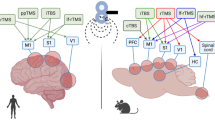
The dentate gyrus (DG), which is part of the hippocampal formation, is the main target of neocortical and subcortical afferents received by the hippocampus, and this forms the anatomical basis for its role in cognitive processes such as attention and memory. The DG is involved in organizing many of the cognitive functions of the hippocampus and the brain as a whole, including novelty detection, pattern separation, pattern completion, spatial working memory, information encoding, and memory consolidation. Long-term potentiation – plastic changes in synapses similar to those occurring when information is memorized – was first discovered in the DG. The DG is a unique region of the brain, one of the few where neurogenesis occurs in adult mammals, including humans. Another feature of the DG distinguishing it from the hippocampus is that it contains two types of glutamatergic neurons – granule cells and mossy cells. Granule cells, which normally have low activity, limit the excitability of hippocampal pyramidal neurons in adverse conditions. The functions of mossy neurons in the DG are the least well understood; these cells, innervating both glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons, are likely to be involved in the organization of complex network activity both in the DG itself and in the hippocampus. Despite intensive research on the DG, its role in the hippocampal activity is still largely unclear. This review discusses the anatomical, histochemical, and functional features of the DG, the activity of its individual cellular elements, and its role in the hippocampal functions of the normal brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, W. C., Christie, B. R., Logan, B., et al., “Immediate early gene expression associated with the persistence of heterosynaptic longterm depression in the hippocampus,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 91, 10049–10053 (1994).
Abraham, W. C., Logan, B., Greenwood, J. M., and Dragunow, M., “Induction and experience-dependent consolidation of stable longterm potentiation lasting months in the hippocampus,” J. Neurosci., 22, 9626–9634 (2002).
Abraham, W. C., Mason-Parker, S. E., Bear, M. F., et al., “Heterosynaptic metaplasticity in the hippocampus in vivo: A BCM-like modifiable threshold for LTP,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 10,924–10,929 (2001).
Acsády, L., Kamondi, A., Sik, A., Freund, T., and Buzsaki, G., “GABAergic cells are the major postsynaptic targets of mossy fibers in the rat hippocampus,” J. Neurosci., 18, 3386–3403 (1998).
Adams, B., Lee, M., Fahnestock, M., and Racine, R., “Long-term potentiation trains induce mossy fiber sprouting,” Brain Res., 775, 193–197 (1997).
Aggleton, J. P., Brown, M. W., and Albasser, M. M., “Contrasting brain activity patterns for item recognition memory and associative recognition memory: insights from immediate-early gene functional imaging,” Neuropsychologia, 50, 3141–3155 (2013).
Aizenman, E., Stout, A. K., Hartnett, K. A., et al., “Induction of neuronal apoptosis by thiol oxidation: putative role of intracellular zinc release,” J. Neurochem., 75, 1878–1888 (2000).
Althaus, A., Zhang, H., and Parent, J., “Axonal plasticity of age-defi ned dentate granule cells in a rat model of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy,” Neurobiol. Dis., 86, 187–96 (2016).
Alvarez-Salvado, E., Pallares, V., Moreno, A., and Canals, S., “Functional MRI of long-term potentiation: imaging network plasticity,” Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B., 369, 20130152 (2014).
Amaral, D. G. and Campbell, M. J., “Transmitter systems in the primate dentate gyrus,” Hum. Neurobiol., 5, 169–180 (1986).
Amaral, D. G. and Dent, J. A., “Development of the mossy fibers of the dentate gyrus: I. A light and electron microscopic study of the mossy fibers and their expansions,” J. Comp. Neurol., 195, 51–86 (1981).
Amaral, D. G., “A Golgi study of cell types in the hilar region of the hippocampus in the rat,” J. Comp. Neurol., 15, 851–914 (1978).
Amaral, D. G., Ishizuka, N., and Claiborne, B., “Neurons, numbers and the hippocampal network,” Prog. Brain Res., 83, 1–11 (1990).
Amaral, D. G., Scharfman, H. E., and Lavenex, P., “The dentate gyrus: fundamental neuroanatomical organization (dentate gyrus for dummies),” Prog. Brain Res., 163, 3–22 (2007).
Axmacher, N., Elger, C. E., and Fell, J., “Ripples in the medial temporal lobe are relevant for human memory consolidation,” Brain, 131, 1806–1817 (2008).
Beck, H., Blumcke, I., Kral, T., et al., “Properties of a delayed rectifier potassium current in dentate granule cells isolated from the hippocampus of patients with chronic temporal lobe epilepsy,” Epilepsia, 37, 892–901 (1996).
Bekinschtein, P., Kent, B. A., Oomen, C. A., et al., “Brain-derived neurotrophic factor interacts with adult-born immature cells in the dentate gyrus during consolidation of overlapping memories,” Hippocampus, 24, 905–911 (2014).
Bekirov, I. H., Nagy, V., Svoronos, A., et al., “Cadherin-8 and N-cadherin differentially regulate pre- and postsynaptic development of the hippocampal mossy fiber pathway,” Hippocampus, 18, 349–63 (2008).
Berger, T. W., Semple-Rowland, S., and Bassett, J. L., “Hippocampal polymorph neurons are the cells of origin for ipsilateral association and commissural afferents to the dentate gyrus,” Brain Res., 224, 329–336 (1981).
Binder, D. K., Croll, S. D., Gall, C. M., and Scharfman, H. E., “BDNF and epilepsy: too much of a good thing?” Trends Neurosci., 24, 47–53 (2001).
Bittencourt, S., Covolan, L., Hamani, C., et al., “Replacement of asymmetric synaptic profiles in the molecular layer of dentate gyrus following cycloheximide in the pilocarpine model in rats,” Front. Psychiatry, 6, 157 (2015).
Blackstad, T. W. and Kjaerheim, A., “Special axo-dendritic synapses in the hippocampal cortex: electron and light microscopic studies on the layer of mossy fibers,” J. Comp. Neurol., 117, 133–159 (1961).
Blackstad, T. W., Brink, K., Hem, J., and Jeun, B., “Distribution of hippocampal mossy fibers in the rat. An experimental study with silver impregnation methods,” J. Comp. Neurol., 138, 433–447 (1970).
Blasco-Ibáñez, J. M. and Freund, T. F., “Distribution, ultrastructure, and connectivity of calretinin immunoreactive mossy cells of the mouse dentate gyrus,” Hippocampus, 7, 307–320 (1997).
Bliss, T. V. and Collingridge, G. L., “A synaptic model of memory: longterm potentiation in the hippocampus,” Nature, 361, 31–39 (1993).
