahy, R. M., “Source localization using recursively applied and projected (RAP) MUSIC,” IEEE Trans. Signal Proc., 47, No. 2, 332–340 (1999).
Muller, L., Chavane, F., Reynolds, J., and Sejnowski, T. J., “Cortical travelling waves: mechanisms and computational principles,” Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 19, No. 5, 255–268 (2018).
Muller, L., Reynaud, A., Chavane, F., and Destexhe, A., “The stimulus- evoked population response in visual cortex of awake monkey is a propagating wave,” Nat. Commun., 5, No. 1 (2014).
Nasiotis, K., Clavagnier, S., Baillet, S., and Pack, C. C., “High-resolution retinotopic maps estimated with magnetoencephalography,” Neuro- Image, 145, 107–117 (2017).
Oostenveld, R., Fries, P., Maris, E., and Schoffelen, J. M., “FieldTrip: Open source software for advanced analysis of MEG, EEG, and invasive electrophysiological data,” Computat. Intell. Neurosci., 2011, Article ID 156869 (2011).
Ossadtchi, A., Baillet, S., Mosher, J. C., et al., “Automated interictal spike detection and source localization in magnetoencephalography using independent components analysis and spatiotemporal clustering,” Clin. Neurophysiol., 115, No. 3, 508–522 (2004).
Ossadtchi, A., Mosher, J. C., Sutherling, W. W., et al., “Hidden Markov modelling of spike propagation from interictal MEG data,” Phys. Med. Biol., 50, No. 14, 3447–3469 (2005).
Patten, T. M., Rennie, C. J., Robinson, P. A., and Gong, P., “Human cortical traveling waves: Dynamical properties and correlations with responses,” PLoS One, 7, No. 6, e38392 (2012).
Petrov, Y., “Harmony: EEG/MEG linear inverse source reconstruction in the anatomical basis of spherical harmonics,” PLoS One, 7, No. 10, e44439 (2012).
Prechtl, J. C., Cohen, L. B., Pesaran, B., et al., “Visual stimuli induce waves of electrical activity in turtle cortex,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, No. 14, 7621–7626 (1997).
Stead, M., Bower, M., Brinkmann, B. H., et al., “Microseizures and the spatiotemporal scales of human partial epilepsy,” Brain, 133, No. 9, 2789–2797 (2010).
Tadel, F., Baillet, S., Mosher, J., et al., “Brainstorm: A user-friendly application for MEG/EEG analysis,” Computat. Intell. Neurosci., (2011).
Tibshirani, R., “Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso,” J. R. Stat. Soc., 58, No. 1, 267–288 (1996).
Tomlinson, S. B., Bermudez, C., Conley, C., et al., “Spatiotemporal mapping of interictal spike propagation: A novel methodology applied to pediatric intracranial EEG recordings,” Front. Neurol., 7, 229 (2016).
Wu, J.-Y., Huang, X., and Zhang, C., “Propagating waves of activity in the neocortex: What they are, what they do,” Neuroscientist, 14, No. 5, 487–502 (2007).
Zhang, H., Watrous, A. J., Patel, A., and Jacobs, J., “Theta and alpha oscillations are traveling waves in the human neocortex,” Neuron, 98, No. 6, 1269–1281. e4 (2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Zhurnal Vysshei Nervnoi Deyatel’nosti imeni I. P. Pavlova, Vol. 72, No. 3, pp. 370–386, May–June, 2022.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kuznetsova, A.A., Ossadtchi, A.E. Analysis of the Local Dynamics of Interictal Discharge Propagation Using a Traveling Wave Model. Neurosci Behav Physi 52, 1436–1447 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-023-01375-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-023-01375-y