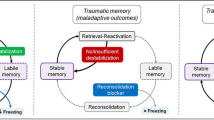
It is well known that nitric oxide (NO) is involved in forming signal memory for stimulation of different modalities. We studied the involvement of nitric oxide in processes of the reconsolidation (repeated consolidation of a long-term memory on reminding) of conditioned reflex contextual fear memory in rats. After a single training session, animals demonstrated significant increases in freezing on presentation of the conditioned context. Reactivation of this memory on the background of blockade of de novo protein synthesis with cycloheximide led to a significant decrease in freezing time in the conditioned context in rats. Administration of the selective neuronal NO synthase blocker 3-bromo-7-indazole in conditions of memory reactivation on the background of protein synthesis blockade prevented weakening of conditioned reflex freezing reactions, as demonstrated by subsequent testing of animals in the conditioned context. In addition, administration of 3-bromo-7-indazole without reactivation did not elicit significant changes in measures of conditioned reflex freezing in rats. These results suggest that nitric oxide is involved in the labilization of conditioned reflex contextual fear memory on reminding, and is thus a necessary component of the triggering of the reconsolidation process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonov, I., Ha, T., Antonova, I., et al., “Role of nitric oxide in classical conditioning of siphon withdrawal in Aplysia,” J. Neurosci., 27, No. 41, 10993–11002 (2007).
Bal, N. V., Rysakova, M. P., Vinarskaya, A. K., et al., “Cued memory reconsolidation in rats requires nitric oxide,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 45, No. 5, 643–647 (2017a).
Bal, N., Roshchin, M., Salozhin, S., and Balaban, P., “Nitric oxide upregulates proteasomal protein degradation in neurons,” Cell. Mol. Neurobiol., 37, No. 5, 763–769 (2017b).
Balaban, P. M., Roshchin, M., Timoshenko, A. K., et al., “Nitric oxide is necessary for labilization of a consolidated context memory during reconsolidation in terrestrial snails,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 40, No. 6, 2963–2970 (2014).
Bingor, A., Haham, N., Thornton, C., et al., “Zeta inhibitory peptide attenuates learning and memory by inducing NO-mediated downregulation of AMPA receptors,” Nat. Commun., 11, No. 1, 1–11 (2020).
Bradley, S. A. and Steinert, J. R., “Nitric oxide-mediated posttranslational modifications: impacts at the synapse,” Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev., 2016, 5681036 (2016).
Cai, C. Y., Chen, C., Zhou, Y., et al., “PSD-95-nNOS coupling regulates contextual fear extinction in the dorsal CA3,” Sci. Rep., 8, No. 1, 12775 (2018).
Chaaya, N., Battle, A. R., and Johnson, L. R., “An update on contextual fear memory mechanisms: transition between amygdala and hippocampus,” Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev., 92, 43–54 (2018).
Chen, W., Yan, M., Wang, Y., et al., “Effects of 7-nitroindazole, a selective neural nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, on context-shock associative learning in a two-process contextual fear conditioning paradigm,” Neurobiol. Learn. Mem., 134, No. Pt B, 287–293 (2016).
Dyer, R. R., Ford, K. I., and Robinson, R. A. S., “The roles of S-nitrosylation and S-glutathionylation in Alzheimer’s disease,” Methods Enzymol., 626, 499–538 (2019).
Gainutdinova, T. Kh., Tagirova, R. R., Ismailova, A. I., et al., “Protein synthesis-dependent reactivation of a contextual conditioned reflex in the common snail,” Neurosci. Behav. Physiol., 36, No. 2, 203–207 (2006).
Haubrich, J. and Nader, K., “Memory reconsolidation,” Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci., 37, 151–176 (2018).
Hott, S. C., Gomes, F. V., Uliana, D. L., et al., “Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis NMDA receptors and nitric oxide modulate contextual fear conditioning in rats,” Neuropharmacology, 112, Pt. A, 135–143 (2017).
Izquierdo, I., Furini, C. R., and Myskiw, J. C., “Fear memory,” Physiol. Rev., 96, No. 2, 695–750 (2016).
Jarome, T. J., Ferrara, N. C., Kwapis, J. L., and Helmstetter, F. J., “CaMKII regulates proteasome phosphorylation and activity and promotes memory destabilization following retrieval,” Neurobiol. Learn. Mem., 128, 103–109 (2016).
Jarome, T. J., Werner, C. T., Kwapis, J. L., and Helmstetter, F. J., “Activity dependent protein degradation is critical for the formation and stability of fear memory in the amygdala,” PLoS One, 6, No. 9, e24349 (2011).
Kida, S., “Reconsolidation/destabilization, extinction and forgetting of fear memory as therapeutic targets for PTSD,” Psychopharmacology (Berlin), 236, No. 1, 49–57 (2019).
Lee, J. L. C., Nader, K., and Schiller, D., “An update on memory reconsolidation updating,” Trends Cogn. Sci., 21, No. 7, 531–545 (2017).
Lee, S. H., Choi, J. H., Lee, N., et al., “Synaptic protein degradation underlies destabilization of retrieved fear memory,” Science, 319, No. 5867, 1253–1256 (2008).
Li, J., Han, Z., Cao, B., et al., “Disrupting nNOS-PSD-95 coupling in the hippocampal dentate gyrus promotes extinction memory retrieval,” Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun, 493, No. 1, 862–868 (2017).
Lisboa, S. F., Gomes, F. V., Silva, A. L., et al., “Increased contextual fear conditioning in iNOS knockout mice: additional evidence for the involvement of nitric oxide in stress-related disorders and contribution of the endocannabinoid system,” Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol., 18, No. 8, pyv005 (2015).
Misanin, J. R., Miller, R. R., and Lewis, D. J., “Retrograde amnesia produced by electroconvulsive shock after reactivation of a consolidated memory trace,” Science, 160, No. 3827, 554–555 (1968).
Nader, K., Schafe, G. E., and Le Doux, J. E., “Fear memories require protein synthesis in the amygdala for reconsolidation after retrieval,” Nature, 406, No. 6797, 722–726 (2000).
Noriega-Prieto, J. A., Maglio, L. E., Gallero-Salas, Y., and Fernández de Sevilla, D., “Nitric oxide-dependent LTD at infralimbic cortex,” Neuroscience, 418, 149–156 (2019).
Przybyslawski, J., Roullet, P., and Sara, S. J., “Attenuation of emotional and nonemotional memories after their reactivation: role of beta adrenergic receptors,” J. Neurosci., 19, No. 15, 6623–6628 (1999).
Song, S., Lee, J., Park, S., and Choi, S., “Fear renewal requires nitric oxide signaling in the lateral amygdala,” Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun, 523, No. 1, 86–90 (2020).
Zhang, L., Yuan, H. J., Cao, B., et al., “MGE-derived nNOS+ interneurons promote fear acquisition in nNOS–/– mice,” Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun, 493, No. 4, 1560–1566 (2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Zhurnal Vysshei Nervnoi Deyatel’nosti imeni I. P. Pavlova, Vol. 71, No. 2, pp. 286–292, March–April, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vinarskaya, A.K., Zuzina, A.B. & Balaban, P.M. Nitric Oxide Is Required for Labilization (destabilization) of Contextual Memory in Rats. Neurosci Behav Physi 51, 1273–1277 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-021-01190-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-021-01190-3