Bliss, T. V. and Gardner-Medwin, A. R., “Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the dentate area of the unanaestetized rabbit following stimulation of the perforant path,” J. Physiol., 232, 357– 374 (1973).
Bliss, T. V. and Lomo, T., “Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the dentate area of the anaesthetized rabbit following stimulation of the perforant path,” J. Physiol., 232, 331–356 (1973).
Blümcke, I., Zuschratter, W., Schewe, J. C., et al., “Cellular pathology of hilar neurons in Ammon’s horn sclerosis,” J. Comp. Neurol., 414, 437–453 (1999).
Bragin, A. G. and Vinogradova, O. S., “Signs of chronic potentiation in the cortical afferent input to pyramidal neurons in hippocampal field CA3,” in: the Physiological Mechanisms of Memory, NTsBI Pushchino Press Pushchino-na-Oke (1973), pp. 8–24.
Bragin, A. G., The Nature of the Responses of Hippocampal Field CA3 Pyramidal Neurons to Electrical Stimulation of the Dentate Fascia of the Limbic System of the Brain, Cherkashin, A. N. and Kul’ta, K. N. (eds.), Pushchino (1973), pp. 141–160.
Bragin, A. G., Vinogradova, O. S., and Emel’yanov V. V., “Spatial organization of neurons in hippocampal field CA3 to electrical stimulation of the dentate fascia,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 26, No. 3, 605–611 (1976).
Bragin, A., Jandó, G., Nádasdy, Z., et al., “Dentate EEG spikes and associated interneuronal population bursts in the hippocampal hilar region of the rat,” J. Neurophysiol., 73, 1691–1705 (1995).
Bromer, C., Bartol, T. M., Bowden, J. B., et al., “Long-term potentiation expands information content of hippocampal dentate gyrus synapses,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 115, No. 10, E2410–E2418 (2018).
Bronzino, J. D., Kehoe, P., Mallinson, K., and Fortin, D. A., “Increased extracellular release of hippocampal NE is associated with tetanization of the medial perforant pathway in the freely moving adult male rat,” Hippocampus, 11, 423–429 (2001).
Brown, R. A., Walling, S. G., Milway, J. S., and Harley, C. W., “Locus ceruleus activation suppresses feedforward interneurons and reduces β-γ electroencephalogram frequencies while it enhances θ frequencies in rat dentate gyrus,” J. Neurosci., 25, 1985–1991 (2005).
Buckmaster, P. S., Abrams, E., and Wen, X., “Seizure frequency correlates with loss of dentate gyrus GABAergic neurons in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy,” J. Comp. Neurol., 525, No. 11, 2592–2610 (2017).
Buckmaster, P. S., Strowbridge, B. W., Kunkel, D. D., et al., “Mossy cell axonal projections to the dentate gyrus molecular layer in the rat hippocampal slice,” Hippocampus, 2, 349–362 (1992).
Buckmaster, P. S., Wenzel, H. J., Kunkel, D. D., and Schwartzkroin, P. A., “Axon arbors and synaptic connections of hippocampal mossy cells in the rat in vivo,” J. Comp. Neurol., 366, 271–292 (1996).
Buckmaster, P., “Does mossy fiber sprouting give rise to the epileptic state?” in: Issues in Clinical Epileptology: A View From the Bench, Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, Scharfman, H. and Buckmaster, P. (eds.), Springer, Dordrecht (2014), Vol. 813.
Buonomano, D. V., “Distinct functional types of associative long-term potentiation in neocortical and hippocampal pyramidal neurons,” J. Neurosci., 19, No. 16, 6748–6754 (1999).
Burgess, N., Maguire, E., and O’Keefe, J., “The human hippocampus and spatial and episodic memory,” Neuron, 35, 625–641 (2002).
Burghardt, N. S., Park, E. H., Hen, R., and Fenton, A. A., “Adult-born hippocampal neurons promote cognitive flexibility in mice,” Hippocampus, 22, 1795–1808 (2012).
Chawla, M. K., Guzowski, J. F., Ramirez-Amaya, V., et al., “Sparse, environmentally selective expression of Arc RNA in the upper blade of the rodent fascia dentata by brief spatial experience,” Hippocampus, 15, 579–586 (2005).
Chicurel, M. E. and Harris, K. M., “Three-dimensional analysis of the structure and composition of CA3 branched dendritic spines and their synaptic relationships with mossy fiber boutons in the rat hippocampus,” J. Comp. Neurol., 325, 169–182 (1992).
Clelland, C. D., Choi, M., Romberg, C., et al., “A functional role for adult hippocampal neurogenesis in spatial pattern separation,” Science, 325, 210–213 (2009).
Cole, T. B., Wenzel, H. J., Kafer, K. E., et al., “Elimination of zinc from synaptic vesicles in the intact mouse brain by disruption of the ZnT3 gene,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 1716–1721 (1999).
Colling, S., Khana, M., Collinge, J., and Jefferys, J., “Mossy fibre reorganization in the hippocampus of prion protein null mice,” Brain Res., 755, 28–35 (1997).
Colom, L. V., Castañeda, M. T., Reyna, T., et al., “Characterization of medial septal glutamatergic neurons and their projection to the hippocampus,” Synapse, 58, 151–164 (2005).
Conquet, F., Bashir, Z. I., Davies, C. H., et al., “Motor deficit and impairment of synaptic plasticity in mice lacking mGluR1,” Nature, 372, 237–243 (1994).
Cossart, R., Dinocourt, C., Hirsch, J. C., et al., “Dendritic but not somatic GABAergic inhibition is decreased in experimental epilepsy,” Nat. Neurosci., 4, 52–62 (2001).
Coulter, D. A. and Carlson, G. C., “Functional regulation of the dentate gyrus by GABA-mediated inhibition,” Prog. Brain Res., 163, 235–243 (2007).
Cronin, J., Obenaus, A., Houser, C., and Dudek, F., “Electrophysiology of dentate granule cells after kainate-induced synaptic reorganization of the mossy fibers,” Brain Res., 573, 305–310 (1992).
Danielson, N. B., Kaifosh, P., Zaremba, J. D., et al., “Distinct contribution of adult-born hippocampal granule cells to context encoding,” Neuron, 90, 101–112 (2016).
Das, A., Wallace, G. C., Holmes, C., et al., “Hippocampal tissue of patients with refractory temporal lobe epilepsy is associated with astrocyte activation, inflammation, and altered expression of channels and receptors,” Neuroscience, 220, 237–246 (2012).
