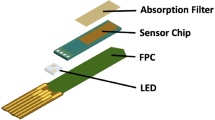
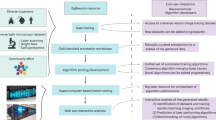
A miniature fluorescence microscope (miniscope) is a promising tool for visualizing in vivo neuronal activity in behaving animals. The data obtained by a miniscope contain massive amounts of information about neuronal activity. However, the extraction and analysis of these data are complex tasks. There are various difficulties in the processing of data obtained by a miniscope, both in the extraction of neural activity data and in the subsequent analysis. A software page, constrained nonnegative matrix factorization for microendoscopic data (CNMF-E), was developed previously to assist in the processing of miniscope data. In this paper, we present a novel software package, NeuroInfoViewer (NIV), for high-level analysis and visualization of miniscope data following initial processing. We present an example of the analysis data flow, from raw miniscope imaging data to CNMF-E and to NIV. We suggest that NIV may serve as a useful tool for high-level analysis of miniscope data and we have deposited NIV in the public domain to facilitate its use by the neuroscience community.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. K. Ghosh, L. D. Burns, E. D. Cocker, et al., “Miniaturized integration of a fluorescence microscope,” Nat. Methods, 8, No. 10, 871–878 (2011), https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1694.
D. J. Cai, D. Aharoni, T. Shuman, et al., “A shared neural ensemble links distinct contextual memories encoded close in time,” Nature, 534, No. 7605, 115–118 (2016), https://doi.org/10.1038/nature17955.
A. de Groot, B. J. van den Boom, R. M. van Genderen, et al., “NINscope, a versatile miniscope for multi-region circuit investigations,” Elife, 9 (2020), https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.49987.
B. A. Flusberg, A. Nimmerjahn, E. D. Cocker, et al., “High-speed, miniaturized fluorescence microscopy in freely moving mice,” Nat. Methods, 5, No. 11, 935–938 (2008), https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1256.
T. Shuman, D. Aharoni, D. J. Cai, et al., “Breakdown of spatial coding and interneuron synchronization in epileptic mice,” Nat. Neurosci, 23, No. 2, 229–238 (2020), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-019-0559-0.
C. T. Werner, C. J. Williams, M. R. Fermelia, et al., “Circuit mechanisms of neurodegenerative diseases: a new frontier with miniature fluorescence microscopy,” Front Neurosci, 13, No. 1174 (2019), https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.01174.
Y. Ziv and K. K. Ghosh, “Miniature microscopes for large-scale imaging of neuronal activity in freely behaving rodents,” Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 32, No. 141–147 (2015), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2015.04.001.
E. I. Gerasimov, A. I. Erofeev, S. A. Pushkareva,.et al.,.“Miniature fluorescent microscope: history, application, and data processing,” Zh. Vyssh. Nervn. Deyat., 70, No. 6, 852–864 (2020), https://doi.org/10.31857/S0044467720060040.
G. Barbera, B. Liang, L. Zhang, et al., “Spatially compact neural clusters in the dorsal striatum encode locomotion relevant information,” Neuron, 92, No. 1, 202–213 (2016), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.08.037.
A. Klaus, G. J. Martins, V. B. Paixao, et al., “The spatiotemporal organization of the striatum encodes action space,” Neuron, 96, No. 4, 949 (2017), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.10.031.
E. A. Mukamel, A. Nimmerjahn, and M. J. Schnitzer, “Automated analysis of cellular signals from large-scale calcium imaging data,” Neuron, 63, No. 6, 747–760 (2009), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2009.08.009.
E. A. Pnevmatikakis, D. Soudry, Y. Gao, et al., “Simultaneous denoising, deconvolution, and demixing of calcium imaging data,” Neuron, 89, No. 2, 285–299 (2016), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2015.11.037.
P. Zhou, S. L. Resendez, J. Rodriguez-Romaguera, et al., “Efficient and accurate extraction of in vivo calcium signals from microendoscopic video data,” Elife, 7 (2018), https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28728.
J. Lu, C. Li, J. Singh-Alvarado, et al., “MIN1PIPE: a miniscope 1-photon-based calcium imaging signal extraction pipeline,” Cell Rep., 23, No. 12, 3673–3684 (2018), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.05.062.
C. Blanco-Centurion, S. Luo, D. J. Spergel, et al., “Dynamic network activation of hypothalamic MCH neurons in REM sleep and exploratory behavior,” J. Neurosci., 39, No. 25, 4986–4998 (2019), https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0305-19.2019.
N. A. Frost, A. Haggart, and V. S. Sohal, “Dynamic patterns of correlated activity in the prefrontal cortex encode information about social behavior,” bioRxiv, No. 2020.08.05.238741 (2020), https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.08.05.238741.
W. G. Gonzalez, H. Zhang, A. Harutyunyan, et al., “Persistence of neuronal representations through time and damage in the hippocampus,” Science, 365, No. 6455, 821–825 (2019), https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aav9199.
L. Sheintuch, A. Rubin, N. Brande-Eilat, et al., “Tracking the same neurons across multiple days in Ca(2+) imaging data,” Cell Rep., 21, No. 4, 1102–1115 (2017), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erofeev, A.I., Barinov, D.S., Gerasimov, E.I. et al. NeuroInfoViewer: A Software Package for Analysis of Miniscope Data. Neurosci Behav Physi 51, 1199–1205 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-021-01179-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-021-01179-y