Deller, T., Katona, I., Cozzari, C., et al., “Cholinergic innervation of mossy cells in the rat fascia dentata,” Hippocampus, 9, 314–320 (1999).
Deller, T., Nitsch, R., and Frotscher, M., “Phaseolus vulgaris-leucoagglutinin tracing of commissural fibers to the rat dentate gyrus: evidence for a previously unknown commissural projection to the outer molecular layer,” J. Comp. Neurol., 352, 55–68 (1995).
Deng, W., Mayford, M., and Gage, F. H., “Selection of distinct populations of dentate granule cells in response to inputs as a mechanism for pattern separation in mice,” eLife, 2, e00312 (2013).
Dengler, C. G. and Coulter, D. A., “Normal and epilepsy-associated pathologic function of the dentate gyrus,” Prog. Brain Res., 226, 155–178 (2016).
Denny, C. A., Kheirbek, M. A., Alba, E. L., et al., “Hippocampal memory traces are differentially modulated by experience, time, and adult neurogenesis,” Neuron, 83, 189–201 (2014).
Douglas, R. M. and Goddard, G. V., “Long-term potentiation of the perforant path-granule cell synapse in the rat hippocampus,” Brain Res., 86, 205–215 (1975).
Doyère, V., Srebro, B., and Laroche, S., “Heterosynaptic LTD, depotentiation in the medial perforant path of the dentate gyrus in the freely moving rat,” J. Neurophysiol., 77, 571–578 (1997).
El Bahh, B., Lespinet, V., Lurton, D., et al., al lobe epilepsy,” Epilepsia, 40, 1393–1401 (1999).
Elmer, E., Kokaia, Z., Kokaia, M., Lindvall, O., and McIntyre, D., “Mossy fibre sprouting: evidence against a facilitatory role in epileptogenesis,” Neuroreport, 8, 1193–1196 (1997).
Engel, J. Jr., “A proposed diagnostic scheme for people with epileptic seizures and with epilepsy: report of the ILAE Task Force on Classifi cation and Terminology,” Epilepsia, 42, 796–803 (2001).
Etter, G. and Krezel, W., “Dopamine D2 receptor controls hilar mossy cells excitability,” Hippocampus, 24, 725–732 (2014).
Ezrokhi, V. L., Zosimovskii, V. A., Korshunov, V. A., and Markevich, V. A., “Restoration of decaying long-term potentiation in the hippocampal formation by stimulation of neuromodulatory nuclei in freely moving rats,” Neuroscience, 88, 741–753 (1999).
Frederickson, C. J. and Bush, A. I., “Synaptically released zinc: physiological functions and pathological effects,” Biometals, 14, 353–366 (2001).
Frederickson, C. J., “Neurobiology of zinc and zinc containing neurons,” Int. Rev. Neurobiol., 31, 145–238 (1989).
Freund, T. F. and Buzsaki, G., “Interneurons of the Hippocampus,” Hippocampus, 4, 347–470 (1996).
Freund, T. F., “GABAergic septal and serotonergic median raphe afferents preferentially innervate inhibitory interneurons in the hippocampus and dentate gyrus,” Epilepsy Res., Supplement, 7, 79–91 (1992).
Freund, T. F., Hajos, N., Acsady, L., et al., “Mossy cells of the rat dentate gyrus are immunoreactive for calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP),” Eur. J. Neurosci., 9, 1815–1830 (1997).
Fricke, R. and Prince, D., “Electrophysiology of dentate gyrus granule cells,” J. Neurophysiol., 51, 195–209 (1984).
Frotscher, M., Seress, L., Schwerdtfeger, W. K., and Buhl, E., “The mossy cells of the fascia dentata: a comparative study of their fine structure and synaptic connections in rodents and primates,” J. Comp. Neurol., 312, 145–163 (1991).
Garthe, A., Behr, J., and Kempermann, G., “Adult-generated hippocampal neurons allow the flexible use of spatially precise learning strategies,” PLoS One, 4, e5464 (2009).
Gaykema, R. P., Luiten, P. G., Nyakas, C., and Traber, J., “Cortical projection patterns of the medial septum-diagonal band complex,” J. Comp. Neurol., 293, 103–124 (1990).
Gelinas, J. N. and Nguyen, P. V., “Beta-adrenergic receptor activation facilitates induction of a protein synthesis-dependent late phase of long-term potentiation,” J. Neurosci., 25, 3294–3303 (2005).
Gilbert, P. E., Kesner, R. P., and Lee, I., “Dissociating hippocampal subregions: double dissociation between dentate gyrus and CA1,” Hippocampus, 11, 626–636 (2001).
Gloor, P., The Temporal Lobe and Limbic System, Oxford University Press, New York, NY (1997).
Goh, J. J. and Manahan-Vaughan, D., “Hippocampal long-term depression in freely behaving mice requires the activation of beta-adrenergic receptors,” Hippocampus, 23, 1299–1308 (2013).
Goodman, J. H. and Sloviter, R. S., “Evidence for commissurally projecting parvalbumin-immunoreactive basket cells in the dentate gyrus of the rat,” Hippocampus, 2, 13–21 (1992).
GoodSmith, D., Chen, X., Wang, C., et al., “Spatial representations of granule cells and mossy cells of the dentate gyrus,” Neuron, 93, No. 3, 677–690.e5 (2017).
Gorter, J., van Vliet, E., Aronica, E., and Lopes da Silva, F., “Progression of spontaneous seizures after status epilepticus is associated with mossy fibre sprouting and extensive bilateral loss of hilar parvalbumin and somatostatin-immunoreactive neurons,” Eur. J. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev., 13, 657–669 (2001).
Grover, L. M. and Teyler, T. J., “Two components of long-term potentiation induced by different patterns of afferent activation,” Nature, 347, 477–479 (1990).
Guo, N., Soden, M. E., Herber, C., et al., “Dentate granule cell recruitment of feedforward inhibition governs engram maintenance and remote memory generalization,” Nat. Med., 24, 438–449 (2018).
Hagena, H. and Manahan-Vaughan, D., “Learning-facilitated long-term depression and long-term potentiation at mossy fiber-CA3 synapses requires activation of b-adrenergic receptors,” Front. Integr. Neurosci., 6, 23 (2012).
Hainmueller, T. and Bartos, M., “Parallel emergence of stable and dynamic memory engrams in the hippocampus,” Nature, 558, 292–296 (2018).
Halabisky, B., Parada, I., Buckmaster, P. S., and Prince, D. A., “Excitatory input onto hilar somatostatin interneurons is increased in a chronic model of epilepsy,” J. Neurophysiol., 104, No. 4, 2214–2223 (2010).
Halasy, K. and Somogyi, P., “Subdivisions in the multiple GABAergic innervation of granule cells in the dentate gyrus of the rat hippocampus,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 5, 411–429 (1993).
Hamlyn, L. H., “An electron microscope study of pyramidal neurons in the Ammon’s Horn of the rabbit,” J. Anat., 97, No. Pt 2, 189–201 (1963).
Han, Z. S., Buhl, E. H., Lorinczi, Z., and Somogyi, P., “A high degree of spatial selectivity in the axonal and dendritic domains of physiologically identified local-circuit neurons in the dentate gyrus of the rat hippocampus,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 5, 395–410 (1993).
Hansen, N. and Manahan-Vaughan, D., “Locus coeruleus stimulation facilitates long-term depression in the dentate gyrus that requires activation of β-adrenergic receptors,” Cereb. Cortex, 25, No. 7, 1889–1896 (2015).
Hashimotodani, Y., Karube, F., Yanagawa, Y., et al., “Supramammillary nucleus afferents to the dentate gyrus co-release glutamate and GABA and potentiate granule cell output,” Cell Rep., 25, No. 10, 2704–2715.e4 (2018).
Haug, F. M., “Electron microscopical localization of the zinc in hippocampal mossy fibre synapses by a modified sulfide silver procedure,” Histochemie, 8, 355–368 (1967).
Hendricks, L., Chen, Y., Bensen, A., et al., “Short-term depression of sprouted mossy fiber synapses from adult-born granule cells,” J. Neurosci., 37, 5722–5735 (2017).
Heng, K., Haney, M., and Buckmaster, P., “High-dose rapamycin blocks mossy fiber sprouting but not seizures in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy,” Epilepsia, 54, 1535–1341 (2013).
Henze, D. A. and Buzsáki, G., “Hilar mossy cells: functional identifi cation and activity in vivo,” Prog. Brain Res., 163, 199–216 (2007).
Henze, D. A., Wittner, L., and Buzsáki, G., “Single granule cells reliably discharge targets in the hippocampal CA3 network in vivo,” Nat. Neurosci., 5, 790–795 (2002).
Hetherington, P. A., Austin, K. B., and Shapiro, M. L., “Ipsilateral associational pathway in the dentate gyrus: an excitatory feedback system that supports N-methyl-D-aspartate-dependent long-term potentiation,” Hippocampus, 4, 422–438 (1994).
Hofmann, M. E. and Frazier, C. J., “Muscarinic receptor activation modulates the excitability of hilar mossy cells through the induction of an afterdepolarization,” Brain Res., 1318, 42–51 (2010).
Holtmaat, A., Gorter, J., De Wit, J., et al., “Transient downregulation of Sema3A mRNA in a rat model for temporal lobe epilepsy. A novel molecular event potentially contributing to mossy fi ber sprouting,” Exp. Neurol., 182, 142–150 (2003).
Honoré, E., Khlaifia, A., Bosson, A., and Lacaille, J.-C., “Hippocampal somatostatin interneurons, long-term synaptic plasticity and memory,” Front. Neural Circuits, 15, 687558 (2021).
Houser, C. R., “Interneurons of the dentate gyrus: an overview of cell types, terminal fields and neurochemical identity,” Prog. Brain Res., 163, 217–232 (2007).
Houser, C. R., Peng, Z., Wei, X., et al., “Mossy cells in the dorsal and ventral dentate gyrus differ in their patterns of axonal projections,” J. Neurosci., 41, No. 5, 991–1004 (2021).
Hsia, A. Y., Salin, P. A., Catillo, P. E., et al., “Evidence against a role for metabotropic glutamate receptors in mossy fibre LTP: the use of mutant mice and pharmacological antagonists,” Neuropharmacology, 34, 1567–1572 (1995).
Hsu, T. T., Lee, C. T., Tai, M. H., and Lien, C. C., “Differential recruitment of dentate gyrus interneuron types by commissural versus perforant pathways,” Cereb. Cortex, 26, 2715–2727 (2016).
Hunsaker, M. R., Mooy, G. G., Swift, J. S., and Kesner, R. P., “Dissociations of the medial and lateral perforant path projections into dorsal DG, CA3, and CA1 for spatial and nonspatial (visual object) information processing,” Behav. Neurosci., 121, No. 4, 742–750 (2007).
Hunsaker, M. R., Rosenberg, J. S., and Kesner, R. P., “The role of the dentate gyrus, CA3a,b, and CA3c for detecting spatial and environmental novelty,” Hippocampus, 18, 1064–1073 (2008).
Igarashi, K. M., Lu, L., Colgin, L. L., et al., “Coordination of entorhinal- hippocampal ensemble activity during associative learning,” Nature, 510, 143–147 (2014).
Ikegaya, Y., “Abnormal targeting of developing hippocampal mossy fibers after epileptiform activities via L-type Ca2+ channel activation in vitro,” J. Neurosci., 19, 802–812 (1999).
Ishizuka, N., Weber, J., and Amaral, D. G., “Organization of intrahippocampal projections originating from CA3 pyramidal cells in the rat,” J. Comp. Neurol., 295, 580–623 (1990).
Jinde, S., Zsiros, V., Jiang, Z., et al., “Hilar mossy cell degeneration causes transient dentate granule cell hyperexcitability and impaired pattern separation,” Neuron, 76, 1189–1200 (2012).
Jung, H. J., Lee, J. M., Yang, S. H., et al., “Nuclear lamins in the brain – new insights into function and regulation,” Mol. Neurobiol., 47, 290–301 (2013).
Jung, M. W. and McNaughton, B. L., “Spatial selectivity of unit activity in the hippocampal granular layer,” Hippocampus, 3, 165–182 (1993).
Kay, A. and Tóth, K., “Is zinc a neuromodulator?” Sci. Signal, 1, re3 (2008).
Kemp, A. and Manahan-Vaughan, D., “Beta-adrenoreceptors comprise a critical element in learning-facilitated long-term plasticity,” Cereb. Cortex, 18, 1326–1334 (2008a).
Kemp, A. and Manahan-Vaughan, D., “The hippocampal CA1 region and dentate gyrus differentiate between environmental and spatial feature encoding through long-term depression,” Cereb. Cortex, 18, 968–977 (2008b).
Kesner, R. P., “A behavioral analysis of dentate gyrus function,” Prog. Brain Res., 163, 567–576 (2007).
Kheirbek, M. A., Drew, L. J., Burghardt, N. S., et al., “Differential control of learning and anxiety along the dorsoventral axis of the dentate gyrus,” Neuron, 77, 955–968 (2013).
Khuu, M. A., Pagan, C. M., Nallamothu, T., et al., “Intermittent hypoxia disrupts adult neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity in the dentate gyrus,” J. Neurosci., 39, No. 7, 1320–1331 (2019).
Kitchigina, V. F. and Bragin, A. G., “Functional characteristics of the main internal systems of hippocampal connections,” Neirofiziologiya, 6, No. 3, 259–266 (1976).
Kitamura T, Pignatelli, M., Suh, J., et al., “Island cells control temporal association memory,” Science, 343, 896–901 (2014).
Kitamura, T., Sun, C., Martin, J., et al., “Entorhinal cortical ocean cells encode specifi c contexts and drive context-specifi c fear memory,” Neuron, 87, 1317–1331 (2015).
Kitchigina, V., Vankov, A., Harley, C., and Sara, S. J., “Novelty-elicited, noradrenaline-dependent enhancement of excitability in the dentate gyrus,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 9, 41–47 (1997).
Kleschevnikov, A. M. and Routtenberg, A., “Long-term potentiation recruits a trisynaptic excitatory associative network within the mouse dentate gyrus,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 17, 2690–2702 (2003).
Koyama, R., Yamada, M. K., Fujisawa, S., et al., “Brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces hyperexcitable reentrant circuits in the dentate gyrus,” J. Neurosci., 24, 7215–7224 (2004).
Larimer, P. and Strowbridge, B. W., “Representing information in cell assemblies: persistent activity mediated by semilunar granule cells,” Nat. Neurosci., 13, 213–222 (2010).
Lassalle, J. M., Bataille, T., and Halley, H., “Reversible inactivation of the hippocampal mossy fiber synapses in mice impairs spatial learning, but neither consolidation nor memory retrieval, in the Morris navigation task,” Neurobiol. Learn. Mem., 73, 243–257 (2000).
Lee, I. and Kesner, R. P., “Encoding versus retrieval of spatial memory: double dissociation between the dentate gyrus and the perforant path inputs into CA3 in the dorsal hippocampus,” Hippocampus, 14, 66– 76 (2004).
Leranth, C. and Frotscher, M., “Cholinergic innervation of hippocampal GAD- and somatostatin-immunoreactive commissural neurons,” J. Comp. Neurol., 261, 33–47 (1987).
Leranth, C. and Hajszan, T., “Extrinsic afferent systems to the dentate gyrus,” Prog. Brain Res., 163, 63–84 (2007).
Leutgeb, J. K., Leutgeb, S., Moser, M. B., and Moser, E. I., “Pattern separation in the dentate gyrus and CA3 of the hippocampus,” Science, 315, 961–966 (2007).
Levy, W. B. and Steward, O., “Synapses as associative memory elements in the hippocampal formation,” Brain Res., 175, 233–245 (1979).
Li, X., Somogyi, P., Ylinen, A., and Buzsáki, G., “The hippocampal CA3 network: an in vivo intracellular labeling study,” J. Comp. Neurol., 339, 181–208 (1994).
Lindvall, O. and Stenevi, U., “Dopamine and noradrenaline neurons projecting to the septal area in the rat,” Cell Tissue Res., 190, 383–407 (1978).
Lisman, J. E., Talamini, L. M., and Raffone, A., “Recall of memory sequences by interaction of the dentate and CA3: a revised model of the phase precession,” Neural Netw., 18, 1191–1201 (2005).
Lituma, P. J., Kwon, H.-B., Alviña, K., et al., “Presynaptic NMDA receptors facilitate short-term plasticity and BDNF release at hippocampal mossy fiber synapses,” eLife, 10, e66612 (2021).
Liu, R. S., Lemieux, L., Bell, G. S., et al., “Cerebral damage in epilepsy: a population-based longitudinal quantitative MRI study,” Epilepsia, 46, 1482–1494 (2005).
Liu, X., Ramirez, S., Pang, P. T., et al., “Optogenetic stimulation of a hippocampal engram activates fear memory recall,” Nature, 484, 381–385 (2012).
Longo, B., Covolan, L., Chadi, G., and Mello, L., “Sprouting of mossy fibers and the vacating of postsynaptic targets in the inner molecular layer of the dentate gyrus,” Exp. Neurol., 181, 57–67 (2003).
Lopez-Rojas, J., Heine, M., and Kreutz, M. R., “Plasticity of intrinsic excitability in mature granule cells of the dentate gyrus,” Sci. Rep., 6, 21615 (2016).
Lorente de No, R., “Studies on the structure of the cerebral cortex. II. Continuation of the of the study of the ammonic system,” J. Psychol. Neurol. (Leipzig), 46, 113 (1934).
Lynch, M. A., “Long-term potentiation and memory,” Physiol. Rev., 84, 87–136 (2004).
Lysetskiy, M., Foldy, C., and Soltesz, I., “Long- and short-term plasticity at mossy fiber synapses on mossy cells in the rat dentate gyrus,” Hippocampus, 15, 691–696 (2005).
Madroñal, N., Delgado-García, J. M., Fernández-Guizán, A., et al., “Rapid erasure of hippocampal memory following inhibition of dentate gyrus granule cells,” Nat. Commun., 7, 10923 (2016).
Malenka, R. C. and Bear, M. F., “LTP and LTD: an embarrassment of riches,” Neuron, 44, 5–21 (2004).
Malheiros, J., Paiva, F., Longo, B., et al., “Manganese-enhanced MRI: biological applications in neuroscience,” Front. Neurol., 6, 161 (2015).
Marr, D., “Simple memory: a theory for archicortex,” Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B, Biol. Sci., 262, 23–81 (1971).
Mathern, G., Cifuentes, F., Leite, J., et al., “Hippocampal EEG excitability and chronic spontaneous seizures are associated with aberrant synaptic reorganization in the rat intrahippocampal kainate model,” Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol., 87, 326–339 (1993).
McHugh, T. J., Jones, M. W., Quinn, J. J., et al., “Dentate gyrus NMDA receptors mediate rapid pattern separation in the hippocampal network,” Science, 317, No. 5834, 94–99 (2007).
McNamara, J., “Cellular and molecular basis of epilepsy,” J. Neurosci., 14, 3413–3425 (1994).
McNaughton, B. L. and Morris, R. G., “Hippocampal synaptic enhancement and information storage within a distributed memory system,” Trends Neurosci., 10, 408–415 (1987).
McNaughton, B. L. and Nadel, L., “Hebb-Marr networks and the neurobiological representation of action in space,” in: Neuroscience and Connectionist Theory, Gluck, M. A. and Rumelhart, D. E. (eds), Erlbaum (1990), pp. 1–63.
McNaughton, B. L., Barnes, C. A., Meltzer, J., and Sutherland, R. J., “Hippocampal granule cells are necessary for normal spatial learning but not for spatially-selective pyramidal cell discharge,” Exp. Brain Res., 76, 485–496 (1989).
Meier, K., Merseburg, A., Isbrandt, D., et al., “Dentate gyrus sharp waves, a local field potential correlate of learning in the dentate gyrus of mice,” J. Neurosci., 40, 7105–7118 (2020).
Mello, L. and Covolan, L., “Neuronal injury and progressive cell damage,” in: Encyclopedia of Basic Epilepsy Research, Schwartzkroin, P. A. (ed.), Academic Press, Cambridge, MA; London (2009), pp. 125–128.
Messaoudi, E., Bardsen, K., Srebro, B., and Bramham, C. R., “Acute intrahippocampal infusion of BDNF induces lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the rat dentate gyrus,” J. Neurophysiol., 79, 496–499 (1998).
Messaoudi, E., Ying, S. W., Kanhema, T., et al., “Brain-derived neurotrophic factor triggers transcription-dependent, late phase long-term potentiation in vivo,” J. Neurosci., 22, 7453–7461 (2002).
Mitsueda-Ono, T., Ikeda, A., Sawamoto, N., et al., “Internal structural changes in the hippocampus observed on 3-tesla MRI in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy,” Intern. Med., 52, 877–885 (2013).
Mori, M., Abegg, M. H., Gähwiler, B. H., and Gerber, U., “A frequency- dependent switch from inhibition to excitation in a hippocampal unitary circuit,” Nature, 431, 453–456 (2004).
Morimoto, K., Fahnestock, M., and Racine, R. J., “Kindling and status epilepticus models of epilepsy: rewiring the brain,” Prog. Neurobiol., 73, 1–60 (2004).
Moser, M. B. and Moser, E. I., “Functional differentiation in the hippocampus,” Hippocampus, 8, 608–619 (1998).
Mu, J. S., Li, W. P., Yao, Z. B., and Zhou, X. F., “Deprivation of endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor results in impairment of spatial learning and memory in adult rats,” Brain Res., 835, 259–265 (1999).
Myers, C. E. and Scharfman, H. E., “Pattern separation in the dentate gyrus: a role for the CA3 backprojection,” Hippocampus, 21, 1190– 1215 (2011).
Nadler, J. V., Perry, B. W., and Cotman, C. W., “Selective reinnervation of hippocampal area CA1 and the fascia dentata after destruction of CA3–CA4 afferents with kainic acid,” Brain Res., 182, 1–9 (1980).
Nakashiba, T., Cushman, J. D., Pelkey, K. A., et al., “Young dentate granule cells mediate pattern separation, whereas old granule cells facilitate pattern completion,” Cell, 149, 188–201 (2012).
Nakashiba, T., Young, J. Z., McHugh, T. J., et al., “Transgenic inhibition of synaptic transmission reveals role of CA3 output in hippocampal learning,” Science, 319, 1260–1264 (2008).
Namgung, U., Matsuyama, S., and Routtenberg, A., “Long-term potentiation activates the GAP-43 promoter: selective participation of hippocampal mossy cells,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 11675–11680 (1997).
Nissinen, J., Lukasiuk, K., and Pitkänen, A., “Is mossy fiber sprouting present at the time of the fi rst spontaneous seizures in rat experimental temporal lobe epilepsy?” Hippocampus, 11, 299–310 (2001).
Nosten-Bertrand, M., Errington, M. L., Murphy, K. P., et al., “Normal spatial learning despite regional inhibition of LTP in mice lacking thy- 1,” Nature, 379, 826–829 (1996).
Parent, J. M., Elliott, R. C., Pleasure, S. J., et al., “Aberrant seizure-induced neurogenesis in experimental temporal lobe epilepsy,” Ann. Neurol., 59, 81–91 (2006).
Park, E. H., Burghardt, N. S., Dvorak, D., et al., “Experience-dependent regulation of dentate gyrus excitability by adult-born granule cells,” J. Neurosci., 35, 11656 –11666 (2015).
Park, S., Kramer, E. E., Mercaldo, V., et al., “Neuronal allocation to a hippocampal engram,” Neuropsychopharmacology, 41, 2987–2993 (2016).
Penttonen, M., Kamondi, A., Sik, A., et al., “Feed-forward and feed-back activation of the dentate gyrus in vivo during dentate spikes and sharp wave bursts,” Hippocampus, 7, 437–450 (1997).
Phillips, R. G. and LeDoux, J. E., “Differential contribution of amygdala and hippocampus to cued and contextual fear conditioning,” Behav. Neurosci., 106, 274–285 (1992).
Pierce, J., Melton, J., Punsoni, M., et al., “Mossy fibers are the primary source of afferent input to ectopic granule cells that are born after pilocarpine-induced seizures,” Exp. Neurol., 196, 316–331 (2005).
Polli, R., Malheiros, J., Dos Santos, R., et al., “Changes in hippocampal volume are correlated with cell loss but not with seizure frequency in two chronic models of temporal lobe epilepsy,” Front. Neurol., 5, 111 (2014).
Raisman, G., Cowan, W. M., and Powel, T. P. S., “The extrinsic afferent, commissural and association fibers of hippocampus,” Brain, 88, 963–981 (1965).
Ramirez, S., Liu, X., Lin, P. A., et al., “Creating a false memory in the hippocampus,” Science, 341, 387–391 (2013).
Ramon y Cajal, S., “Estructura del asfa de Ammon y fascia dentata,” Ann. SOC Esp. Hist. Nat. Madrid, 22, 1 (1893).
Reyes-Garcia, S. Z., Scorza, C. A., Araújo N. S, et al., “Different patterns of epileptiform-like activity are generated in the sclerotic hippocampus from patients with drug-resistant temporal lobe epilepsy,” Sci. Rep., 8, 7116 (2018).
Ribak, C. E. and Seress, L., “Five types of basket cell in the hippocampal dentate gyrus: a combined Golgi and electron microscopic study,” J. Neurocytol., 12, 577–597 (1983).
Ribak, C. E., Seress, L., and Amaral, D. G., “The development, ultrastructure and synaptic connections of the mossy cells of the dentate gyrus,” J. Neurocytol., 14, 835–857 (1985).
Rolls, E. T. and Kesner, R. P., “A computational theory of hippocampal function, and empirical tests of the theory,” Prog. Neurobiol., 79, 1–48 (2006).
Rolls, E. T., “Pattern separation, completion, and categorisation in the hippocampus and neocortex,” Neurobiol. Learn. Mem., 129, 4–28 (2016).
Rolls, E. T., “The storage and recall of memories in the hippocampo-cortical system,” Cell Tissue Res., 373, No. 3, 577–604 (2018).
Roth, B. L., “DREADDs for neuroscientists,” Neuron, 89, No. 4, 683–694 (2016).
Rovira-Esteban, L., Hájos, N., Nagy, G. A., et al., “Semilunar granule cells are the primary source of the perisomatic excitatory innervation onto parvalbumin-expressing interneurons in the dentate gyrus,” eNeuro, 7, No. 4, 1–17 (2020).
Ruediger, S., Vittori, C., Bednarek, E., et al., “Learning-related feedforward inhibitory connectivity growth required for memory precision,” Nature, 473, 514–518 (2011).
Sahay, A., Drew, M. R., and Hen, R., “Dentate gyrus neurogenesis and depression,” Prog. Brain Res., 163, 697–722 (2007).
Sahay, A., Scobie, K. N., Hill, A. S., et al., “Increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis is suffi cient to improve pattern separation,” Nature, 472, No. 7344, 466–470 (2011).
Sajikumar, S. and Frey, J. U., “Late-associativity, synaptic tagging, and the role of dopamine during LTP and LTD,” Neurobiol. Learn. Mem., 82, 12–25 (2004).
Sakon, J. J. and Suzuki, W. A., “A neural signature of pattern separation in the monkey hippocampus,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 116, 9634– 9643 (2019).
Salib, M., Joshi, A., Katona, L., et al., “GABAergic medial septal neurons with low-rhythmic fi ring innervating the dentate gyrus and hippocampal area CA3,” J. Neurosci., 39, No. 23, 4527–4549 (2019).
Sara, S. J., Vankov, A., and Hervé, A., “Locus coeruleus-evoked responses in behaving rats: A clue to the role of noradrenaline in memory,” Brain Res. Bull., 35, 457–465 (1994).
Saxe, M. D., Battaglia, F., Wang, J.-W., et al., “Ablation of hippocampal neurogenesis impairs contextual fear conditioning and synaptic plasticity in the dentate gyrus,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 103, 17501– 17506 (2006).
Scharfman, H. E. and Myers, C. E., “Hilar mossy cells of the dentate gyrus: a historical perspective,” Front. Neural Circuits, 6, 106 (2012).
Scharfman, H. E. and Pierce, J. P., “New insights into the role of hilar ectopic granule cells in the dentate gyrus based on quantitative anatomic analysis and three-dimensional reconstruction,” Epilepsia, 53, Suppl. 1, 98–108 (2012).
Scharfman, H. E., “Characteristics of spontaneous and evoked EPSPs recorded from dentate spiny hilar cells in rat hippocampal slices,” J. Neurophysiol., 70, 742–757 (1993).
Scharfman, H. E., “Dentate hilar cells with dendrites in the molecular layer have lower thresholds for synaptic activation by perforant path than granule cells,” J. Neurosci., 11, 1660–1673 (1991).
Scharfman, H. E., “Electrophysiological evidence that dentate hilar mossy cells are excitatory and innervate both granule cells and interneurons,” J. Neurophysiol., 74, 179–194 (1995).
Scharfman, H. E., “EPSPs of dentate gyrus granule cells during epileptiform bursts of dentate hilar ‘mossy’ cells and area CA3 pyramidal cells in disinhibited rat hippocampal slices,” J. Neurosci., 14, 6041– 6057 (1994).
Scharfman, H. E., “The CA 3 “backprojection” to the dentate gyrus,” Prog. Brain Res., 163, 627–637 (2007).
Scharfman, H. E., “The enigmatic mossy cell of the dentate gyrus,” Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 17, No. 9, 562–575 (2016).
Scharfman, H. E., Goodman, J., and McCloskey, D., “Ectopic granule cells of the rat dentate gyrus,” Dev. Neurosci., 29, 14–27 (2007).
Sensi, S. L., Ton-That, D., and Weiss, J. H., “Mitochondrial sequestration and Ca2+-dependent release of cytosolic Zn2+ loads in cortical neurons,” Neurobiol. Dis., 10, 100–108 (2002).
Senzai, Y. and Buzsáki, G., “Physiological properties and behavioral correlates of hippocampal granule cells and mossy cells,” Neuron, 93, No. 3, 691–704.e5 (2017).
Shi, Y., Grieco, S. F., Holmes, T. C., and Xu, X., “Development of local circuit connections to hilar mossy cells in the mouse dentate gyrus,” eNeuro, 6, No. 2, e0370-18, 1–14 (2019).
Shibata, K., Nakahara, S., Shimizu, E., et al., “Repulsive guidance molecule a regulates hippocampal mossy fi ber branching in vitro,” Neuroreport, 24, 609–615 (2013).
Sloviter, R. S., “Decreased hippocampal inhibition and selective loss of interneurons in experimental epilepsy,” Science, 235, 73–76 (1987).
Sloviter, R. S., “Feedforward and feedback inhibition of hippocampal principal cell activity evoked by perforant path stimulation: GABA-mediated mechanisms that regulate excitability in vivo,” Hippocampus, 1, 31–40 (1991a).
Sloviter, R. S., “Permanently altered hippocampal structure, excitability, and inhibition after experimental status epilepticus in the rat: the “dormant basket cell” hypothesis and its possible relevance to temporal lobe epilepsy,” Hippocampus, 1, 41–66 (1991b).
Sloviter, R. S., “Status epilepticus-induced neuronal injury and network reorganization,” Epilepsia, 40, S34–9 (1999).
Sloviter, R. S., Zappone, C. A., Harvey, B. D., et al., “Dormant basket cell hypothesis revisited: relative vulnerabilities of dentate gyrus mossy cells and inhibitory interneurons after hippocampal status epilepticus in the rat,” J. Comp. Neurol., 459, 44–76 (2003).
Sloviter, R., Bumanglag, A., Schwarcz, R., and Frotscher, M., “Abnormal dentate gyrus network circuitry in temporal lobe epilepsy,” in: Jasper’s Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies, Noebels, J. et al. (eds.), National Center for Biotechnology Information, Bethesda, MD (2012).
Smith, R. L., Mensah, P., and Cotman, C., “Tracing the dentate gyrus mossy fi ber system with horseradish peroxidase histochemistry,” Exp. Neurol., 40, No. 2, 516–524 (1973).
Snyder, J. S., Kee, N., and Wojtowicz, J. M., “Effects of adult neurogenesis on synaptic plasticity in the rat dentate gyrus,” J. Neurophysiol., 85, 2423–2431 (2001).
Song, M. Y., Tian, F. F., Wang, Y. Z., et al., “Potential roles of the RGMa-FAK-Ras pathway in hippocampal mossy fi ber sprouting in the pentylenetetrazole kindling model,” Mol. Med. Rep., 11, 1738–1744 (2015).
Steward, O. and Scoville, S. A., “Cells of origin of entorhinal cortical afferents to the hippocampus and fascia dentata of the rat,” J. Comp. Neurol., 169, 347–370 (1976).
Strowbridge, B. W. and Schwartzkroin, P. A., “Transient potentiation of spontaneous EPSPs in rat mossy cells induced by depolarization of a single neuron,” J. Physiol., 494, 493–510 (1996).
Strüber, M., Sauer, J. F., Jonas, P., and Bartos, M., “Distance-dependent inhibition facilitates focality of gamma oscillations in the dentate gyrus,” Nat. Commun., 8, No. 1, 758 (2017).
Sun, C., Mtchedlishvili, Z., Bertram, E. H., et al., “Selective loss of dentate hilar interneurons contributes to reduced synaptic inhibition of granule cells in an electrical stimulation-based animal model of temporal lobe epilepsy,” J. Comp. Neurol., 500, 876–893 (2007).
Swan, A. A., Clutton, J. E., Chary, P. K., et al., “Characterization of the role of adult neurogenesis in touch-screen discrimination learning,” Hippocampus, 24, 1581–1591 (2014).
Swanson, L. W., Kohler, C., and Bjorklund, A., Handbook of Chemical Neuroanatomy, Hokfelt, T. et al. (eds.), Elsevier (1987), Vol. 5, pp. 125–277.
Takeuchi, T., Duszkiewicz, A. J., Sonneborn, A., et al., “Locus coeruleus and dopaminergic consolidation of everyday memory,” Nature, 537, No. 7620, 357–362 (2016).
Tamagnone, L. and Comoglio, P., “Signalling by semaphorin receptors: cell guidance and beyond,” Trends Cell Biol., 10, 377–383 (2000).
Tauck, D. and Nadler, J., “Evidence of functional mossy fi ber sprouting in hippocampal formation of kainic acid-treated rats,” J. Neurosci., 5, 1016–1022 (1985).
Toni, N., Laplagne, D. A., Zhao, C., et al., “Neurons born in the adult dentate gyrus form functional synapses with target cells,” Nat. Neurosci., 11, 901–907 (2008).
Treves, A. and Rolls, E. T., “Computational analysis of the role of the hippocampus in memory,” Hippocampus, 4, 374–391 (1994).
Tronel, S., Belnoue, L., Grosjean, N., et al., “Adult-born neurons are necessary for extended contextual discrimination,” Hippocampus, 22, 292–298 (2012).
Tulving, E., “Episodic memory: from mind to brain,” Annu. Rev. Psychol., 53, 1–25 (2002).
van Dijk, M. T. and Fenton, A. A., “On how the dentate gyrus contributes to memory discrimination,” Neuron, 98, 832–845.e5 (2018).
Van Paesschen, W., Revesz, T., Duncan, J. S., et al., “Quantitative neuropathology and quantitative magnetic resonance imaging of the hippocampus in temporal lobe epilepsy,” Ann. Neurol., 42, 756–766 (1997).
Vinogradova, O. S. and Dudaeva, K. I., “The comparator function the hippocampus,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR, 202, No. 1, 241–244 (1972).
Vinogradova, O. S., “Hippocampus as comparator: Role of the two input and two output systems of the hippocampus in selection and registration of information,” Hippocampus, 11, 578–597 (2001).
Vinogradova, O. S., The Hippocampus and Memory, Nauka, Moscow (1975).
Vogt, K., Mellor, J., Tong, G., and Nicoll, R., “The actions of synaptically released zinc at hippocampal mossy fiber synapses,” Neuron, 26, 187–196 (2000).
Williams, P. A., Larimer, P., Gao, Y., and Strowbridge, B. W., “Semilunar granule cells: glutamatergic neurons in the rat dentate gyrus with axon collaterals in the inner molecular layer,” J. Neurosci., 27, 13756– 13761 (2007).
Witter, M. P., “The perforant path: projections from the entorhinal cortex to the dentate gyrus,” Prog. Brain Res., 163, 43–61 (2007).
Wittner, L., Maglóczky, Z., Borhegyi, Z., et al., “Preservation of perisomatic inhibitory input of granule cells in the epileptic human dentate gyrus,” Neuroscience, 108, 587–600 (2021).
Wright, B. J. and Jackson, M. B., “Long-term potentiation in hilar circuitry modulates gating by the dentate gyrus,” J. Neurosci., 34, 9743–9753 (2014).
Wuarin, J. and Dudek, F., “Excitatory synaptic input to granule cells increases with time after kainate treatment,” J. Neurophysiol., 85, 1067–1077 (2001).
Yamawaki, R., Thind, K., and Buckmaster, P. S., “Blockade of excitatory synaptogenesis with proximal dendrites of dentate granule cells following rapamycin treatment in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy,” J. Comp. Neurol., 523, 281–297 (2015).
Yassa, M. A. and Stark, C. E., “Pattern separation in the hippocampus,” Trends Neurosci., 34, 515–525 (2011).
Zimmer, J., “Changes in the Timm sulfi de silver staining patter of the rat hippocampus and fascia dentata following early postnatal deaferentiation,” Brain Res., 64, 313–326 (1973).
Zimmer, J., “Ipsilateral afferents to the commissural zone of the fascia dentata, demonstrated in decommissurated rats by silver impregnation,” J. Comp. Neurol., 142, 393–416 (1971).
Zimmer, J., “Long-term synaptic reorganization in rat fascia dentate deafferented at adolescent and adult stages: observations with the Timm method,” Brain Res., 76, 336–242 (1974).
Zucca, S., Griguoli, M., Malézieux, M., et al., “Control of spike transfer at hippocampal mossy fiber synapses in vivo by GABA A and GABA B receptor-mediated inhibition,” J. Neurosci., 37, 587–598 (2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Zhurnal Vysshei Nervnoi Deyatel’nosti imeni I. P. Pavlova, Vol. 72, No. 3, pp. 317–342, May–June, 2022.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kitchigina, V.F., Shubina, L.V. & Popova, I.Y. The Role of the Dentate Gyrus in Mediating Hippocampal Functions: The Healthy Brain. Neurosci Behav Physi 52, 1401–1417 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-023-01372-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-023-01372-1